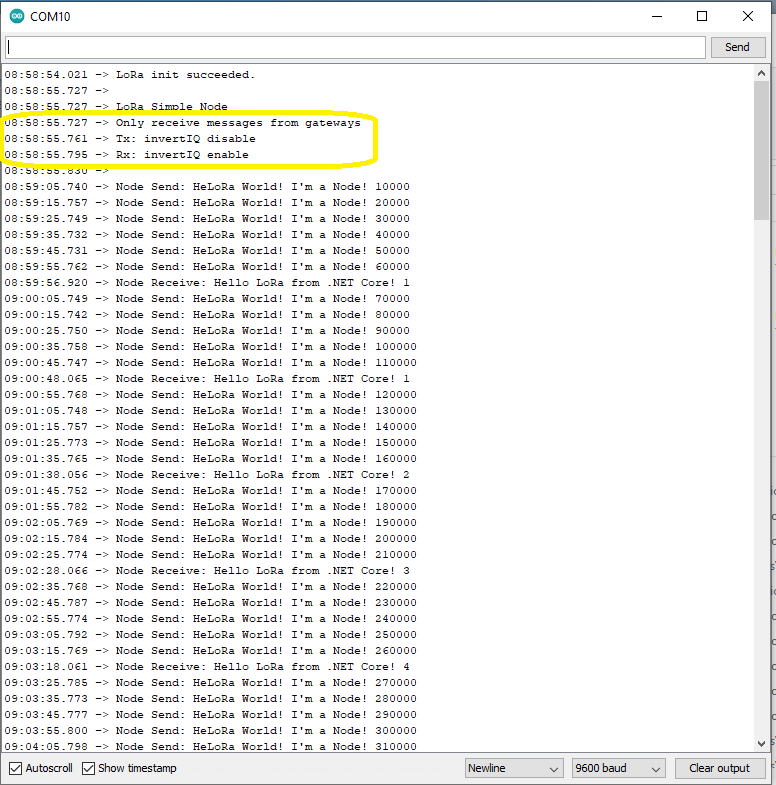
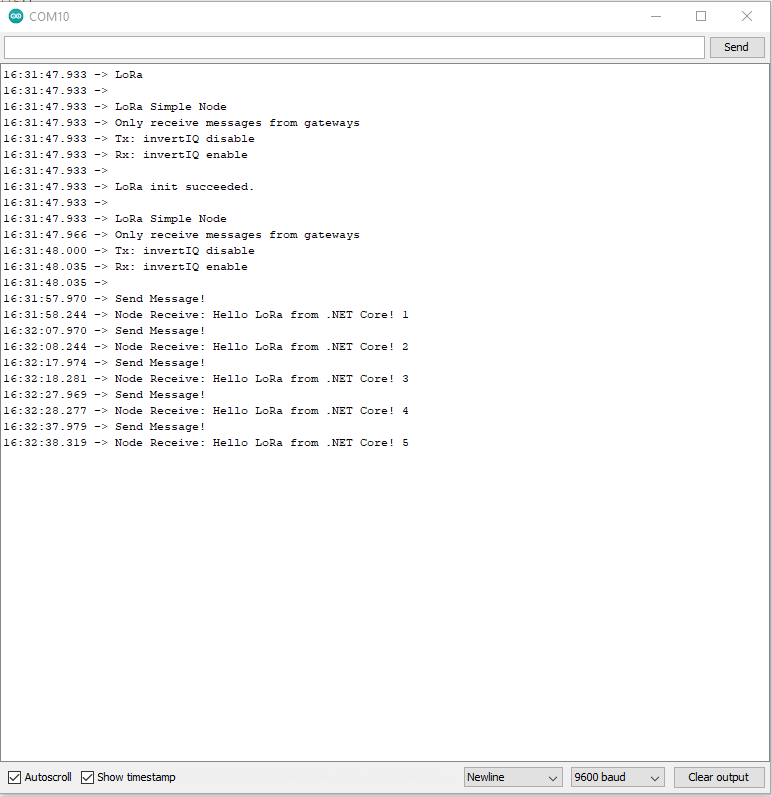
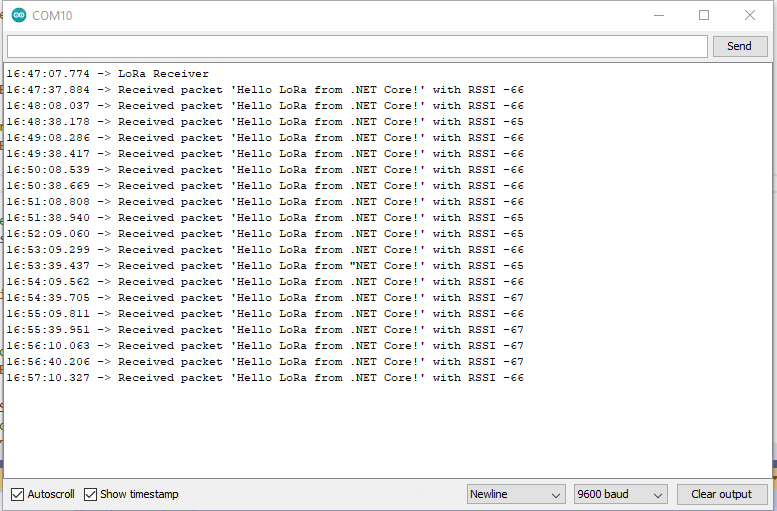
Nasty OTAA connect
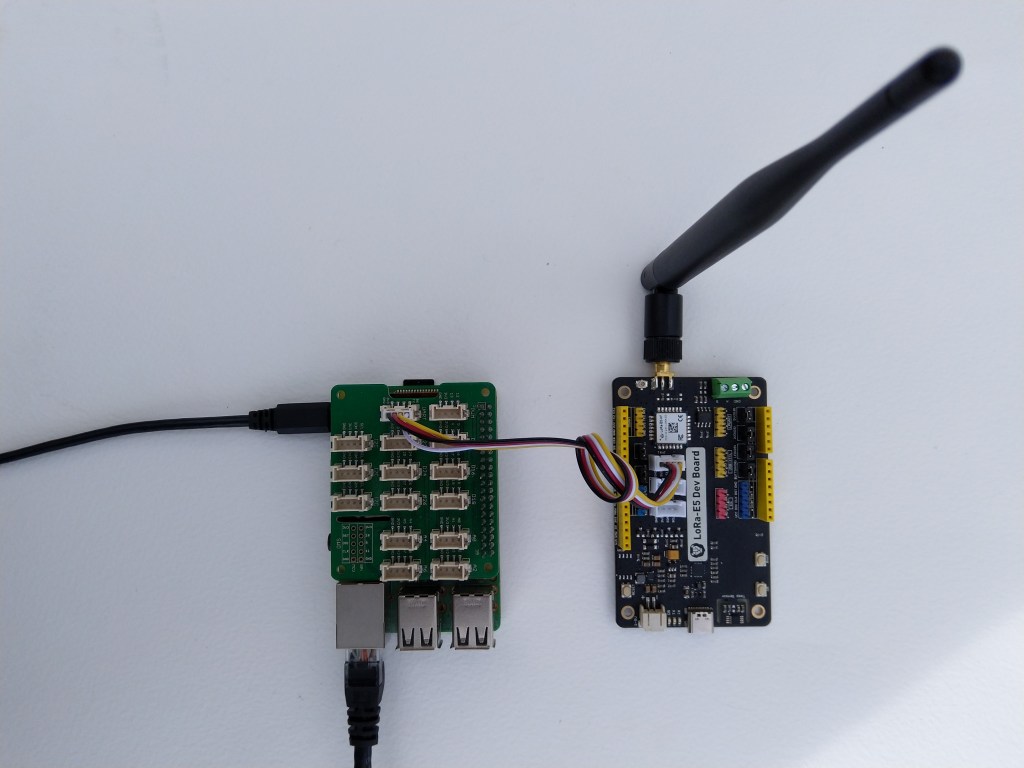
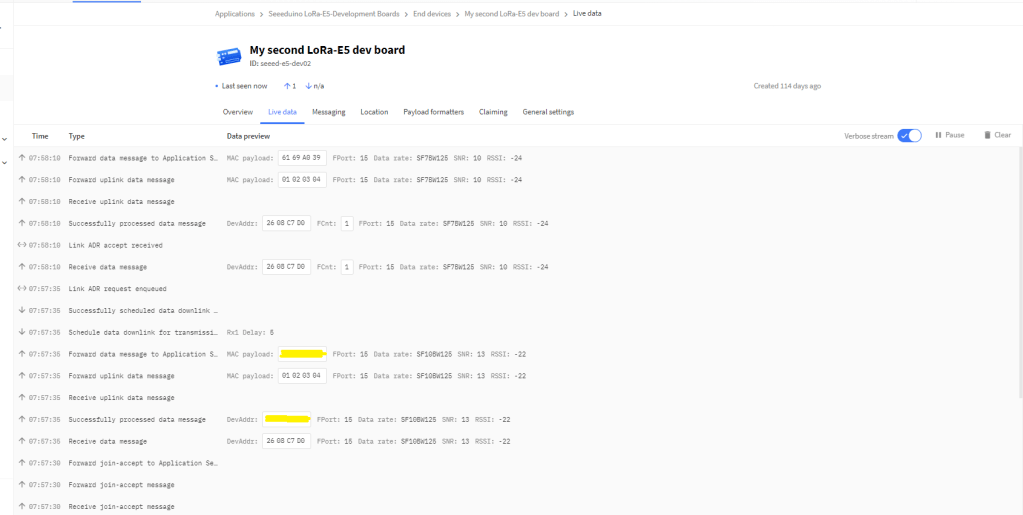
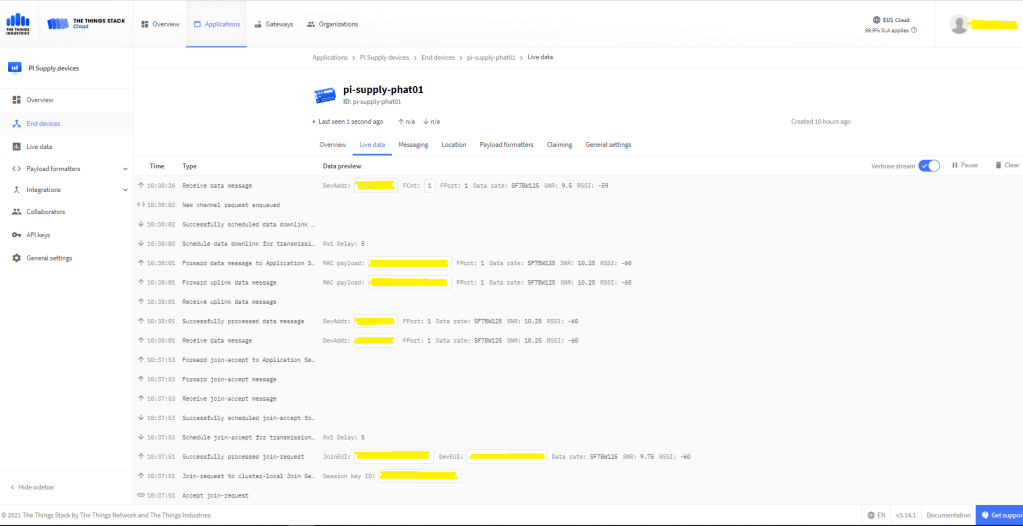
After getting basic connectivity for my Seeed LoRa-E5 test rig sorted I used RAK7246G LPWAN Developer Gateway on my bookcase to connect to The Things Network(TTN)
My Over the Air Activation (OTAA) implementation is very “nasty” I have assumed that there would be no timeouts or failures and I only send one BCD message “48656c6c6f204c6f526157414e” which is “hello LoRaWAN”.
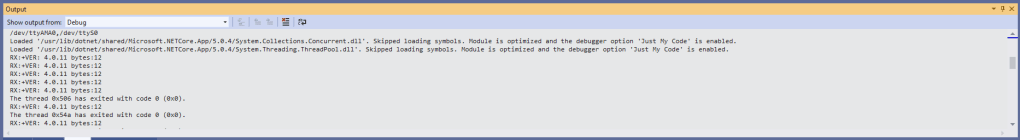
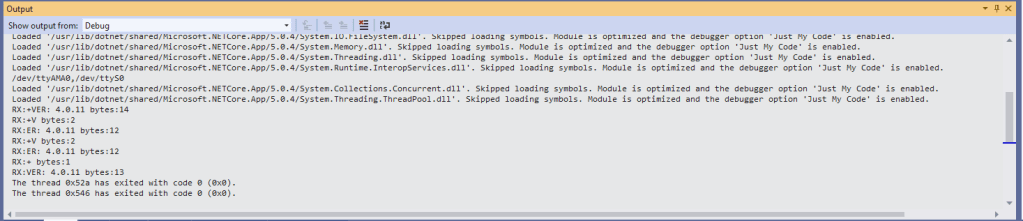
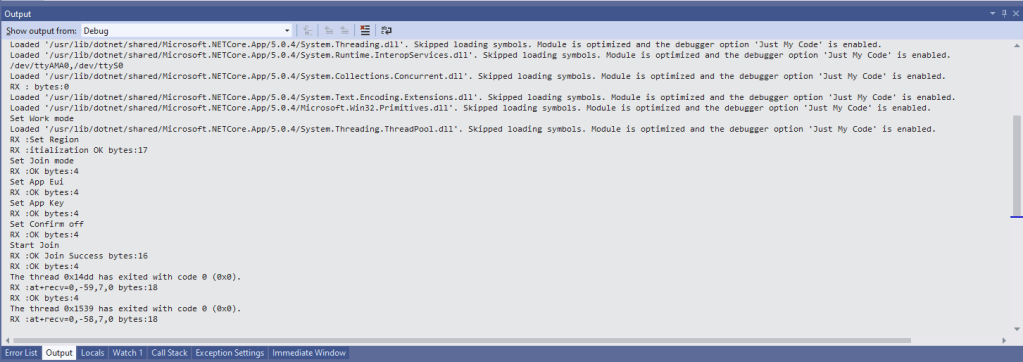
The code just sequentially steps through the necessary configuration to join the TTN network with a suitable delay after each command is sent. There also appeared to be quite a variation in response times, especially for joining the network(most probably network related) and the progress of sending a message.
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Copyright (c) September 2021, devMobile Software
//
// Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
// you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
// You may obtain a copy of the License at
//
// http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
//
// Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
// distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
// WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
// See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
// limitations under the License.
//
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
namespace devMobile.IoT.NetCore.SeeedLoRaE5.NetworkJoinOTAA
{
using System;
using System.Diagnostics;
using System.IO.Ports;
using System.Threading;
class Program
{
private const string SerialPortId = "/dev/ttyS0";
private const string AppKey = "................................";
private const string AppEui = "................";
private const byte MessagePort = 15;
//private const string Payload = "48656c6c6f204c6f526157414e"; // Hello LoRaWAN
private const string Payload = "01020304"; // AQIDBA==
//private const string Payload = "04030201"; // BAMCAQ==
public static void Main()
{
string response;
Debug.WriteLine("devMobile.IoT.SeeedLoRaE5.NetworkJoinOTAA starting");
Debug.WriteLine(String.Join(",", SerialPort.GetPortNames()));
try
{
using (SerialPort serialDevice = new SerialPort(SerialPortId))
{
// set parameters
serialDevice.BaudRate = 9600;
serialDevice.Parity = Parity.None;
serialDevice.StopBits = StopBits.One;
serialDevice.Handshake = Handshake.None;
serialDevice.DataBits = 8;
serialDevice.ReadTimeout = 10000;
serialDevice.NewLine = "\r\n";
serialDevice.Open();
// clear out the RX buffer
serialDevice.ReadExisting();
response = serialDevice.ReadExisting();
Debug.WriteLine($"Response :{response.Trim()} bytes:{response.Length}");
Thread.Sleep(500);
// Set the Region to AS923
serialDevice.WriteLine("AT+DR=AS923\r\n");
response = serialDevice.ReadLine();
Debug.WriteLine($"Response :{response.Trim()} bytes:{response.Length}");
// Set the Join mode
serialDevice.WriteLine("AT +MODE=LWOTAA\r\n");
response = serialDevice.ReadLine();
Debug.WriteLine($"Response :{response.Trim()} bytes:{response.Length}");
// Set the appEUI
serialDevice.WriteLine($"AT+ID=AppEui,\"{AppEui}\"\r\n");
response = serialDevice.ReadLine();
Debug.WriteLine($"Response :{response.Trim()} bytes:{response.Length}");
// Set the appKey
serialDevice.WriteLine($"AT+KEY=APPKEY,{AppKey}\r\n");
response = serialDevice.ReadLine();
Debug.WriteLine($"Response :{response.Trim()} bytes:{response.Length}");
// Set the port number
serialDevice.WriteLine($"AT+PORT={MessagePort}\r\n");
response = serialDevice.ReadLine();
Debug.WriteLine($"Response :{response.Trim()} bytes:{response.Length}");
// Join the network
serialDevice.WriteLine("AT+JOIN\r\n");
// Join start
response = serialDevice.ReadLine();
Debug.WriteLine($"Response :{response.Trim()} bytes:{response.Length}");
// JOIN normal
response = serialDevice.ReadLine();
Debug.WriteLine($"Response :{response.Trim()} bytes:{response.Length}");
Thread.Sleep(5000);
// network joined
response = serialDevice.ReadLine();
Debug.WriteLine($"Response :{response.Trim()} bytes:{response.Length}");
// Net ID
response = serialDevice.ReadLine();
Debug.WriteLine($"Response :{response.Trim()} bytes:{response.Length}");
// Join done
response = serialDevice.ReadLine();
Debug.WriteLine($"Response :{response.Trim()} bytes:{response.Length}");
while (true)
{
Debug.WriteLine("Sending");
serialDevice.WriteLine($"AT+MSGHEX=\"{Payload}\"\r\n");
// Start
response = serialDevice.ReadLine();
Debug.WriteLine($"Response :{response.Trim()} bytes:{response.Length}");
// Fpending
response = serialDevice.ReadLine();
Debug.WriteLine($"Response :{response.Trim()} bytes:{response.Length}");
//Read metrics
response = serialDevice.ReadLine();
Debug.WriteLine($"Response :{response.Trim()} bytes:{response.Length}");
//Done
response = serialDevice.ReadLine();
Debug.WriteLine($"Response :{response.Trim()} bytes:{response.Length}");
Thread.Sleep(30000);
}
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Debug.WriteLine(ex.Message);
}
}
}
}
The code is not suitable for production but it confirmed my software and hardware configuration worked.
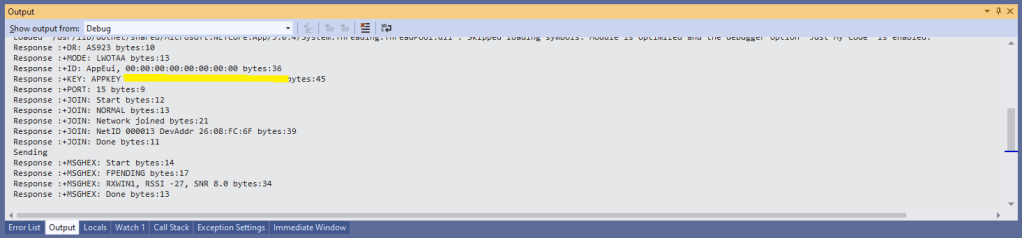
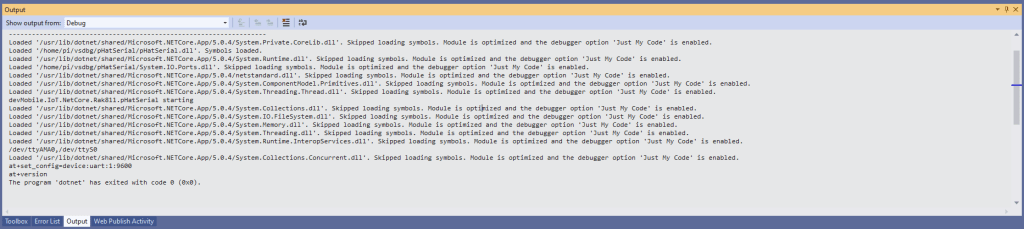
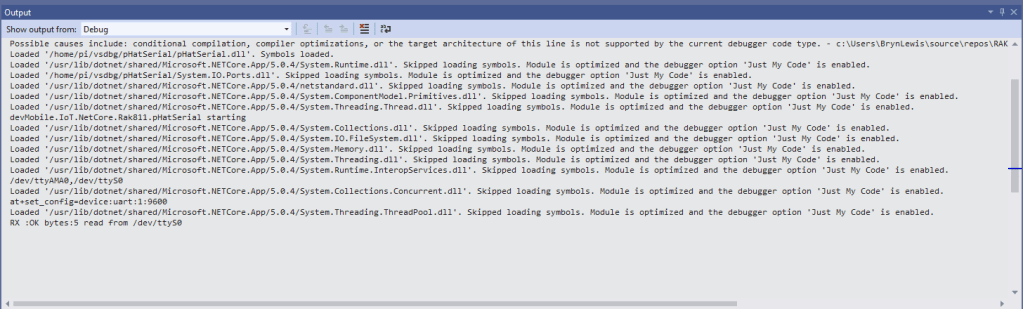
In the Visual Studio 2019 debug output I could see messages getting sent and then after a short delay they were visible in the TTN console.
Most of the LoRaWAN modems I have worked with reply “OK” when a command is successful. The SeeedLoRa-E5 often returns the payload of the request in the response which makes the code a little bit more complex.
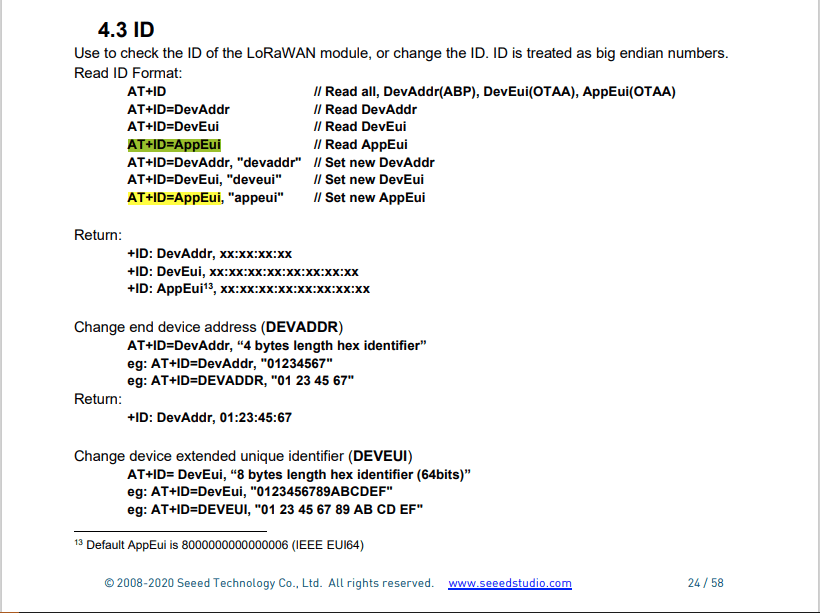
For example the AppEui can be passed in as “00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00” or “0000000000000000” but in the response the format is always “00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00”