This post is for Azure Function developers having issues with the SendGrid binding throwing exceptions like the one below.
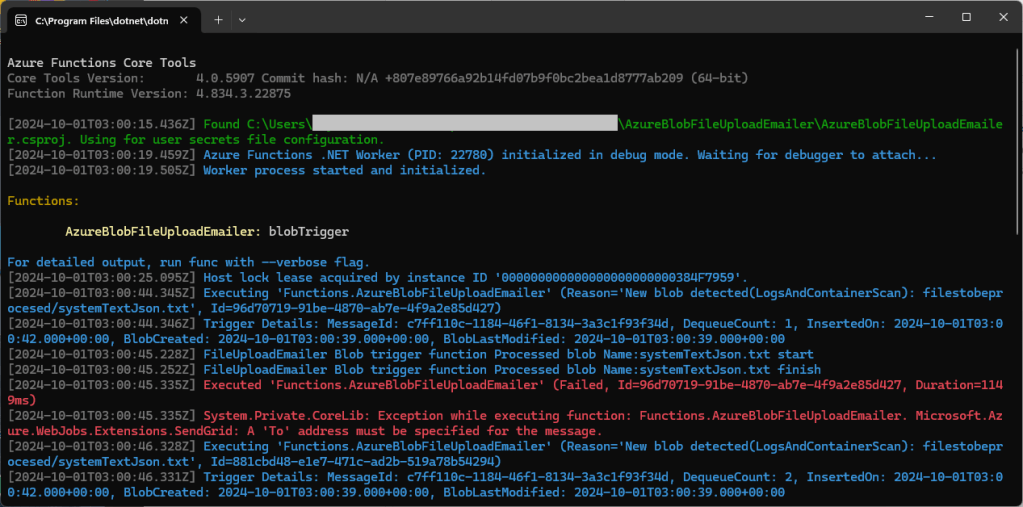
System.Private.CoreLib: Exception while executing function: Functions.AzureBlobFileUploadEmailer. Microsoft.Azure.WebJobs.Extensions.SendGrid: A 'To' address must be specified for the message
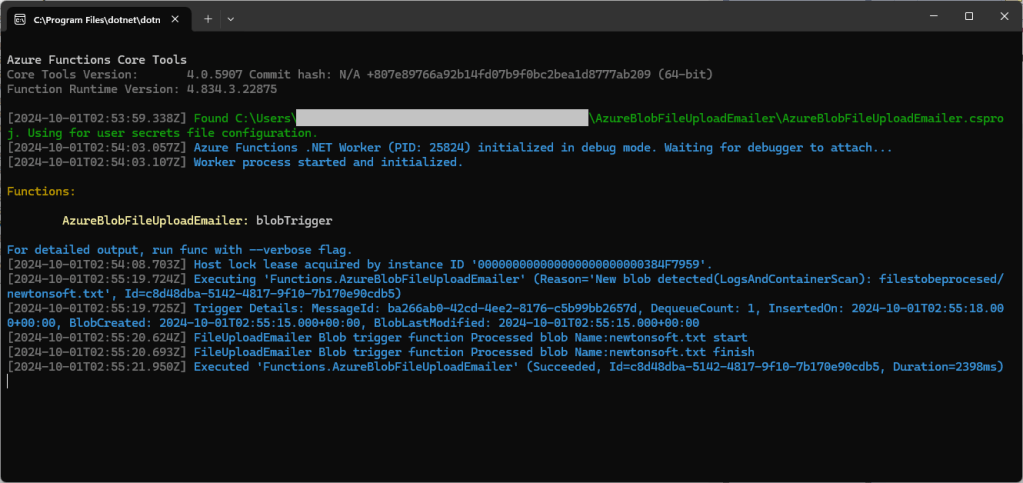
My Azure BlobTrigger Function sends an email (with SendGrid) when a file is uploaded to an Azure Blob Storage Container(a couple of times a day).
public class FileUploadEmailer(ILogger<FileUploadEmailer> logger, IOptions<EmailSettings> emailSettings)
{
private readonly ILogger<FileUploadEmailer> _logger = logger;
private readonly EmailSettings _emailSettings = emailSettings.Value;
[Function(nameof(AzureBlobFileUploadEmailer))]
[SendGridOutput(ApiKey = "SendGridAPIKey")]
public string Run([BlobTrigger("filestobeprocesed/{name}", Connection = "upload-file-storage")] Stream stream, string name)
{
_logger.LogInformation("FileUploadEmailer Blob trigger function Processed blob Name:{0} start", name);
try
{
var message = new SendGridMessage();
message.SetFrom(_emailSettings.From);
message.AddTo(_emailSettings.To);
message.Subject = _emailSettings.Subject;
message.AddContent(MimeType.Html, string.Format(_emailSettings.BodyFormat, name, DateTime.UtcNow));
// WARNING - Use Newtonsoft JSON serializer to produce JSON string. System.Text.Json won't work because property annotations are different
var messageJson = Newtonsoft.Json.JsonConvert.SerializeObject(message);
_logger.LogInformation("FileUploadEmailer Blob trigger function Processed blob Name:{0} finish", name);
return messageJson;
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
_logger.LogError(ex, "FileUploadEmailer Blob trigger function Processed blob Name: {0}", name);
throw;
}
}
}
I missed the first clue when I looked at the JSON and missed the Tos, Ccs, Bccs property names.
{
"From":{"Name":"Foo","Email":"bryn.lewis@devmobile.co.nz"},
"Subject":"Hi 30/09/2024 1:27:49 pm",
"Personalizations":[{"Tos":[{"Name":"Bar","Email":"bryn.lewis@devmobile.co.nz"}],
"Ccs":null,
"Bccs":null,
"From":null,
"Subject":null,
"Headers":null,
"Substitutions":null,
"CustomArgs":null,
"SendAt":null,
"TemplateData":null}],
"Contents":[{"Type":"text/html","Value":"\u003Ch2\u003EHello AssemblyInfo.cs\u003C/h2\u003E"}],
"PlainTextContent":null,
"HtmlContent":null,
"Attachments":null,
"TemplateId":null,
"Headers":null,
"Sections":null,
"Categories":null,
"CustomArgs":null,
"SendAt":null,
"Asm":null,
"BatchId":null,
"IpPoolName":null,
"MailSettings":null,
"TrackingSettings":null,
"ReplyTo":null,
"ReplyTos":null
}
I wasn’t paying close enough attention to the sample code and used the System.Text.Json rather than Newtonsoft.Json to serialize the SendGridMessage object. They use different attributes for property names etc. so the JSON generated was wrong.
Initially, I tried adding System.Text.Json attributes to the SendGridMessage class
namespace SendGrid.Helpers.Mail
{
/// <summary>
/// Class SendGridMessage builds an object that sends an email through Twilio SendGrid.
/// </summary>
[JsonObject(IsReference = false)]
public class SendGridMessage
{
/// <summary>
/// Gets or sets an email object containing the email address and name of the sender. Unicode encoding is not supported for the from field.
/// </summary>
//[JsonProperty(PropertyName = "from")]
[JsonPropertyName("from")]
public EmailAddress From { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// Gets or sets the subject of your email. This may be overridden by personalizations[x].subject.
/// </summary>
//[JsonProperty(PropertyName = "subject")]
[JsonPropertyName("subject")]
public string Subject { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// Gets or sets a list of messages and their metadata. Each object within personalizations can be thought of as an envelope - it defines who should receive an individual message and how that message should be handled. For more information, please see our documentation on Personalizations. Parameters in personalizations will override the parameters of the same name from the message level.
/// https://sendgrid.com/docs/Classroom/Send/v3_Mail_Send/personalizations.html.
/// </summary>
//[JsonProperty(PropertyName = "personalizations", IsReference = false)]
[JsonPropertyName("personalizations")]
public List<Personalization> Personalizations { get; set; }
...
}
SendGridMessage uses other classes like EmailAddress which worked because the property names matched the JSON
namespace SendGrid.Helpers.Mail
{
/// <summary>
/// An email object containing the email address and name of the sender or recipient.
/// </summary>
[JsonObject(IsReference = false)]
public class EmailAddress : IEquatable<EmailAddress>
{
/// <summary>
/// Initializes a new instance of the <see cref="EmailAddress"/> class.
/// </summary>
public EmailAddress()
{
}
/// <summary>
/// Initializes a new instance of the <see cref="EmailAddress"/> class.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="email">The email address of the sender or recipient.</param>
/// <param name="name">The name of the sender or recipient.</param>
public EmailAddress(string email, string name = null)
{
this.Email = email;
this.Name = name;
}
/// <summary>
/// Gets or sets the name of the sender or recipient.
/// </summary>
[JsonProperty(PropertyName = "name")]
public string Name { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// Gets or sets the email address of the sender or recipient.
/// </summary>
[JsonProperty(PropertyName = "email")]
public string Email { get; set; }
...
}
Many of the property name “mismatch” issues were in the Personalization class with the Toos, Ccs, bccs etc. properties
namespace SendGrid.Helpers.Mail
{
/// <summary>
/// An array of messages and their metadata. Each object within personalizations can be thought of as an envelope - it defines who should receive an individual message and how that message should be handled. For more information, please see our documentation on Personalizations. Parameters in personalizations will override the parameters of the same name from the message level.
/// https://sendgrid.com/docs/Classroom/Send/v3_Mail_Send/personalizations.html.
/// </summary>
[JsonObject(IsReference = false)]
public class Personalization
{
/// <summary>
/// Gets or sets an array of recipients. Each email object within this array may contain the recipient’s name, but must always contain the recipient’s email.
/// </summary>
[JsonProperty(PropertyName = "to", IsReference = false)]
[JsonConverter(typeof(RemoveDuplicatesConverter<EmailAddress>))]
public List<EmailAddress> Tos { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// Gets or sets an array of recipients who will receive a copy of your email. Each email object within this array may contain the recipient’s name, but must always contain the recipient’s email.
/// </summary>
[JsonProperty(PropertyName = "cc", IsReference = false)]
[JsonConverter(typeof(RemoveDuplicatesConverter<EmailAddress>))]
public List<EmailAddress> Ccs { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// Gets or sets an array of recipients who will receive a blind carbon copy of your email. Each email object within this array may contain the recipient’s name, but must always contain the recipient’s email.
/// </summary>
[JsonProperty(PropertyName = "bcc", IsReference = false)]
[JsonConverter(typeof(RemoveDuplicatesConverter<EmailAddress>))]
public List<EmailAddress> Bccs { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// Gets or sets the from email address. The domain must match the domain of the from email property specified at root level of the request body.
/// </summary>
[JsonProperty(PropertyName = "from")]
public EmailAddress From { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// Gets or sets the subject line of your email.
/// </summary>
[JsonProperty(PropertyName = "subject")]
public string Subject { get; set; }
...
}
After a couple of failed attempts at decorating the SendGrid SendGridMessage, EmailAddress, Personalization etc. classes I gave up and reverted to the Newtonsoft.Json serialiser.
Note to self – pay closer attention to the samples.