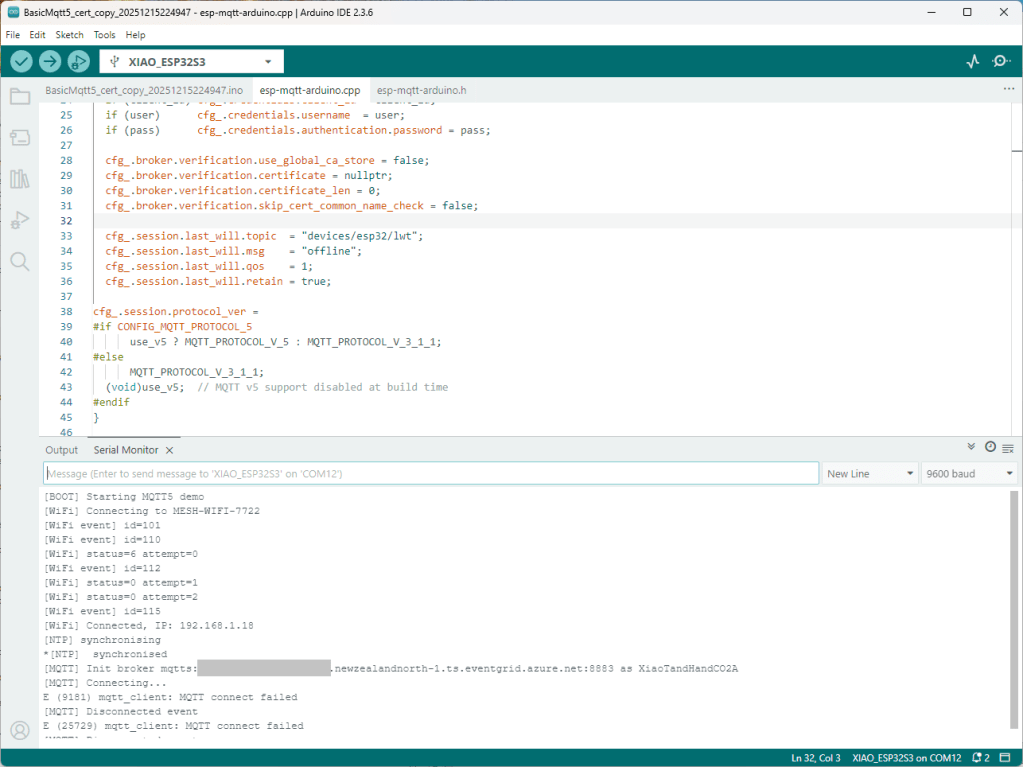
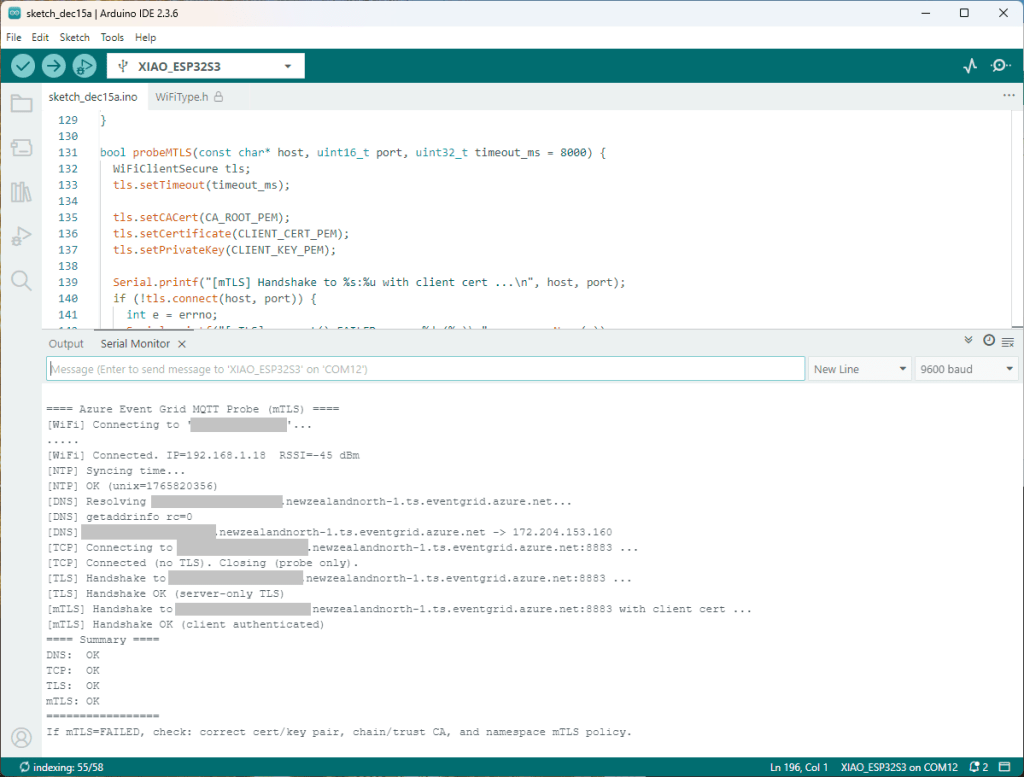
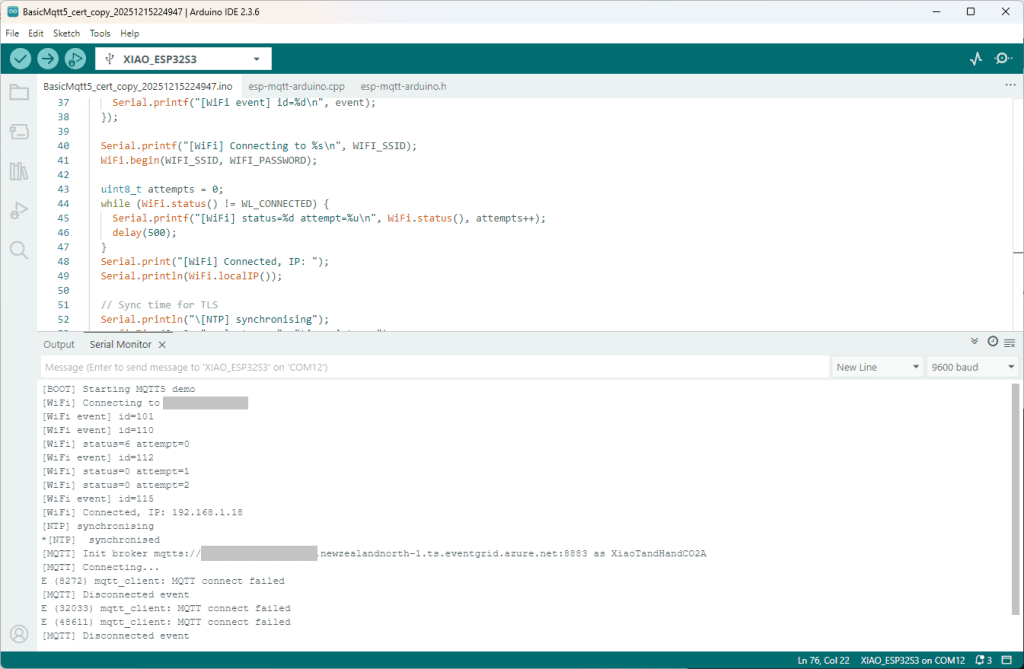
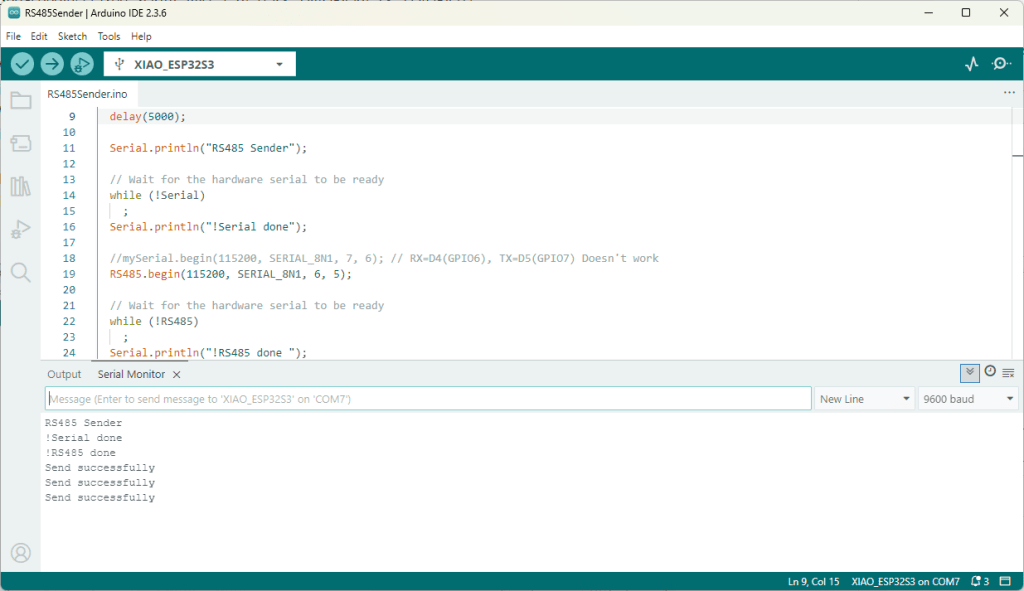
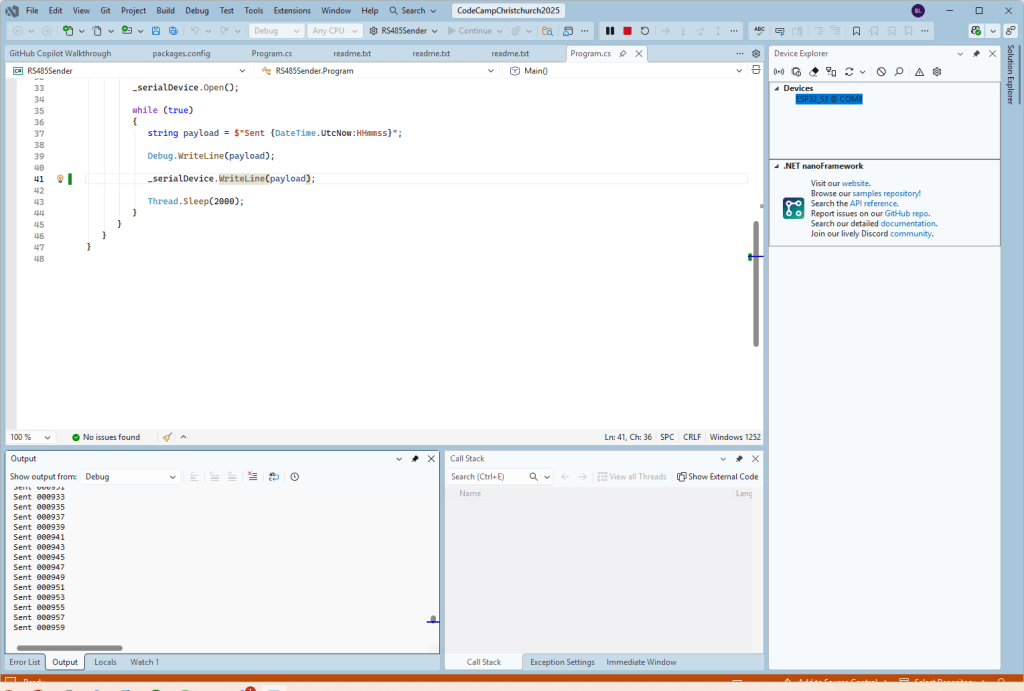
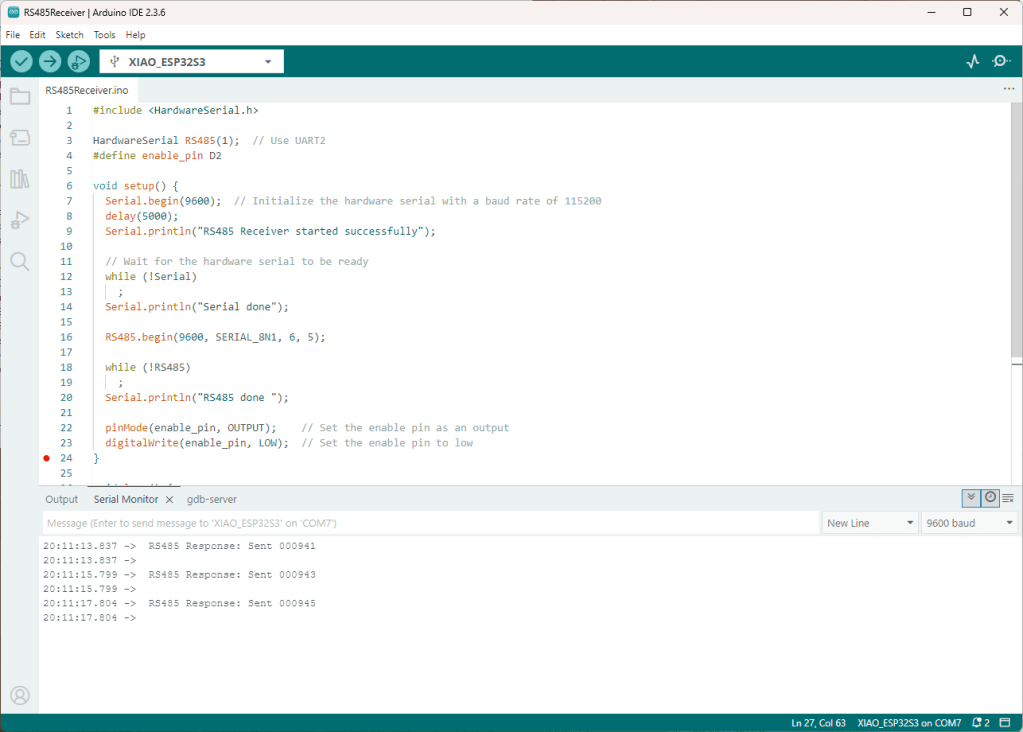
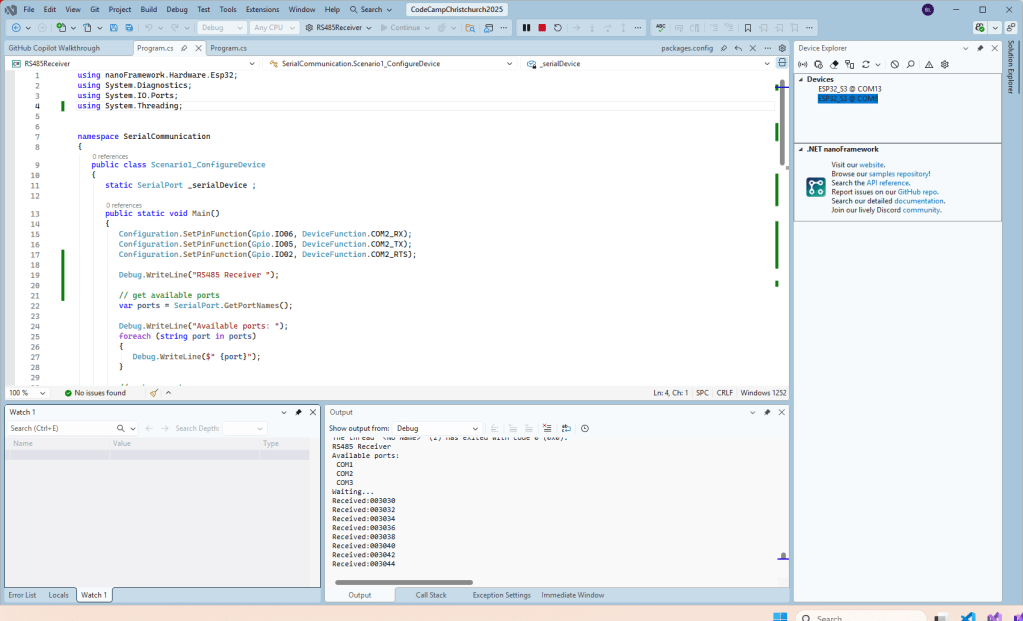
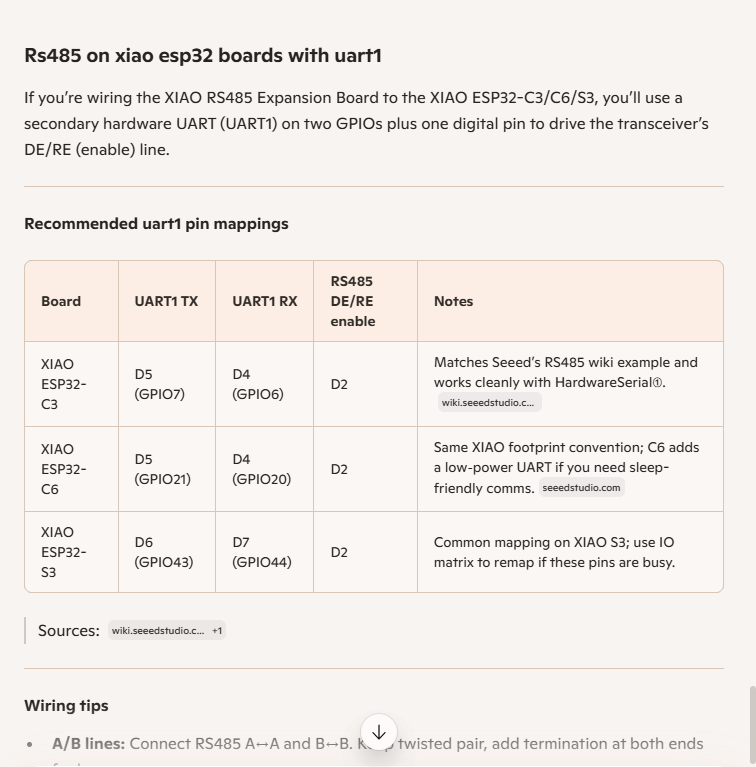
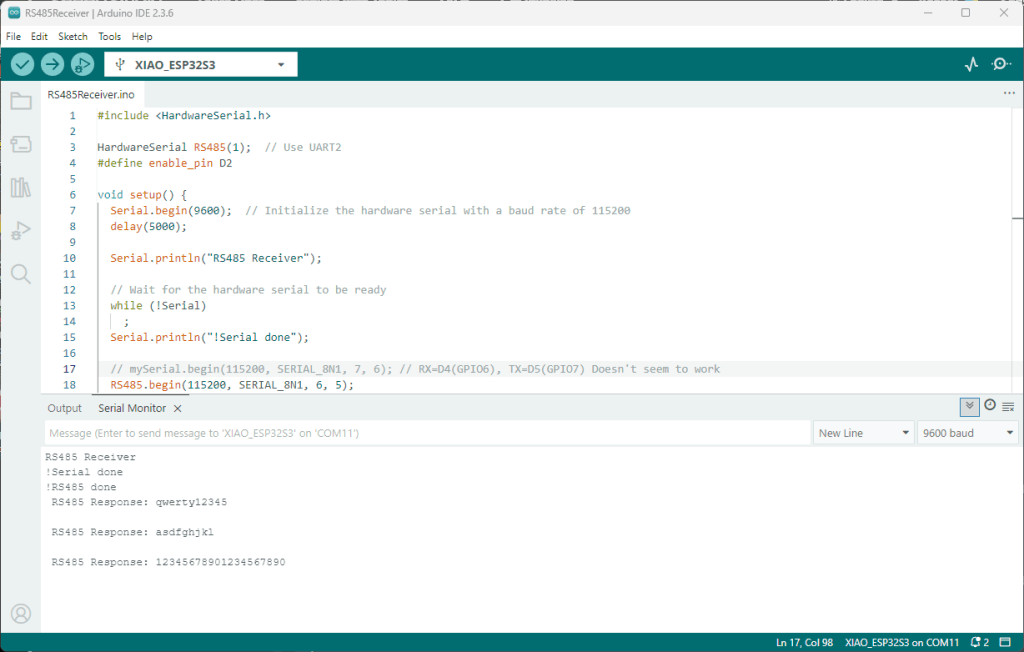
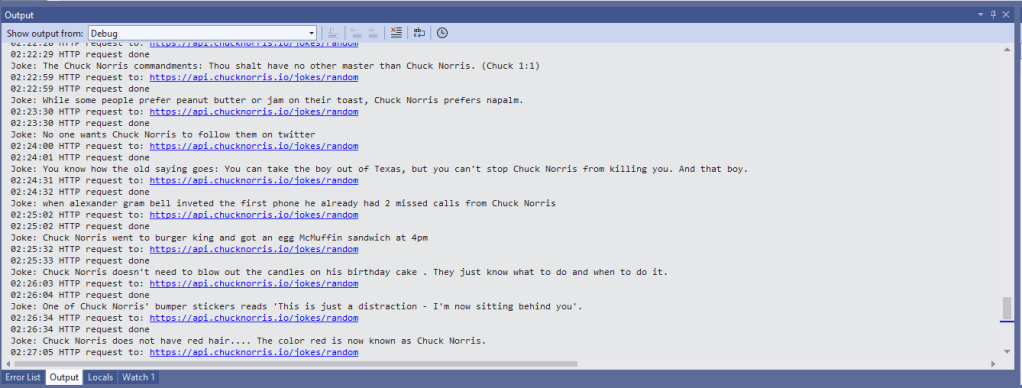
I couldn’t figure out why my code was failing so I gave up. Then the following day the application worked which was really odd. I then fired up my original Arduino PubSubClient library based application to do some testing and went to make a coffee. The application was failing to connect as XiaoTandHandCO2A and even when the bug was fixed (last will setup configuration commented out) it still wouldn’t connect.
The Azure EventGrid MQTT Broker client configuration looked fine
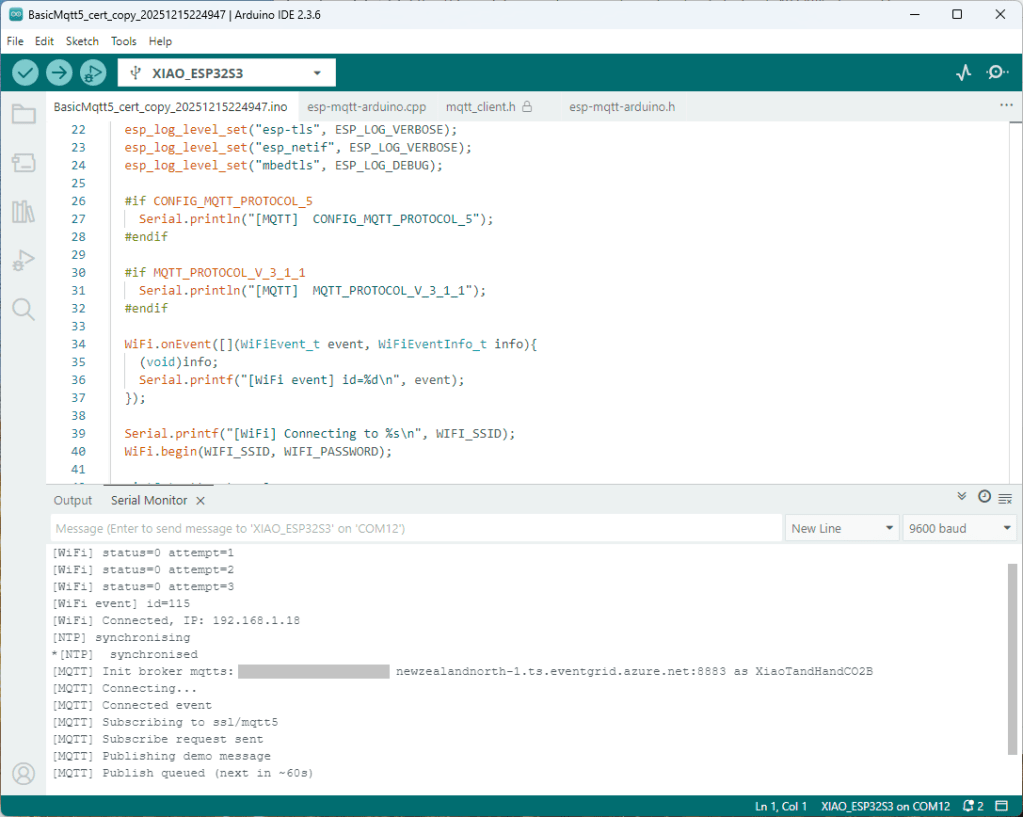
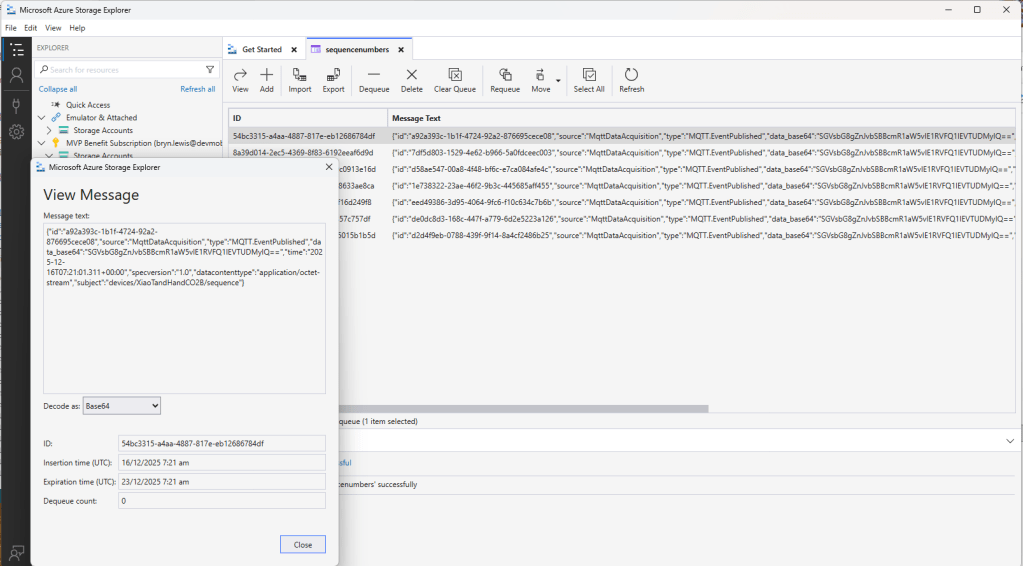
Accidentally the configuration was changed XiaoTandHandCO2B and the application worked which was unexpected. I still couldn’t figure out why my code was failing XiaoTandHandCO2A so I gave up.
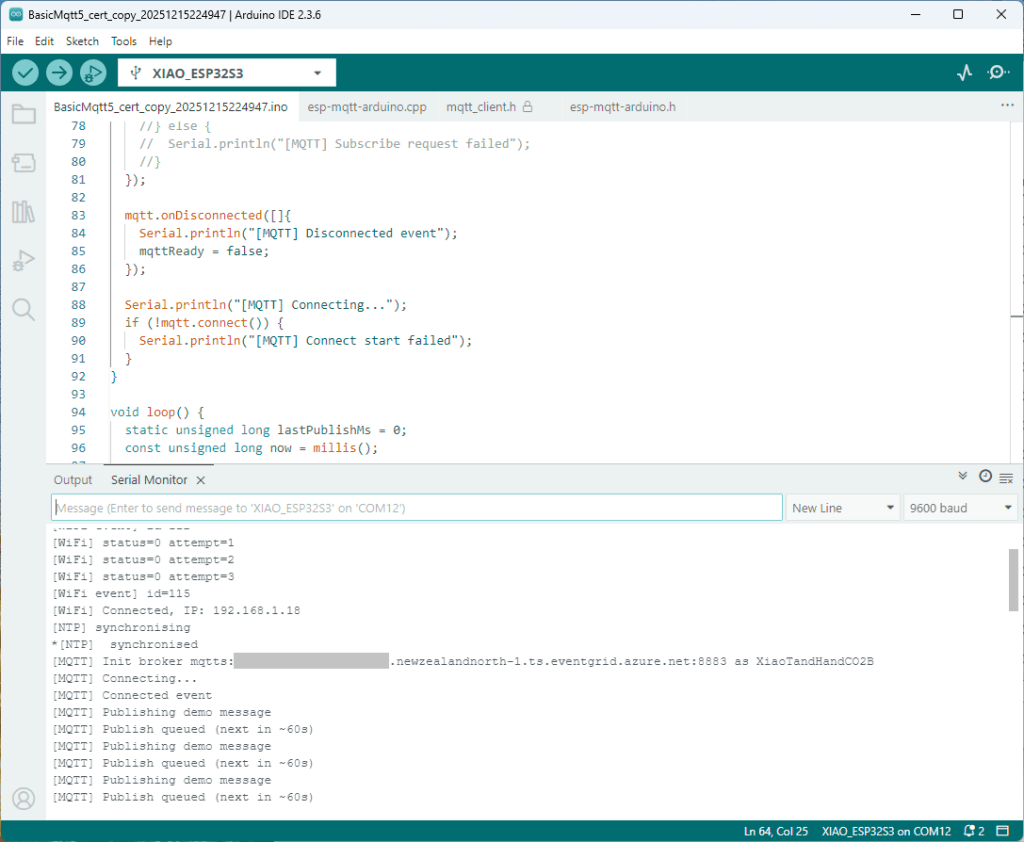
The following morning the XiaoTandHandCO2A configuration worked which was a bit odd. My best guess is that after a number of failed attempts the device is “disabled” for a while (but this is not displayed in the client configuration) and the following morning enough time had passed for the device to be “re-enabled”.
For testing I usually split my constants & secrets into two files, constants has the certificate chains for the Azure Event Grid MQTT Broker and secrets has certificate chains for devices and the Azure EventGrid MQTT Broker. I did consider have a secrets.h file for each device or splitting the device intermediate certificates, but as I was debugging and testing, it was just easier to duplicate them.
// constants.h
#pragma once
const uint16_t MQTT_PORT = 8883;
// This certificate is used to authenticate the host
static const char CA_ROOT_PEM[] PROGMEM = R"PEM(
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
...
-----END CERTIFICATE-----
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
...
-----END CERTIFICATE-----
)PEM";
// Secrets.h
#pragma once
// Wi-Fi credentials
const char* WIFI_SSID = "SSID";
const char* WIFI_PASSWORD = "Password";
// MQTT settings
//const char* MQTT_SERVER_URI = "MyBroker.newzealandnorth-1.ts.eventgrid.azure.net";
const char* MQTT_SERVER_URL = "mqtts://MyBroker.newzealandnorth-1.ts.eventgrid.azure.net:8883";
/*
// This is A setup, below are B, C, D, & E
const char* MQTT_CLIENTID = "XiaoTandHandCO2A";
const char* MQTT_TOPIC_PUBLISH = "devices/XiaoTandHandCO2A/sequence";
const char* MQTT_TOPIC_SUBSCRIBE = "devices/XiaoTandHandCO2A/configuration";
static const char CLIENT_CERT_PEM[] PROGMEM = R"PEM(
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
-----END CERTIFICATE-----
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
Intermediate certificate
-----END CERTIFICATE-----
)PEM";
static const char CLIENT_KEY_PEM[] PROGMEM = R"PEM(
-----BEGIN PRIVATE KEY-----
-----END PRIVATE KEY-----
)PEM";
*/
const char* MQTT_CLIENTID = "XiaoTandHandCO2B";
const char* MQTT_TOPIC_PUBLISH = "devices/XiaoTandHandCO2B/sequence";
const char* MQTT_TOPIC_SUBSCRIBE = "devices/XiaoTandHandCO2V/configuration";
static const char CLIENT_CERT_PEM[] PROGMEM = R"PEM(
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
-----END CERTIFICATE-----
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
Intermediate certificate
-----END CERTIFICATE-----
)PEM";
static const char CLIENT_KEY_PEM[] PROGMEM = R"PEM(
-----BEGIN PRIVATE KEY-----
-----END PRIVATE KEY-----
)PEM";
/*
const char* MQTT_CLIENTID = "XiaoTandHandCO2C";
const char* MQTT_TOPIC_PUBLISH = "devices/XiaoTandHandCO2C/sequence";
const char* MQTT_TOPIC_SUBSCRIBE = "devices/XiaoTandHandCO2V/configuration";
static const char CLIENT_CERT_PEM[] PROGMEM = R"PEM(
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
-----END CERTIFICATE-----
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
Intermediate certificate
-----END CERTIFICATE-----
)PEM";
static const char CLIENT_KEY_PEM[] PROGMEM = R"PEM(
-----BEGIN PRIVATE KEY-----
-----END PRIVATE KEY-----
)PEM";
*/
/*
const char* MQTT_CLIENTID = "XiaoTandHandCO2D";
const char* MQTT_TOPIC_PUBLISH = "devices/XiaoTandHandCO2D/sequence";
const char* MQTT_TOPIC_SUBSCRIBE = "devices/XiaoTandHandCO2V/configuration";
static const char CLIENT_CERT_PEM[] PROGMEM = R"PEM(
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
-----END CERTIFICATE-----
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
Intermediate certificate
-----END CERTIFICATE-----
)PEM";
static const char CLIENT_KEY_PEM[] PROGMEM = R"PEM(
-----BEGIN PRIVATE KEY-----
-----END PRIVATE KEY-----
)PEM";
*/
/*
const char* MQTT_CLIENTID = "XiaoTandHandCO2E";
const char* MQTT_TOPIC_PUBLISH = "devices/XiaoTandHandCO2E/sequence";
const char* MQTT_TOPIC_SUBSCRIBE = "devices/XiaoTandHandCO2V/configuration";
static const char CLIENT_CERT_PEM[] PROGMEM = R"PEM(
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
-----END CERTIFICATE-----
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
Intermediate certificate
-----END CERTIFICATE-----
)PEM";
static const char CLIENT_KEY_PEM[] PROGMEM = R"PEM(
-----BEGIN PRIVATE KEY-----
-----END PRIVATE KEY-----
)PEM";
*/
To make deployments easier I have some software which stores the certificates in an optional “secure element” like the Microchip ATECC608C(The Seeedstudio Edgebox100 documentation refers to an optional Microchip ATECC680A but these are “not recommended for new designs”). This isn’t a great solution but deployments easier and is “better” than a string constant in the binary.