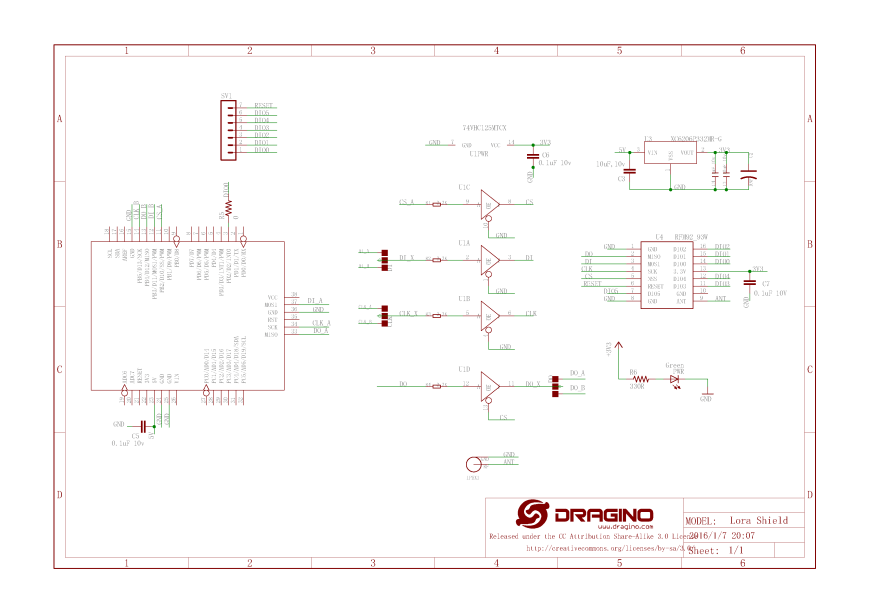
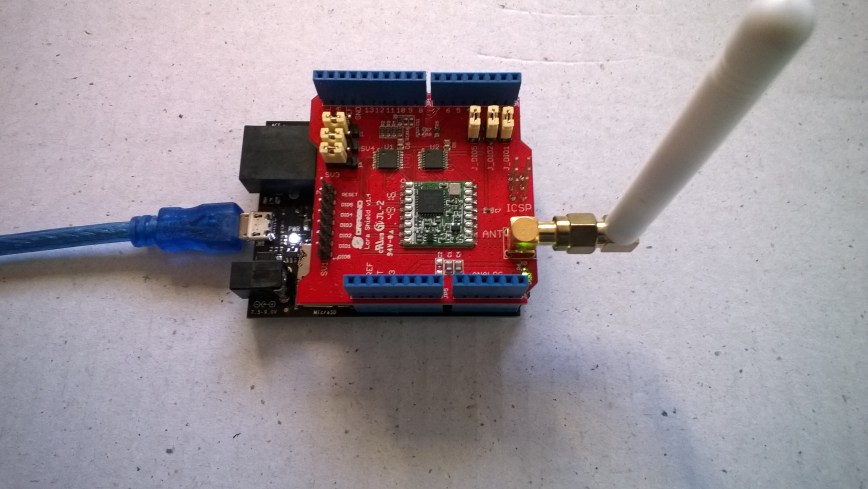
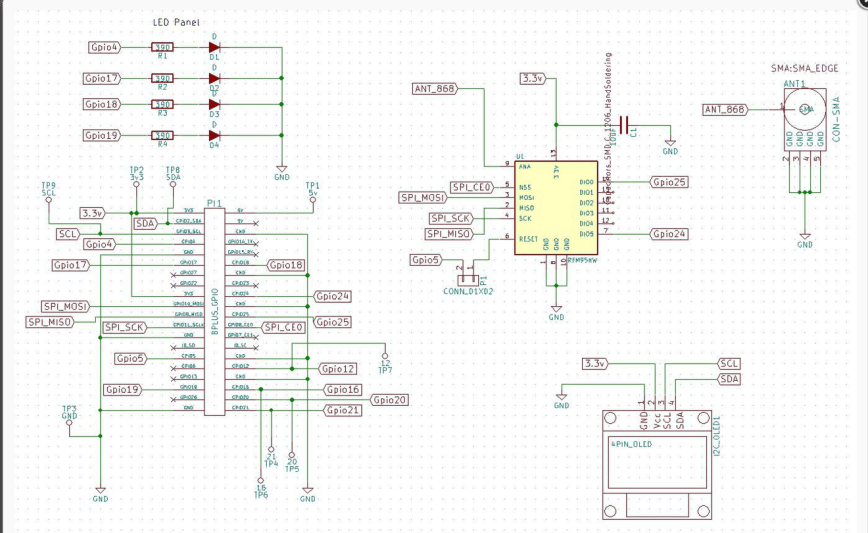
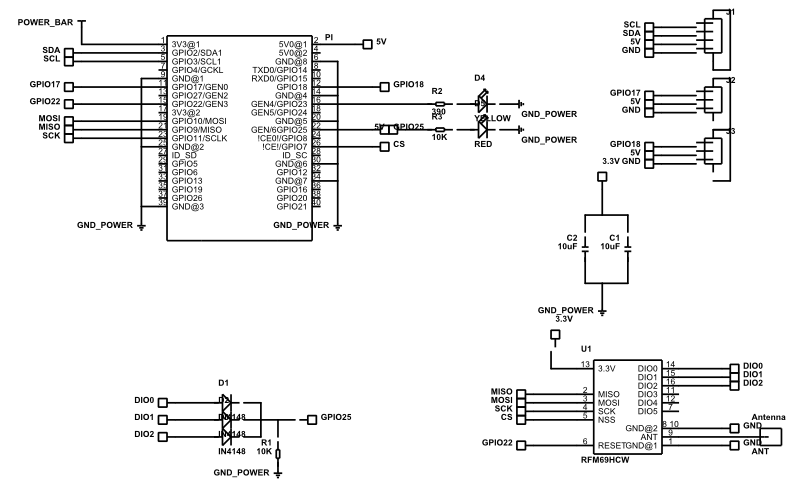
Transmit Interrupt
Starting with the TransmitBasic sample application I modified the code so that a hardware interrupt (specified by SX1276 RegDioMapping1) was generated on TxDone (FIFO Payload Transmission completed).
The application inserts a message into the SX1276 transmit FIFO every 10 seconds with confirmation of transmission displayed shortly afterwards
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Copyright (c) August 2018, devMobile Software
//
// Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
// you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
// You may obtain a copy of the License at
//
// http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
//
// Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
// distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
// WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
// See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
// limitations under the License.
//
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
namespace devMobile.IoT.NetMF.Rfm9X.TransmitInterrupt
{
using System;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading;
using Microsoft.SPOT;
using Microsoft.SPOT.Hardware;
using SecretLabs.NETMF.Hardware.Netduino;
public sealed class Rfm9XDevice
{
private const byte RegisterAddressReadMask = 0X7f;
private const byte RegisterAddressWriteMask = 0x80;
private SPI Rfm9XLoraModem = null;
private OutputPort ResetGpioPin = null;
private InterruptPort InterruptPin = null;
public Rfm9XDevice(Cpu.Pin chipSelect, Cpu.Pin resetPin, Cpu.Pin interruptPin)
{
// Factory reset pin configuration
ResetGpioPin = new OutputPort(Pins.GPIO_PIN_D9, true);
ResetGpioPin.Write(false);
Thread.Sleep(10);
ResetGpioPin.Write(true);
Thread.Sleep(10);
this.Rfm9XLoraModem = new SPI(new SPI.Configuration(chipSelect, false, 0, 0, false, false, 2000, SPI.SPI_module.SPI1));
InterruptPin = new InterruptPort(interruptPin, false, Port.ResistorMode.Disabled, Port.InterruptMode.InterruptEdgeHigh);
InterruptPin.OnInterrupt += InterruptPin_OnInterrupt;
Thread.Sleep(100);
}
public Byte RegisterReadByte(byte registerAddress)
{
byte[] writeBuffer = new byte[] { registerAddress };
byte[] readBuffer = new byte[1];
Debug.Assert(Rfm9XLoraModem != null);
Rfm9XLoraModem.WriteRead(writeBuffer, readBuffer, 1);
return readBuffer[0];
}
public ushort RegisterReadWord(byte address)
{
byte[] writeBuffer = new byte[] { address &= RegisterAddressReadMask };
byte[] readBuffer = new byte[2];
Debug.Assert(Rfm9XLoraModem != null);
readBuffer[0] = RegisterReadByte(address);
readBuffer[1] = RegisterReadByte(address += 1);
return (ushort)(readBuffer[1] + (readBuffer[0] << 8));
}
public byte[] RegisterRead(byte address, int length)
{
byte[] writeBuffer = new byte[] { address &= RegisterAddressReadMask };
byte[] readBuffer = new byte[length];
Debug.Assert(Rfm9XLoraModem != null);
for (byte index = 0; index 4];
// Mask off the upper 4 bits to get the rest of it.
hexString += hexChars[singlebyte & 0x0F];
return hexString;
}
private static string WordToHexString(ushort singleword)
{
string hexString = string.Empty;
byte[] bytes = BitConverter.GetBytes(singleword);
hexString += ByteToHexString(bytes[1]);
hexString += ByteToHexString(bytes[0]);
return hexString;
}
void InterruptPin_OnInterrupt(uint data1, uint data2, DateTime time)
{
byte IrqFlags = this.RegisterReadByte(0x12); // RegIrqFlags
Debug.Print("RegIrqFlags " + ByteToHexString(IrqFlags));
if ((IrqFlags & 0x08) == 0x08) // TxDone
{
Debug.Print("Transmit-Done");
}
this.RegisterWriteByte(0x12, 0xff);// RegIrqFlags
}
public class Program
{
public static void Main()
{
Rfm9XDevice rfm9XDevice = new Rfm9XDevice(Pins.GPIO_PIN_D10, Pins.GPIO_PIN_D9, Pins.GPIO_PIN_D2);
byte MessageCount = byte.MinValue;
while (true)
{
// Put device into LoRa + Sleep mode
rfm9XDevice.RegisterWriteByte(0x01, 0x80); // RegOpMode
// Set the frequency to 915MHz
byte[] frequencyWriteBytes = { 0xE4, 0xC0, 0x00 }; // RegFrMsb, RegFrMid, RegFrLsb
rfm9XDevice.RegisterWrite(0x06, frequencyWriteBytes);
// More power - PA_BOOST
rfm9XDevice.RegisterWriteByte(0x09, 0x80); // RegPaConfig
// Interrupt on TxDone
rfm9XDevice.RegisterWriteByte(0x40, 0x40); // RegDioMapping1 0b00000000 DI0 TxDone
while (true)
{
rfm9XDevice.RegisterWriteByte(0x0E, 0x0); // RegFifoTxBaseAddress
// Set the Register Fifo address pointer
rfm9XDevice.RegisterWriteByte(0x0D, 0x0); // RegFifoAddrPtr
string messageText = "Hello NetMF LoRa! ";
if (MessageCount != 0)
{
messageText += "-" + MessageCount.ToString();
}
else
{
messageText += MessageCount.ToString();
}
MessageCount += 1;
// load the message into the fifo
byte[] messageBytes = UTF8Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(messageText);
foreach (byte b in messageBytes)
{
rfm9XDevice.RegisterWriteByte(0x0, b); // RegFifo
}
// Set the length of the message in the fifo
rfm9XDevice.RegisterWriteByte(0x22, (byte)messageBytes.Length); // RegPayloadLength
Debug.Print("Sending " + messageBytes.Length + " bytes message " + messageText);
/// Set the mode to LoRa + Transmit
rfm9XDevice.RegisterWriteByte(0x01, 0x83); // RegOpMode
Thread.Sleep(10000);
}
}
}
}
}
}
Unlike the Windows 10 IoT core version I can configure the interrupt to only trigger on the leading edge.
InterruptPin = new InterruptPort(interruptPin, false, Port.ResistorMode.Disabled, Port.InterruptMode.InterruptEdgeHigh);
In the Debug output window of VS2K12 I could see
The thread '' (0x2) has exited with code 0 (0x0). Sending 19 bytes message Hello NetMF LoRa! 0 RegIrqFlags 08 Transmit-Done Sending 20 bytes message Hello NetMF LoRa! -1 RegIrqFlags 08 Transmit-Done Sending 20 bytes message Hello NetMF LoRa! -2 RegIrqFlags 08 Transmit-Done
On my Arduino device the message arrived
LoRa Receiver Callback Received packet 'Hello NetMF LoRa! 0' with RSSI -29 Received packet 'Hello NetMF LoRa! -1' with RSSI -29 Received packet 'Hello NetMF LoRa! -2' with RSSI -29 Received packet 'Hello NetMF LoRa! -3' with RSSI -29 Received packet 'Hello NetMF LoRa! -4' with RSSI -29
Next step interrupts for processing inbound messages