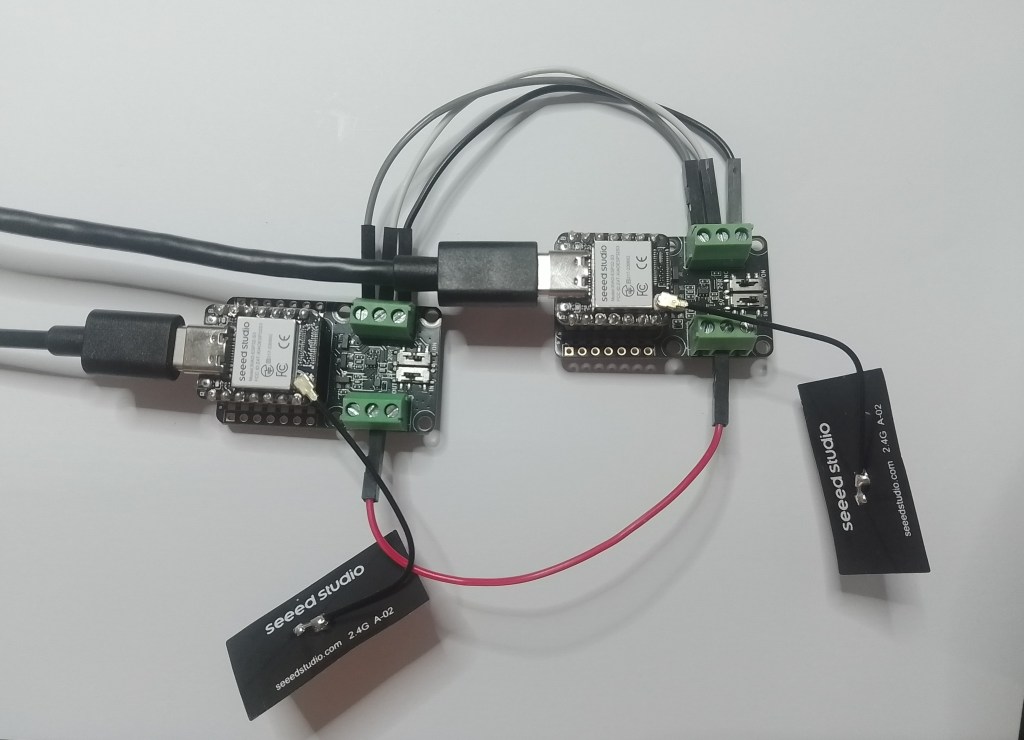
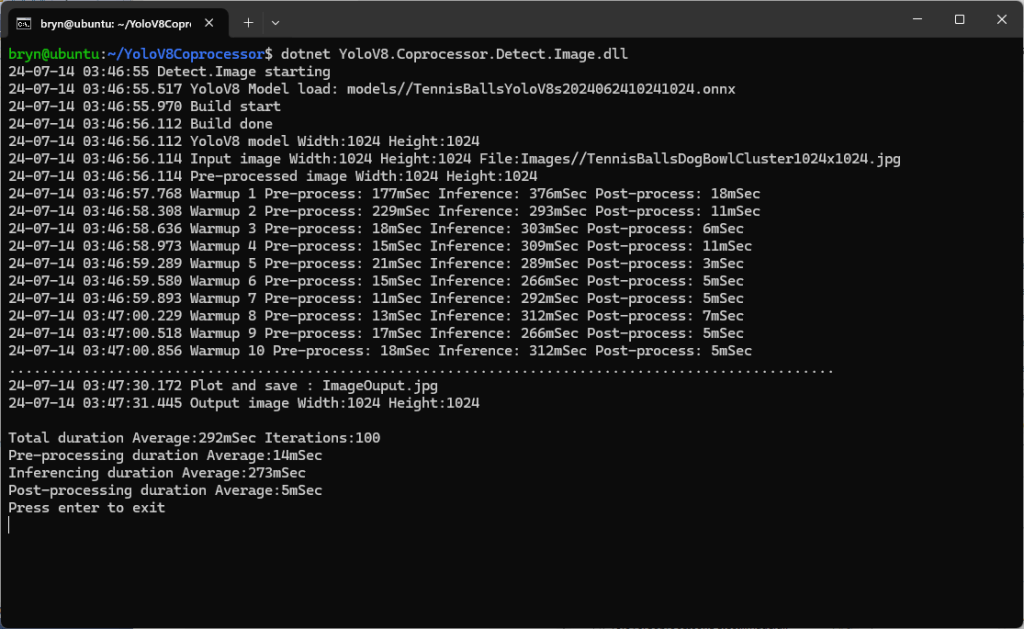
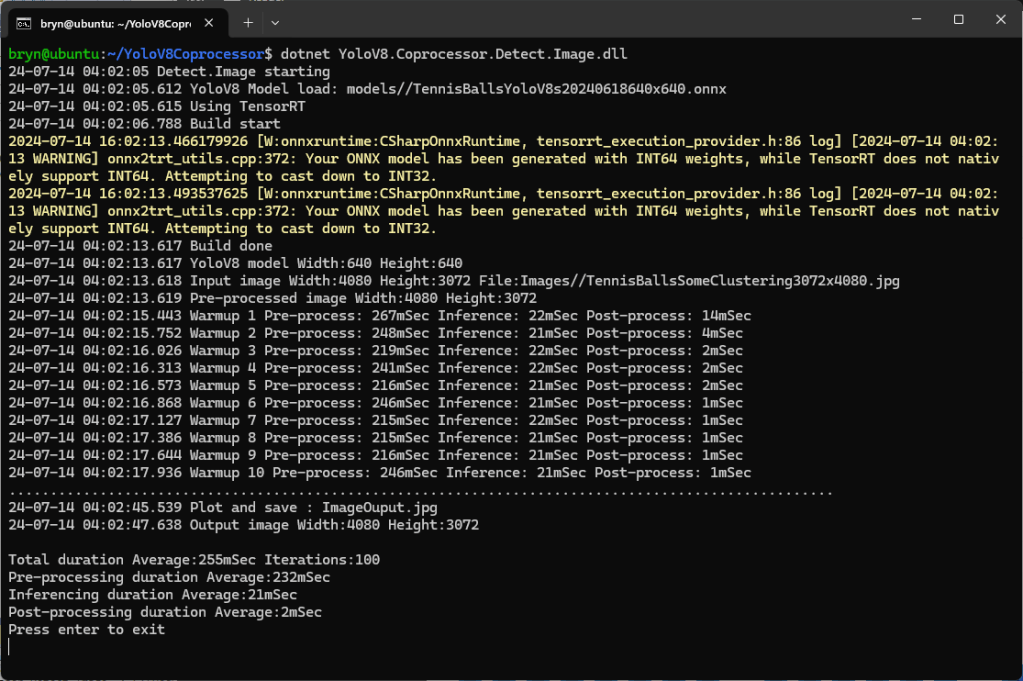
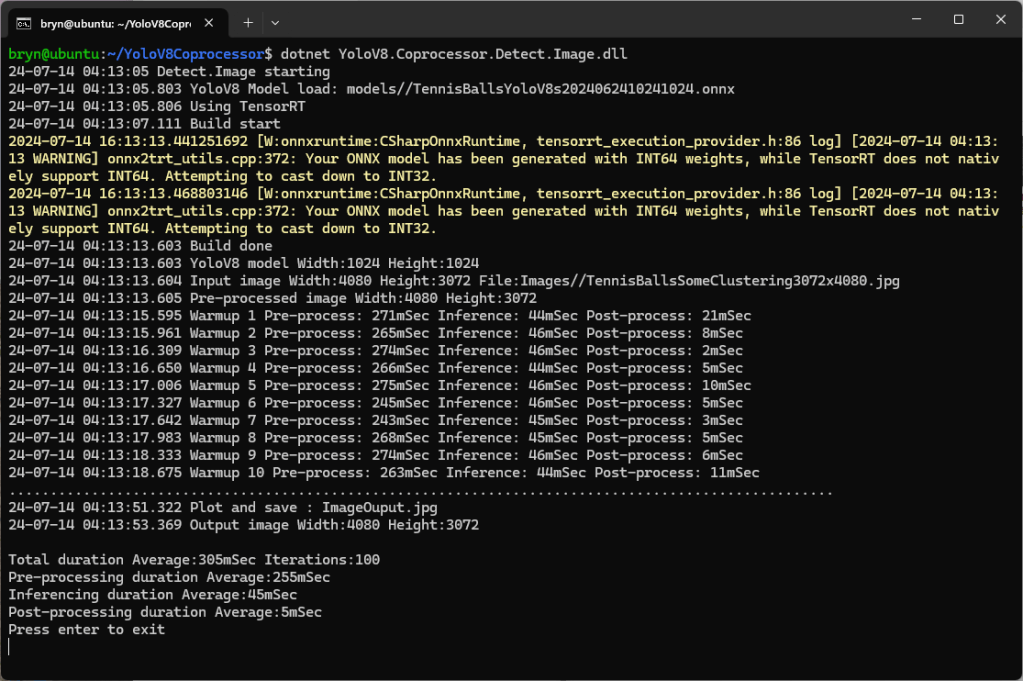
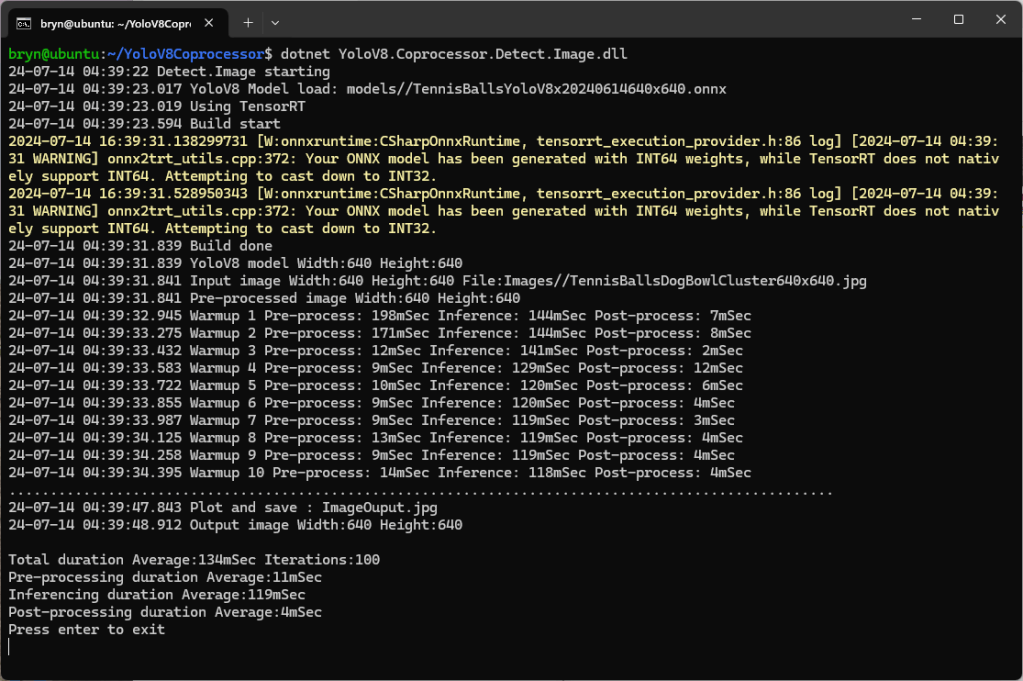
Building a .NET nanoFramework application for testing Azure Event Grid MQTT Broker connectivity that would run on my Seeedstudio EdgeBox ESP100 and Seeedstudio Xiao ESP32S3 devices took a couple of hours. Most of that time was spent figuring out how to generate the certificate and elliptic curve private key
Create an elliptic curve private key
openssl ecparam -name prime256v1 -genkey -noout -out device.key
Generate a certificate signing request
openssl req -new -key device.key -out device.csr -subj "/CN=device.example.com/O=YourOrg/OU=IoT"
Then use the intermediate certificate and key file from earlier to generate a device certificate and key.
openssl x509 -req -in device.csr -CA IntermediateCA.crt -CAkey IntermediateCA.key -CAcreateserial -out device.crt -days 365 -sha256
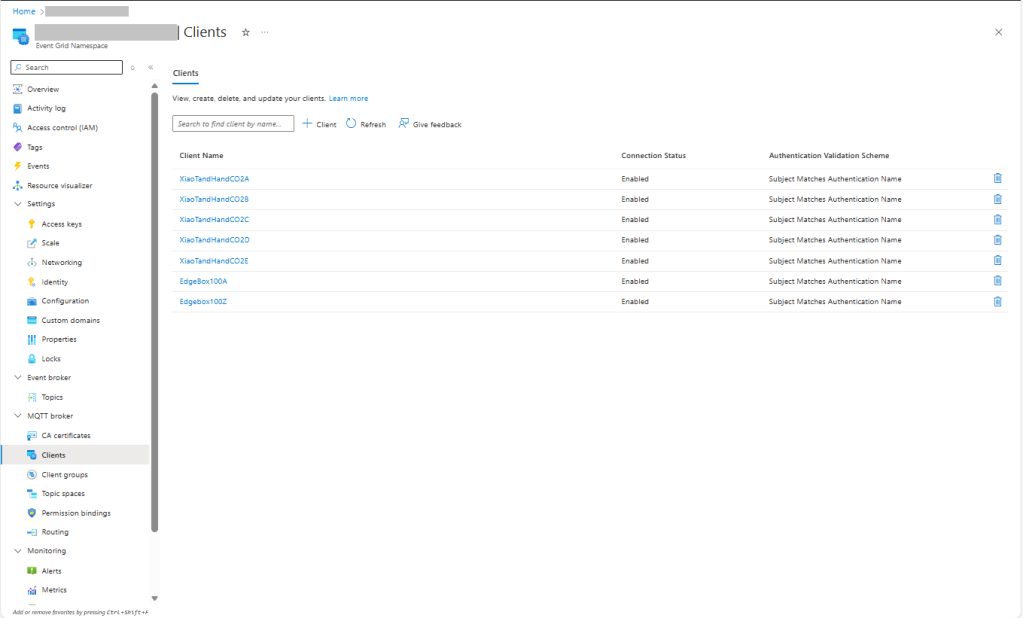
In this post I have assumed that the reader is familiar with configuring Azure Event Grid clients, client groups, topic spaces, permission bindings and routing.
The PEM encoded root CA certificate chain that is used to validate the server
public const string CA_ROOT_PEM = @"-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
CN: CN = Microsoft Azure ECC TLS Issuing CA 03
-----END CERTIFICATE-----
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
CN: CN = DigiCert Global Root G3
-----END CERTIFICATE-----";
The PEM encoded certificate chain that is used to authenticate the device
public const string CLIENT_CERT_PEM_A = @"-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
CN=Self signed device certificate
-----END CERTIFICATE-----
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
CN=Self signed Intermediate certificate
-----END CERTIFICATE-----";
The PEM encoded private key of device
public const string CLIENT_KEY_PEM_A = @"-----BEGIN EC PRIVATE KEY-----
-----END EC PRIVATE KEY-----";
My application was “inspired” by the .NET nanoFramework m2mqtt example.
public static void Main()
{
int sequenceNumber = 0;
MqttClient mqttClient = null;
Thread.Sleep(1000); // Found this works around some issues with running immediately after a reset
bool wifiConnected = false;
Console.WriteLine("WiFi connecting...");
do
{
// Attempt to connect using DHCP
wifiConnected = WifiNetworkHelper.ConnectDhcp(Secrets.WIFI_SSID, Secrets.WIFI_PASSWORD, requiresDateTime: true);
if (!wifiConnected)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Failed to connect. Error: {WifiNetworkHelper.Status}");
if (WifiNetworkHelper.HelperException != null)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Exception: {WifiNetworkHelper.HelperException}");
}
Thread.Sleep(1000);
}
}
while (!wifiConnected);
Console.WriteLine("WiFi connected");
var caCert = new X509Certificate(Constants.CA_ROOT_PEM);
X509Certificate2 clientCert = null;
try
{
clientCert = new X509Certificate2(Secrets.CLIENT_CERT_PEM_A, Secrets.CLIENT_KEY_PEM_A, string.Empty);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Client Certificate Exception: {ex.Message}");
}
mqttClient = new MqttClient(Secrets.MQTT_SERVER, Constants.MQTT_PORT, true, caCert, clientCert, MqttSslProtocols.TLSv1_2);
mqttClient.ProtocolVersion = MqttProtocolVersion.Version_5;
bool mqttConnected = false;
Console.WriteLine("MQTT connecting...");
do
{
try
{
// Regular connect
var resultConnect = mqttClient.Connect(Secrets.MQTT_CLIENTID, Secrets.MQTT_USERNAME, Secrets.MQTT_PASSWORD);
if (resultConnect != MqttReasonCode.Success)
{
Console.WriteLine($"MQTT ERROR connecting: {resultConnect}");
Thread.Sleep(1000);
}
else
{
mqttConnected = true;
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine($"MQTT ERROR Exception '{ex.Message}'");
Thread.Sleep(1000);
}
}
while (!mqttConnected);
Console.WriteLine("MQTT connected...");
mqttClient.MqttMsgPublishReceived += MqttMsgPublishReceived;
mqttClient.MqttMsgSubscribed += MqttMsgSubscribed;
mqttClient.MqttMsgUnsubscribed += MqttMsgUnsubscribed;
mqttClient.ConnectionOpened += ConnectionOpened;
mqttClient.ConnectionClosed += ConnectionClosed;
mqttClient.ConnectionClosedRequest += ConnectionClosedRequest;
string topicPublish = string.Format(MQTT_TOPIC_PUBLISH_FORMAT, Secrets.MQTT_CLIENTID);
while (true)
{
Console.WriteLine("MQTT publish message start...");
var payload = new MessagePayload() { ClientID = Secrets.MQTT_CLIENTID, Sequence = sequenceNumber++ };
string jsonPayload = JsonSerializer.SerializeObject(payload);
var result = mqttClient.Publish(topicPublish, Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(jsonPayload), "application/json; charset=utf-8", null);
Debug.WriteLine($"MQTT published ({result}): {jsonPayload}");
Thread.Sleep(100);
}
}
I then configured my client (Edgebox100Z) and updated the “secrets.cs” file
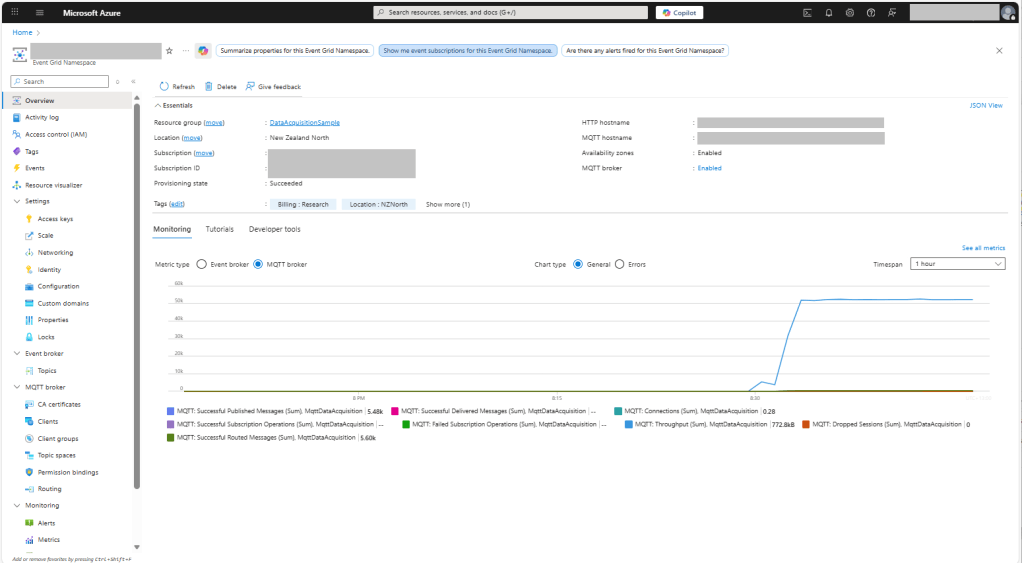
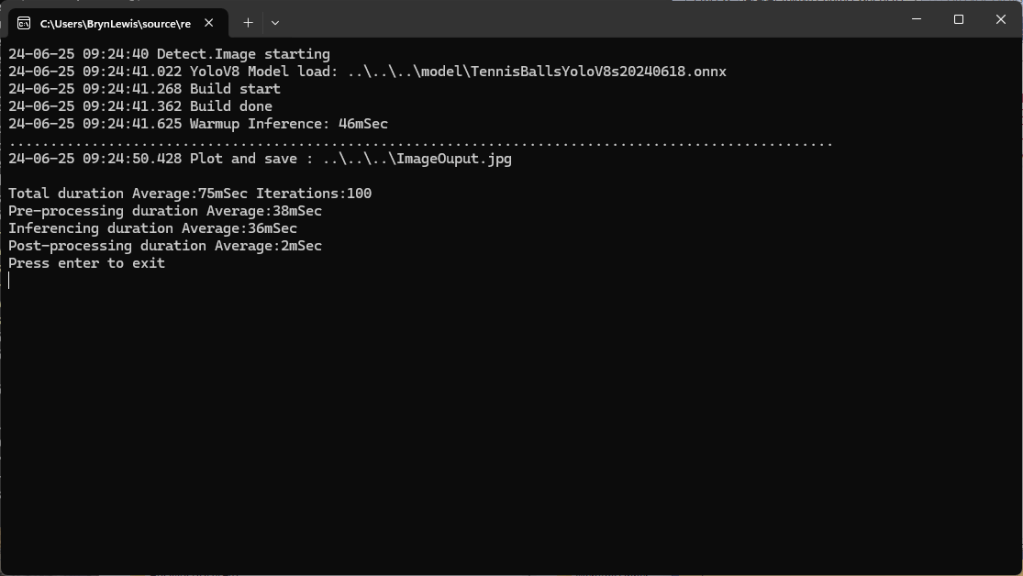
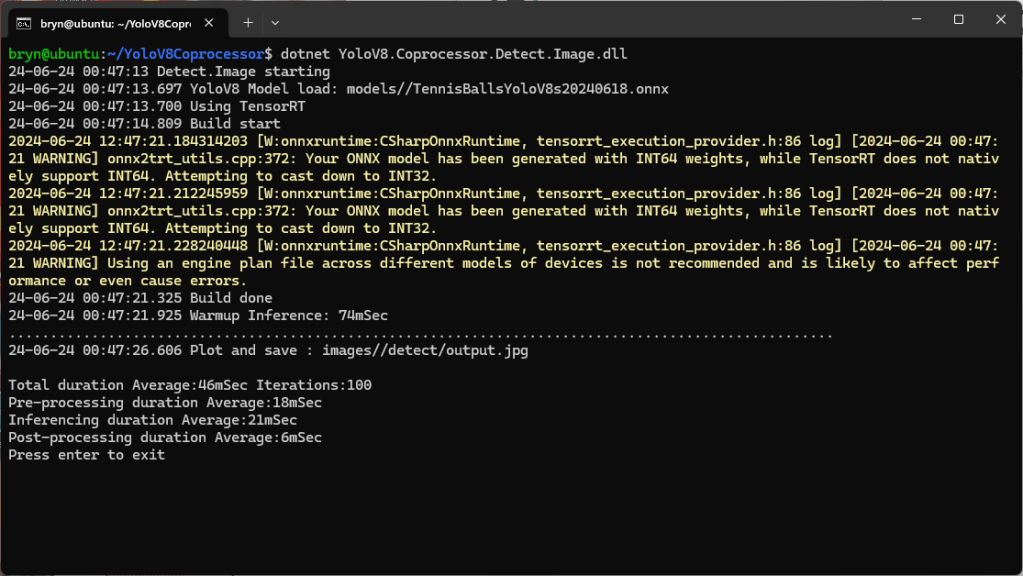
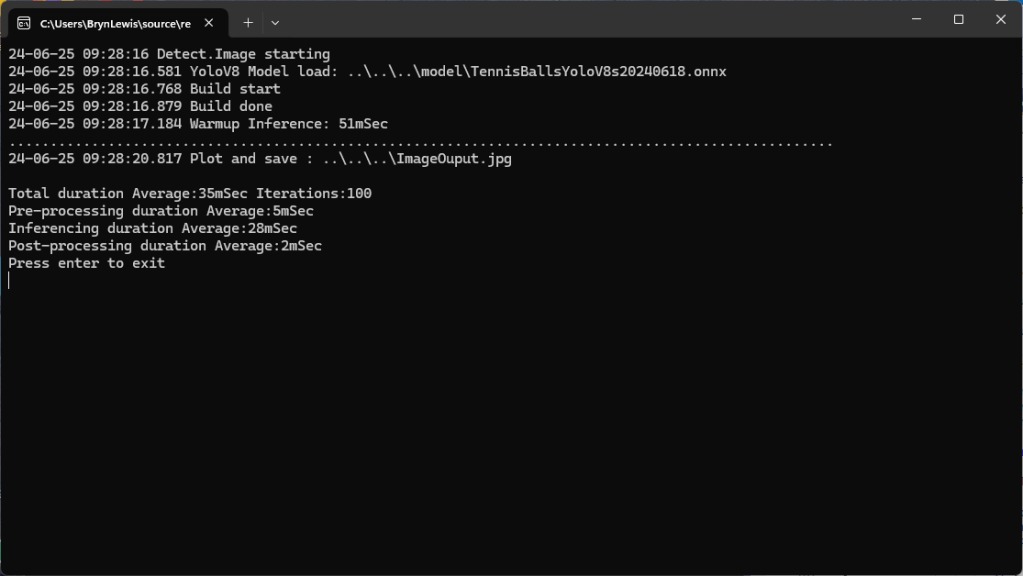
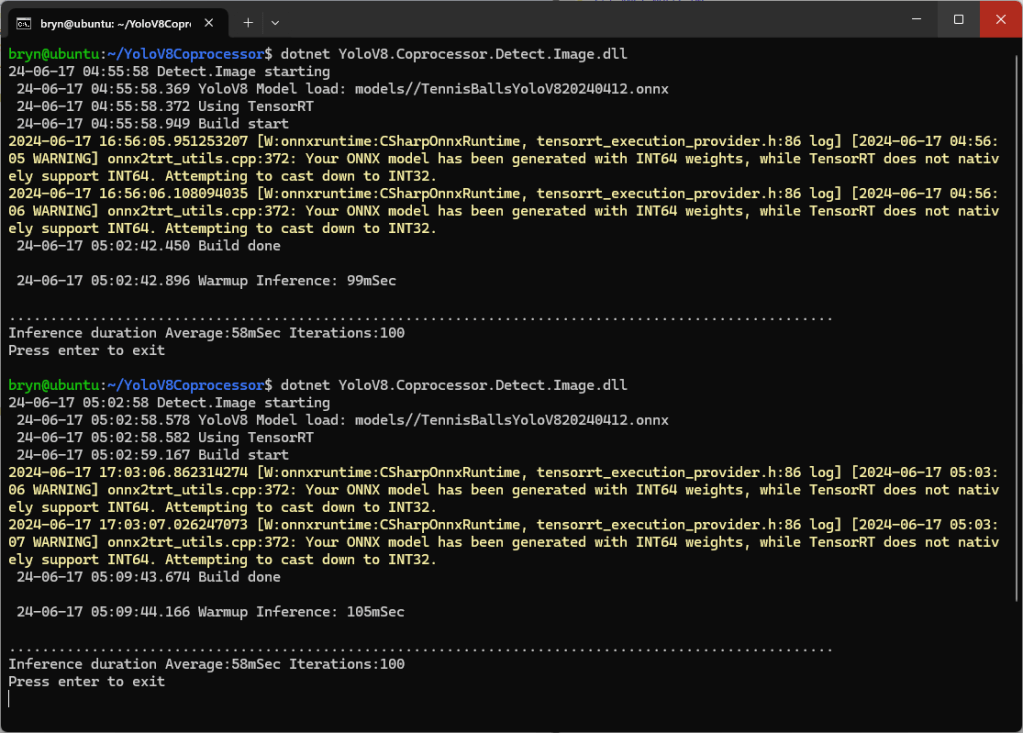
The application connected to the Azure Event Grid MQTT broker and started publishing the JSON payload with the incrementing sequence number.
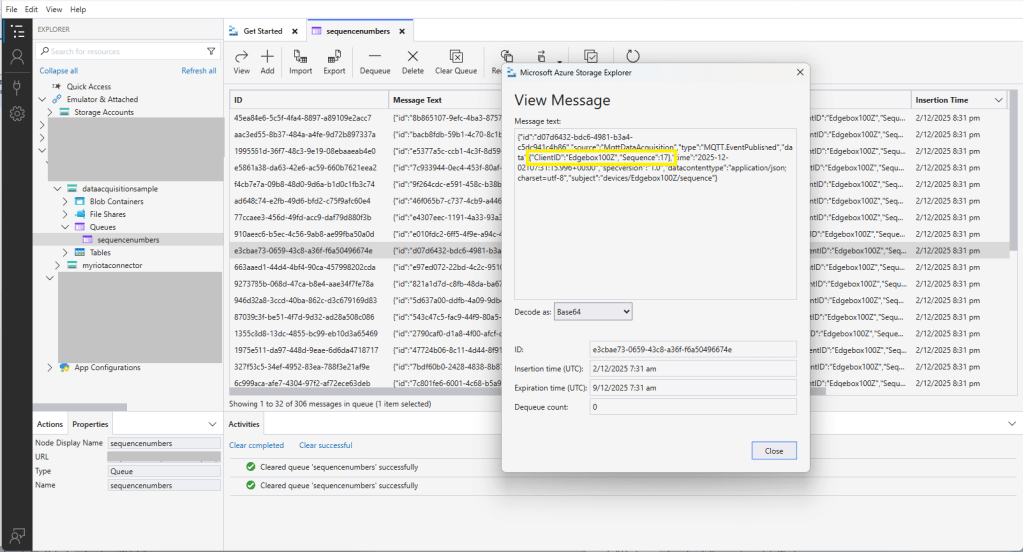
The published messages were “routed” to an Azure Storage Queue where they could be inspected with a tool like Azure Storage Explorer.
I could see the application was working in the Azure Event Grid MQTT broker metrics because the number of messages published was increasing.