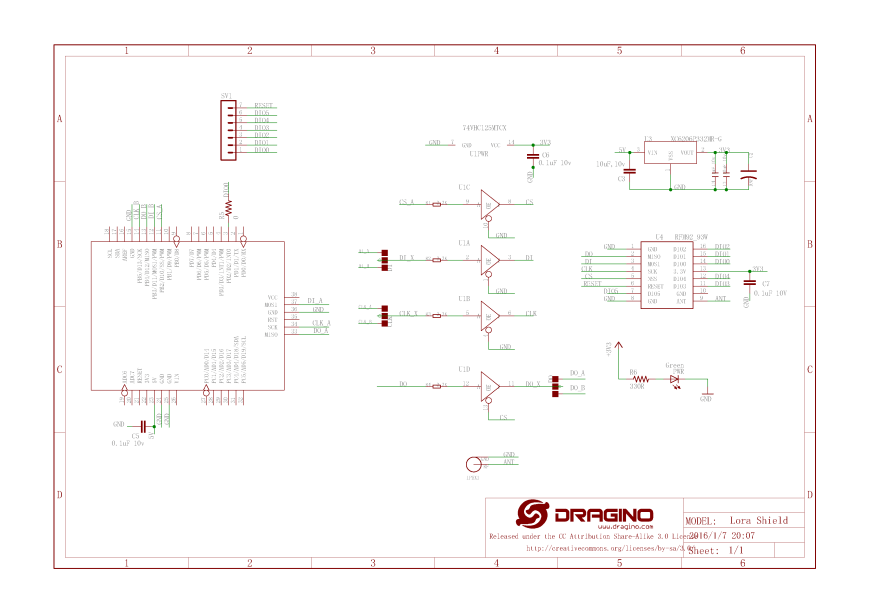
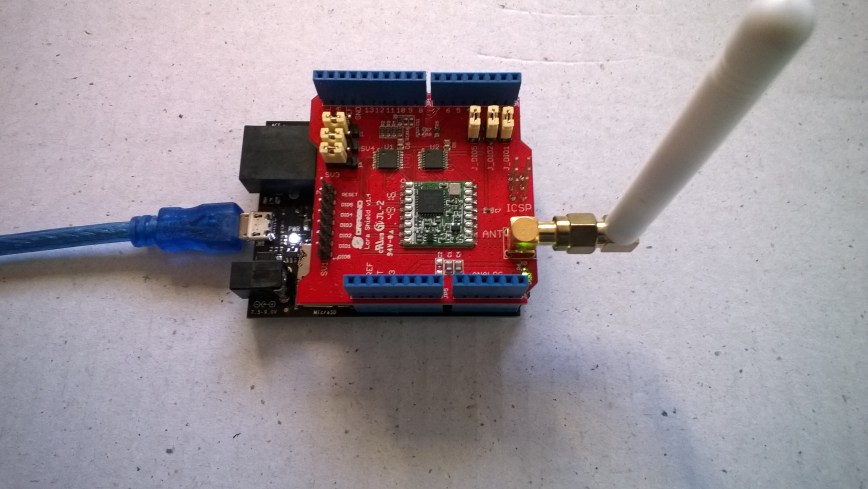
Register Read and Write
For configuration and operation I extended the RegisterManager class with methods for reading/writing bytes, words and byte arrays.
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Copyright (c) August 2018, devMobile Software
//
// Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
// you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
// You may obtain a copy of the License at
//
// http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
//
// Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
// distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
// WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
// See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
// limitations under the License.
//
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
namespace devMobile.IoT.NetMF.Rfm9X.RegisterReadandWrite
{
using System;
using System.Threading;
using Microsoft.SPOT;
using Microsoft.SPOT.Hardware;
using SecretLabs.NETMF.Hardware.Netduino;
public sealed class Rfm9XDevice
{
private const byte RegisterAddressReadMask = 0X7f;
private const byte RegisterAddressWriteMask = 0x80;
private SPI Rfm9XLoraModem = null;
private OutputPort ResetGpioPin = null;
public Rfm9XDevice(Cpu.Pin chipSelect, Cpu.Pin reset)
{
// Factory reset pin configuration
ResetGpioPin = new OutputPort(Pins.GPIO_PIN_D9, true);
ResetGpioPin.Write(false);
Thread.Sleep(10);
ResetGpioPin.Write(true);
Thread.Sleep(10);
//this.Rfm9XLoraModem = new SPI(new SPI.Configuration(chipSelect, false, 0, 0, false, true, 2000, SPI.SPI_module.SPI1));
this.Rfm9XLoraModem = new SPI(new SPI.Configuration(chipSelect, false, 0, 0, false, false, 2000, SPI.SPI_module.SPI1));
Thread.Sleep(100);
}
public Byte RegisterReadByte(byte registerAddress)
{
byte[] writeBuffer = new byte[] { registerAddress };
byte[] readBuffer = new byte[1];
Debug.Assert(Rfm9XLoraModem != null);
//Rfm9XLoraModem.WriteRead(writeBuffer, readBuffer, 1);
Rfm9XLoraModem.WriteRead(writeBuffer, readBuffer, 1 );
return readBuffer[0];
}
public ushort RegisterReadWord(byte address)
{
byte[] writeBuffer = new byte[] { address &= RegisterAddressReadMask };
byte[] readBuffer = new byte[2];
Debug.Assert(Rfm9XLoraModem != null);
//Rfm9XLoraModem.WriteRead(readBuffer, writeBuffer, 4 ); // Check this
readBuffer[0] = RegisterReadByte( address ) ;
readBuffer[1] = RegisterReadByte(address+=1);
return (ushort)(readBuffer[1] + (readBuffer[0] << 8));
}
public byte[] RegisterRead(byte address, int length)
{
byte[] writeBuffer = new byte[] { address &= RegisterAddressReadMask };
byte[] readBuffer = new byte[length];
Debug.Assert(Rfm9XLoraModem != null);
//Rfm9XLoraModem.WriteRead(readBuffer, writeBuffer, 1); // Check this
for (byte index = 0; index 4];
// Mask off the upper 4 bits to get the rest of it.
hexString += hexChars[singlebyte & 0x0F];
return hexString;
}
private static string WordToHexString(ushort singleword)
{
string hexString = string.Empty;
byte[] bytes = BitConverter.GetBytes(singleword);
hexString += ByteToHexString(bytes[1]);
hexString += ByteToHexString(bytes[0]);
return hexString;
}
}
}
I had to add an extra "ToHexString" method so I could display the returned byte and word values
Read RegOpMode (read byte)
RegOpMode 0x09
Set LoRa mode and sleep mode (write byte)
Read the preamble (read word)
Preamble 0x0008
Set the preamble to 0x80 (write word)
Read the centre frequency (read byte array)
Frequency Msb 0x80 Mid 0x00 Lsb 0x4F
Set the centre frequency to 916MHz (write byte array)
—Registers 0x00 thru 0x42—
Register 0x00 – Value 0XF4
Register 0x01 – Value 0X80
Register 0x02 – Value 0X1A
Register 0x03 – Value 0X0B
Register 0x04 – Value 0X00
Register 0x05 – Value 0X52
Register 0x06 – Value 0XE4
Register 0x07 – Value 0XC0
Register 0x08 – Value 0X00
Register 0x09 – Value 0X4F
Register 0x0A – Value 0X09
Register 0x0B – Value 0X2B
Register 0x0C – Value 0X20
Register 0x0D – Value 0X01
Register 0x0E – Value 0X80
Register 0x0F – Value 0X00
Register 0x10 – Value 0X00
Register 0x11 – Value 0X00
Register 0x12 – Value 0X00
Register 0x13 – Value 0X00
Register 0x14 – Value 0X00
Register 0x15 – Value 0X00
Register 0x16 – Value 0X00
Register 0x17 – Value 0X00
Register 0x18 – Value 0X10
Register 0x19 – Value 0X00
Register 0x1A – Value 0X00
Register 0x1B – Value 0X00
Register 0x1C – Value 0X00
Register 0x1D – Value 0X72
Register 0x1E – Value 0X70
Register 0x1F – Value 0X64
Register 0x20 – Value 0X80
Register 0x21 – Value 0X00
Register 0x22 – Value 0X01
Register 0x23 – Value 0XFF
Register 0x24 – Value 0X00
Register 0x25 – Value 0X00
Register 0x26 – Value 0X04
Register 0x27 – Value 0X00
Register 0x28 – Value 0X00
Register 0x29 – Value 0X00
Register 0x2A – Value 0X00
Register 0x2B – Value 0X00
Register 0x2C – Value 0X00
Register 0x2D – Value 0X50
Register 0x2E – Value 0X14
Register 0x2F – Value 0X45
Register 0x30 – Value 0X55
Register 0x31 – Value 0XC3
Register 0x32 – Value 0X05
Register 0x33 – Value 0X27
Register 0x34 – Value 0X1C
Register 0x35 – Value 0X0A
Register 0x36 – Value 0X03
Register 0x37 – Value 0X0A
Register 0x38 – Value 0X42
Register 0x39 – Value 0X12
Register 0x3A – Value 0X49
Register 0x3B – Value 0X1D
Register 0x3C – Value 0X00
Register 0x3D – Value 0XAF
Register 0x3E – Value 0X00
Register 0x3F – Value 0X00
Register 0x40 – Value 0X00
Register 0x41 – Value 0X00
Register 0x42 – Value 0X12
The register dump shows the SX1276 is in LoRa+Sleep mode and the preamble is set to 0x80 etc.
The way I read words and arrays of bytes isn’t very efficient will need to revisit when I have more time and/or access to a digital storage scope.