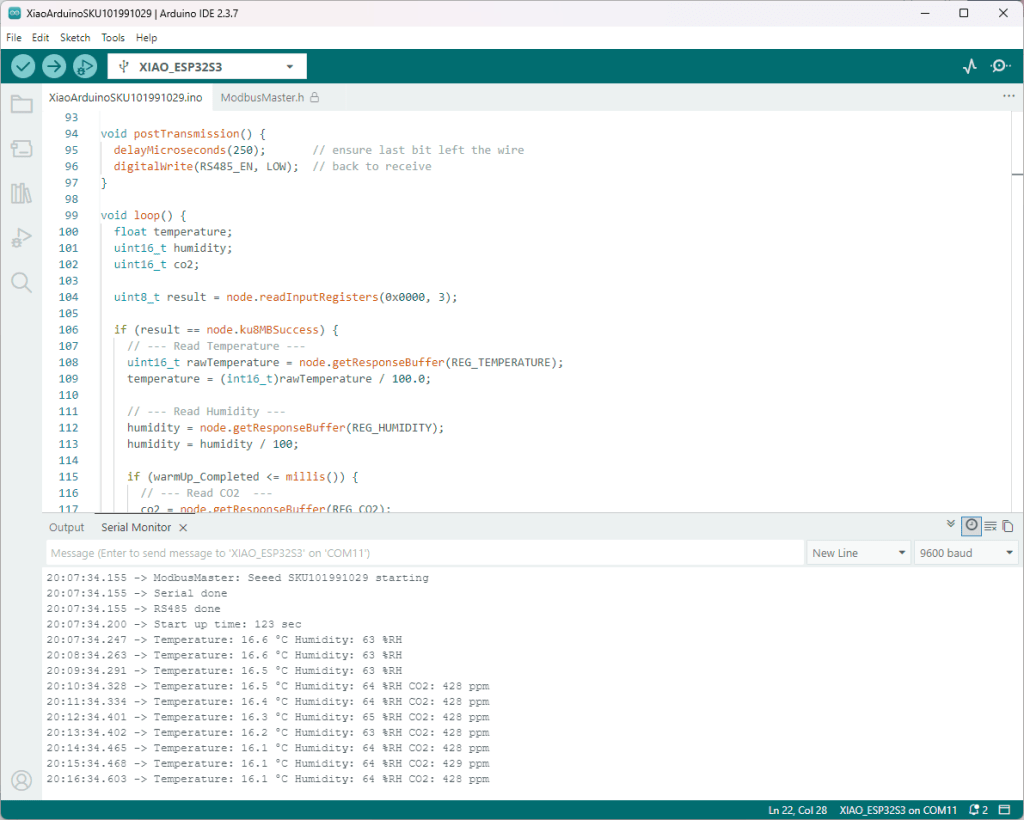
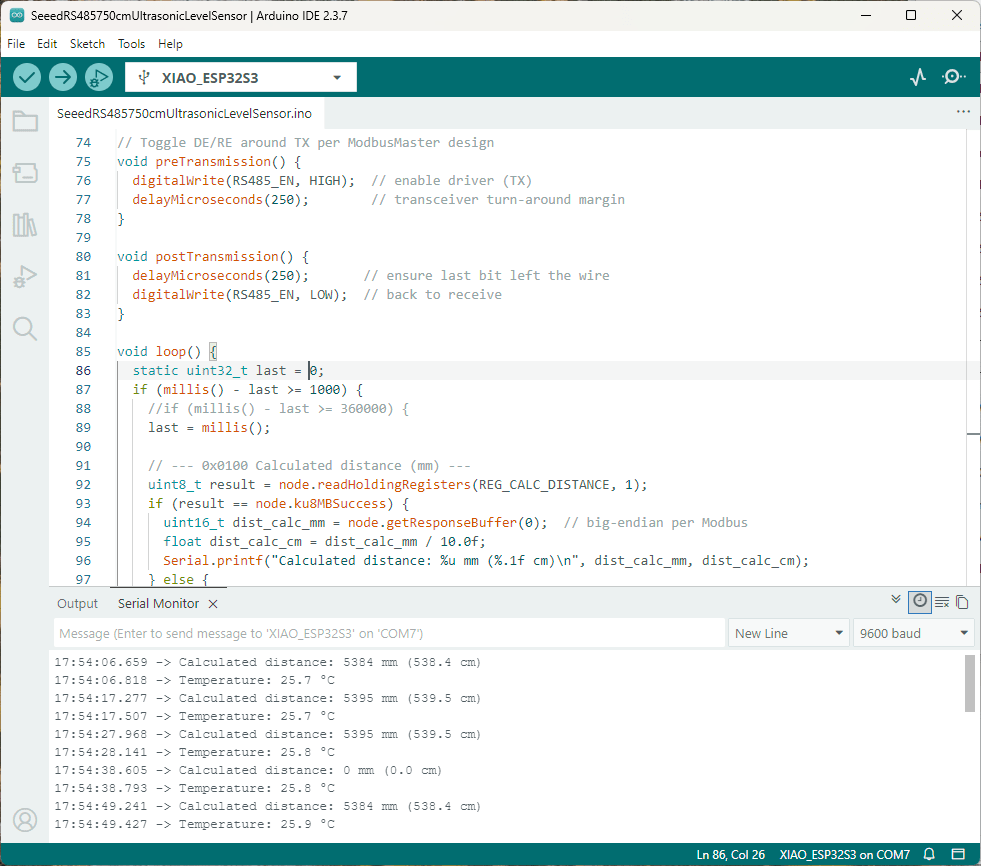
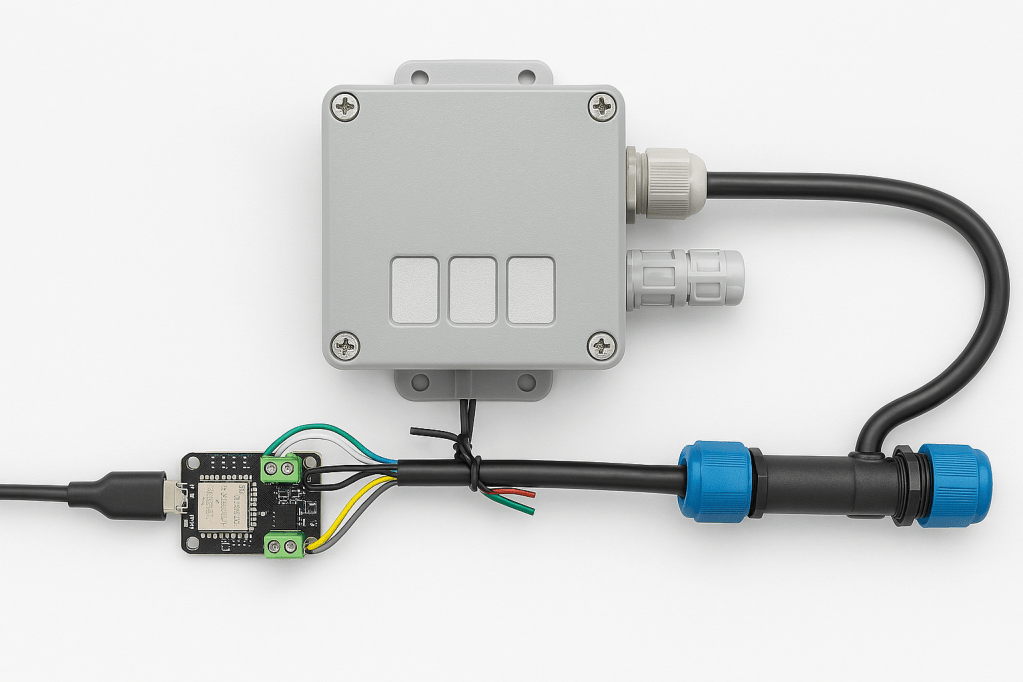
As part of this series of samples comparing Arduino to nanoFramework to .NET IoT Device “Proof of Concept (PoC) applications, several posts use an SenseCap Air Temperature and Humidity Sensor SKU 101990882
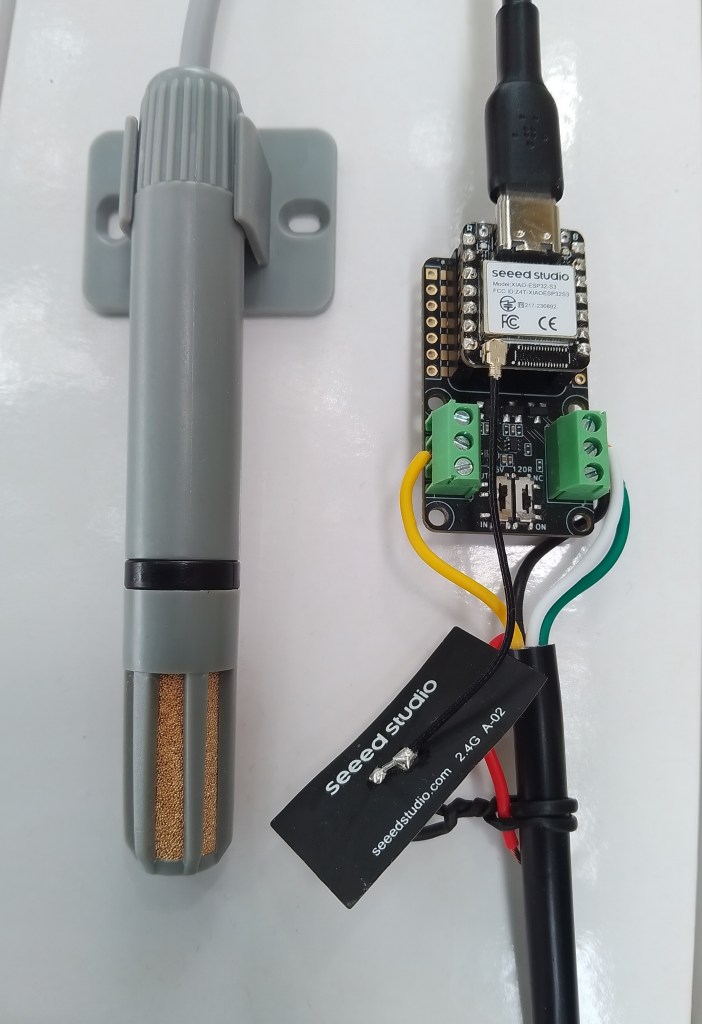
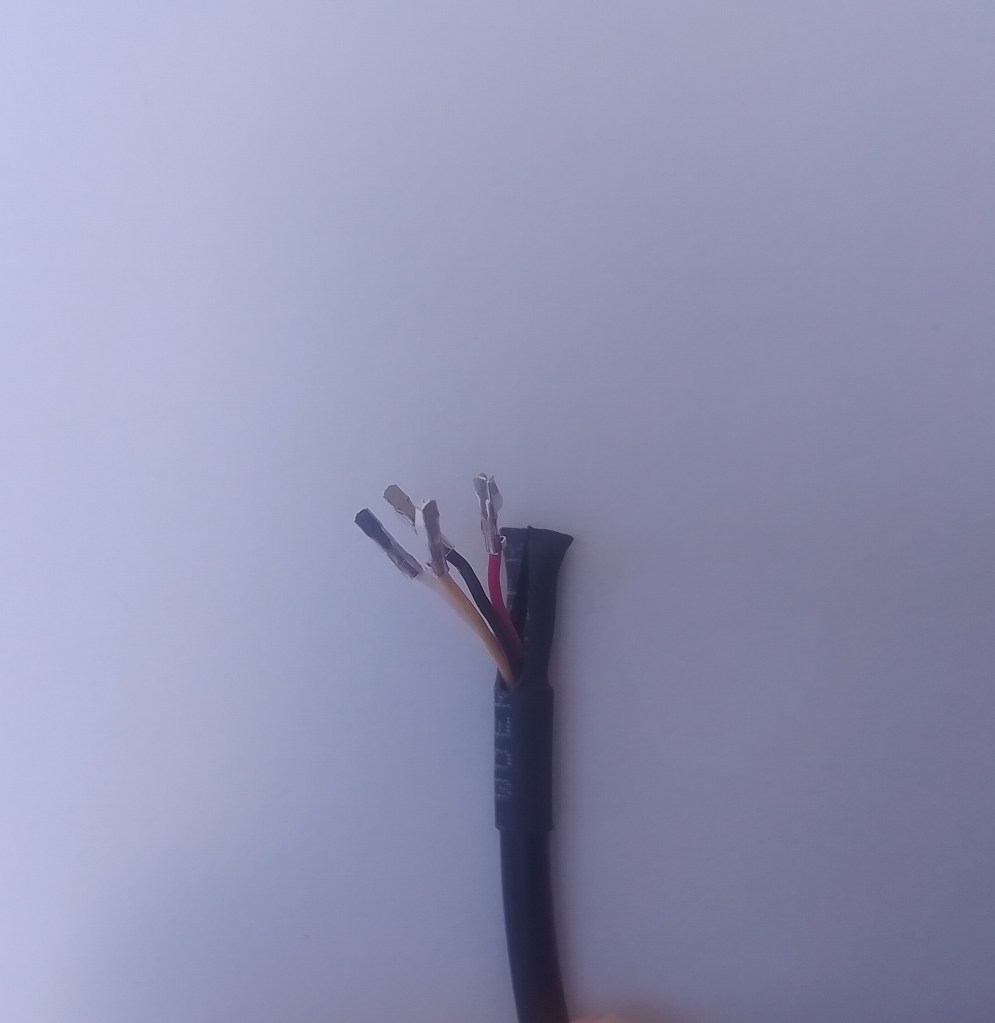
I cut one of the cables of a spare Industrial IP68 Modbus RS485 1-to-4 Splitter/Hub to connect the sensor to the breakout board. This sensor has an operating voltage of 3.6-30V/DC so it can be powered by the 5V output of a RS485 Breakout Board for Seeed Studio XIAO (SKU 113991354)
The red wire is for powering the sensor with a 12V power supply so was tied back so it didn’t touch any of the other electronics.
public class Program
{
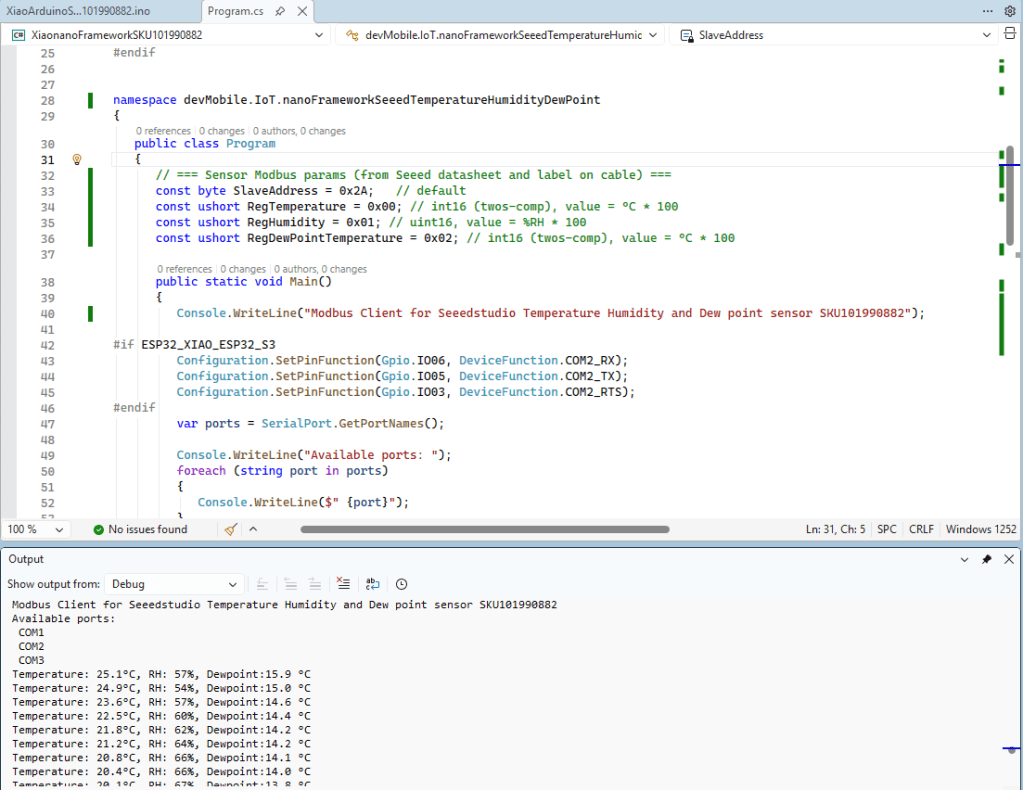
// === Sensor Modbus params (from Seeed datasheet and label on cable) ===
const byte SlaveAddress = 0x2A; // default
const ushort RegTemperature = 0x00; // int16 (twos-comp), value = °C * 100
const ushort RegHumidity = 0x01; // uint16, value = %RH * 100
const ushort RegDewPointTemperature = 0x02; // int16 (twos-comp), value = °C * 100
public static void Main()
{
Console.WriteLine("Modbus Client for Seeedstudio Temperature Humidity and Dew point sensor SKU101990882");
#if ESP32_XIAO_ESP32_S3
Configuration.SetPinFunction(Gpio.IO06, DeviceFunction.COM2_RX);
Configuration.SetPinFunction(Gpio.IO05, DeviceFunction.COM2_TX);
Configuration.SetPinFunction(Gpio.IO03, DeviceFunction.COM2_RTS);
#endif
var ports = SerialPort.GetPortNames();
Console.WriteLine("Available ports: ");
foreach (string port in ports)
{
Console.WriteLine($" {port}");
}
// Modbus Client
using (var _client = new ModbusClient("COM2"))
{
#if DEBUG_LOGGER
_client.Logger = new DebugLogger("ModbusClient")
{
MinLogLevel = LogLevel.Debug
};
#endif
while (true)
{
try
{
// regs[0] = Temperature.
var regs = _client.ReadHoldingRegisters(SlaveAddress, RegTemperature, 3);
short rawTemperature = regs[RegTemperature];
double temperature = rawTemperature / 100.0; // Signed 16 - bit, value = °C * 100
// regs[1] = Humidity.
ushort rawRelativeHumidity = unchecked((ushort)regs[RegHumidity]);
double relativeHumidity = rawRelativeHumidity / 100.0; // Humidity. Unsigned 16-bit, value = %RH * 100
// regs[2] = Dewpoint.
short rawDewPointTemperature = regs[RegDewPointTemperature];
double dewPointTemperature = rawDewPointTemperature / 100.0; // Signed 16 - bit, value = °C * 100
Console.WriteLine($"Temperature: {temperature:F1}°C, RH: {relativeHumidity:F0}%, Dewpoint:{dewPointTemperature:F1} °C");
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Read failed: {ex.Message}");
}
Thread.Sleep(60000);
}
}
}
}
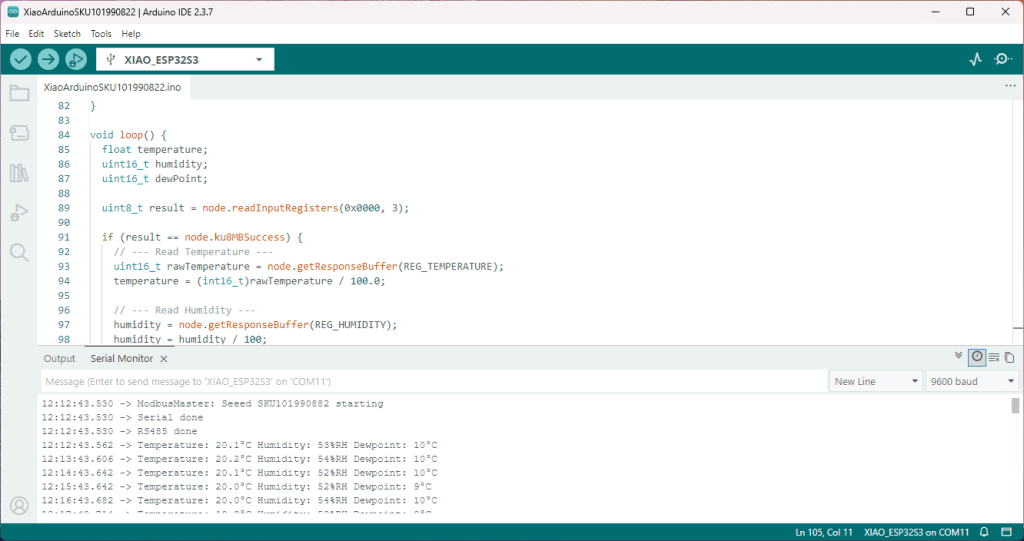
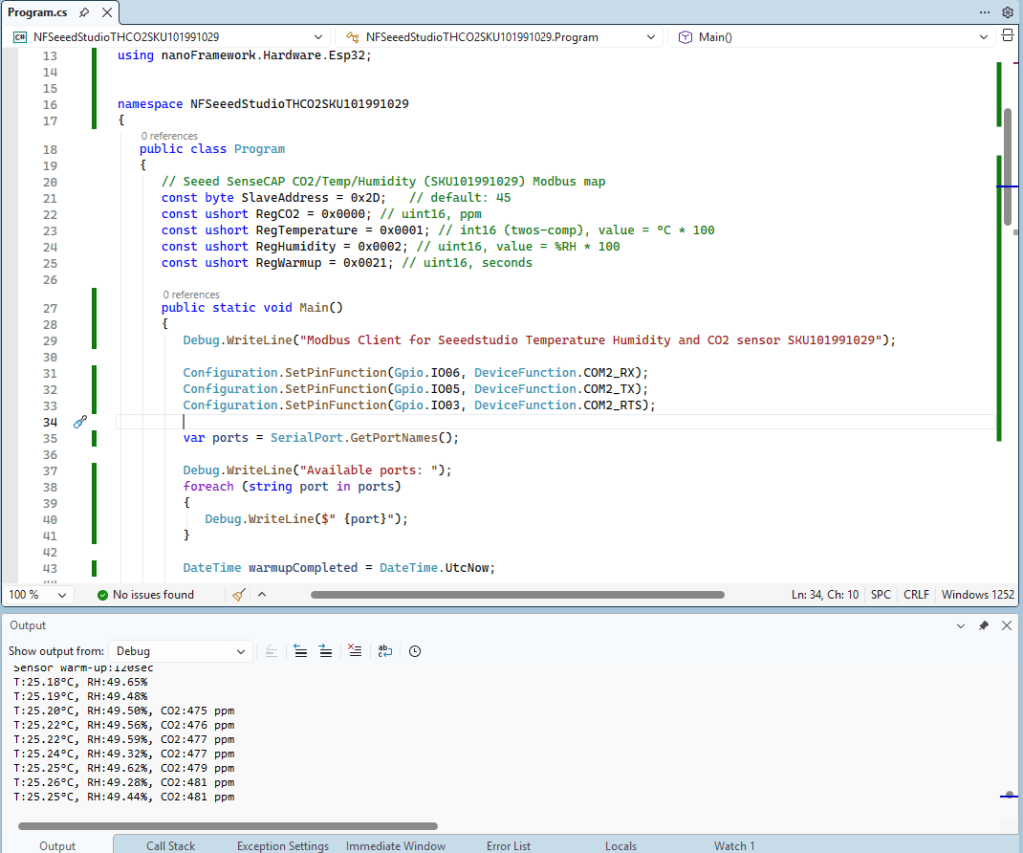
The nanoFramework Modbus Library based application worked second attempt because initially I had the RegDewPointTemperature register value 0x021