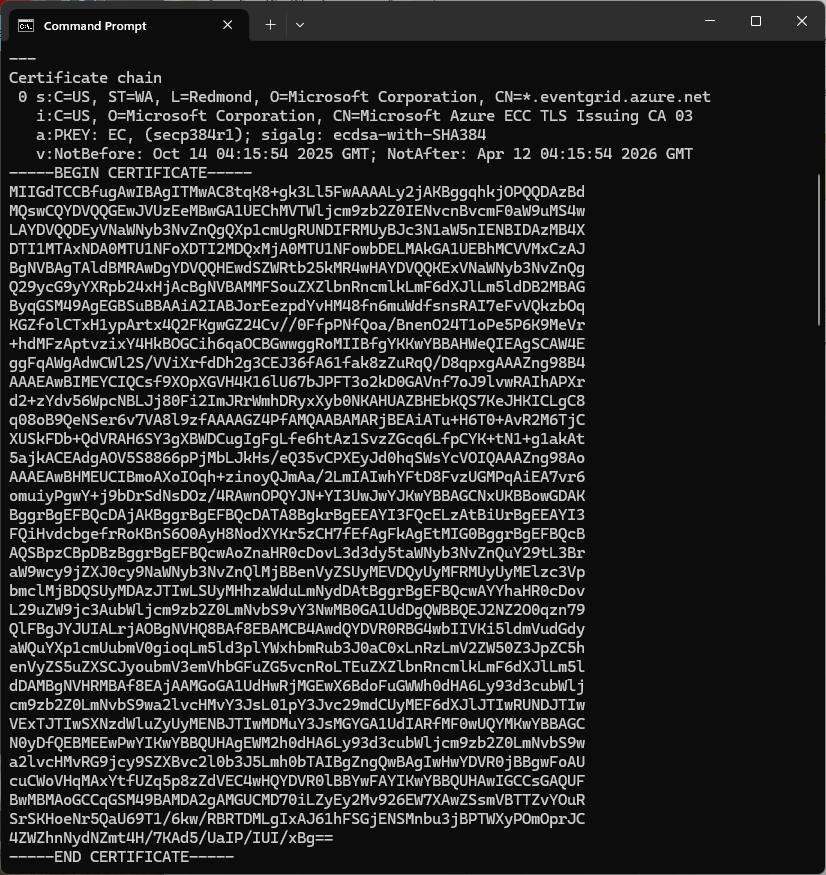
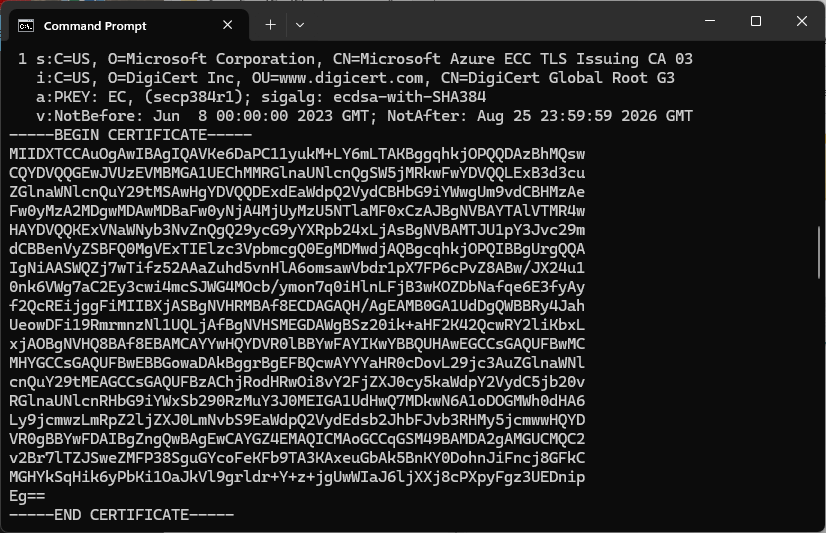
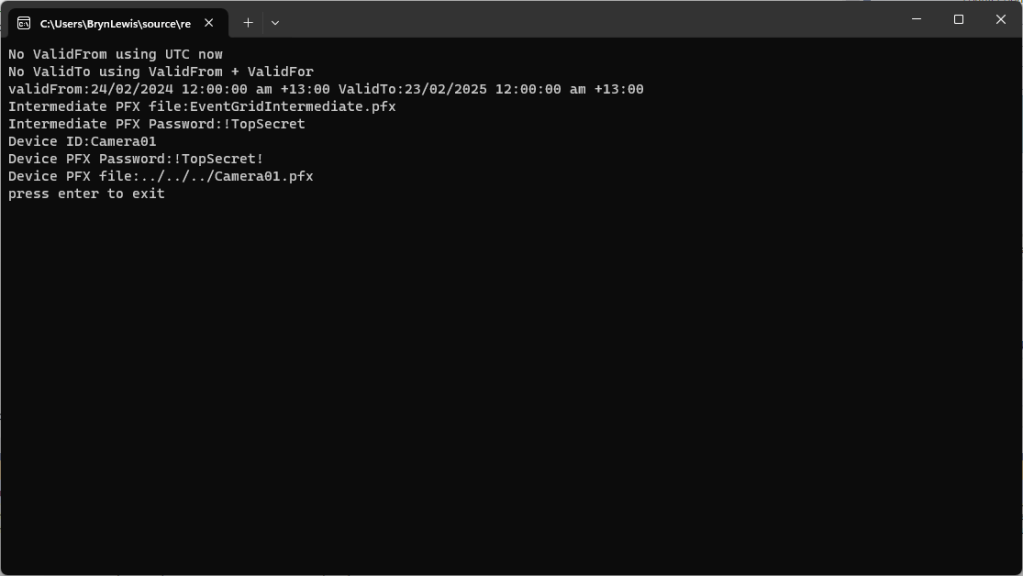
Over the last couple of weekends I had been trying to get a repeatable process for extracting the X509 certificate information in the correct structure so my Arduino application could connect to Azure Event Grid. The first step was to get the certificate chain for my Azure Event Grid MQTT Broker with openssl
openssl s_client -connect YourNameSpaceHere.newzealandnorth-1.ts.eventgrid.azure.net:8883 -showcerts
The CN: CN=DigiCert Global Root G3 and the wildcard CN=*.eventgrid.azure.net certificates were “concatenated” in the constants header file which is included in the main program file. The format of the certificate chain is described in the comments. Avoid blank lines, “rogue” spaces or other formatting as these may cause the WiFiClientSecure Mbed TLS implementation to fail.
/*
Minimalist ESP32 + Azure Event Grid MQTT Event Grid broker namespace certificate validation
copyright (c) November 2025, devMobile Software
*/
#include <WiFi.h>
#include <WiFiClientSecure.h>
#include "secrets.h"
#include "constants.h"
// --- Wi-Fi ---
//const char* WIFI_SSID = "";
//const char* WIFI_PASSWORD = "";
//const char* MQTT_SERVER = "YourNamespace.newzealandnorth-1.ts.eventgrid.azure.net";
const uint16_t MQTT_PORT = 8883;
/*
// The certificate that is used to authenticate the MQTT Broker
const char CA_ROOT_PEM[] PROGMEM = R"PEM(
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
MIIGdTCCBfugAwIBAgITMwAC8tqK8+gk3Ll5FwAAAALy2jAKBggqhkjOPQQDAzBd
....
Thumbprint: 56D955C849887874AA1767810366D90ADF6C8536
CN: CN=Microsoft Azure ECC TLS Issuing CA 03
CN=*.eventgrid.azure.net
....
4ZWZhnNydNZmt4H/7KAd5/UaIP/IUI/xBg==
-----END CERTIFICATE-----
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
MIIDXTCCAuOgAwIBAgIQAVKe6DaPC11yukM+LY6mLTAKBggqhkjOPQQDAzBhMQsw
....
Thumbprint: 7E04DE896A3E666D00E687D33FFAD93BE83D349E
CN: CN=DigiCert Global Root G3
....
MGHYkSqHik6yPbKi1OaJkVl9grldr+Y+z+jgUwWIaJ6ljXXj8cPXpyFgz3UEDnip
Eg==
-----END CERTIFICATE-----
)PEM";
*/
WiFiClientSecure secureClient;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
delay(2000);
Serial.println("\nServerCertificateValidationClient starting");
struct tm timeinfo;
if (getLocalTime(&timeinfo)) {
Serial.printf("Startup DateTime: %04d-%02d-%02d %02d:%02d:%02d\n", timeinfo.tm_year + 1900, timeinfo.tm_mon + 1, timeinfo.tm_mday, timeinfo.tm_hour, timeinfo.tm_min, timeinfo.tm_sec);
}
// Connect to WiFi
Serial.println("WiFi connecting");
WiFi.begin(WIFI_SSID, WIFI_PASSWORD);
Serial.print("*");
while (WiFi.status() != WL_CONNECTED) {
delay(500);
Serial.print("*");
}
Serial.println("\nWiFi connected");
if (getLocalTime(&timeinfo)) {
Serial.printf("Wifi DateTime: %04d-%02d-%02d %02d:%02d:%02d\n", timeinfo.tm_year + 1900, timeinfo.tm_mon + 1, timeinfo.tm_mday, timeinfo.tm_hour, timeinfo.tm_min, timeinfo.tm_sec);
}
// Sync time for TLS
Serial.println("\nTime synchronising");
configTime(0, 0, "pool.ntp.org", "time.nist.gov");
Serial.print("*");
while (time(nullptr) < 100000) {
delay(500);
Serial.print("*");
}
Serial.println("\nTime synchronised");
if (getLocalTime(&timeinfo)) {
Serial.printf("NTP DateTime: %04d-%02d-%02d %02d:%02d:%02d\n", timeinfo.tm_year + 1900, timeinfo.tm_mon + 1, timeinfo.tm_mday, timeinfo.tm_hour, timeinfo.tm_min, timeinfo.tm_sec);
}
Serial.println("\nValidating ServerFQDN-Certificate combination");
secureClient.setCACert(CA_ROOT_PEM);
Serial.print("*");
while (!secureClient.connect(MQTT_SERVER, MQTT_PORT)) {
delay(500);
Serial.print("*");
}
Serial.println("\nTLS Connected");
}
void loop() {
Serial.print("x");
delay(5000);
}
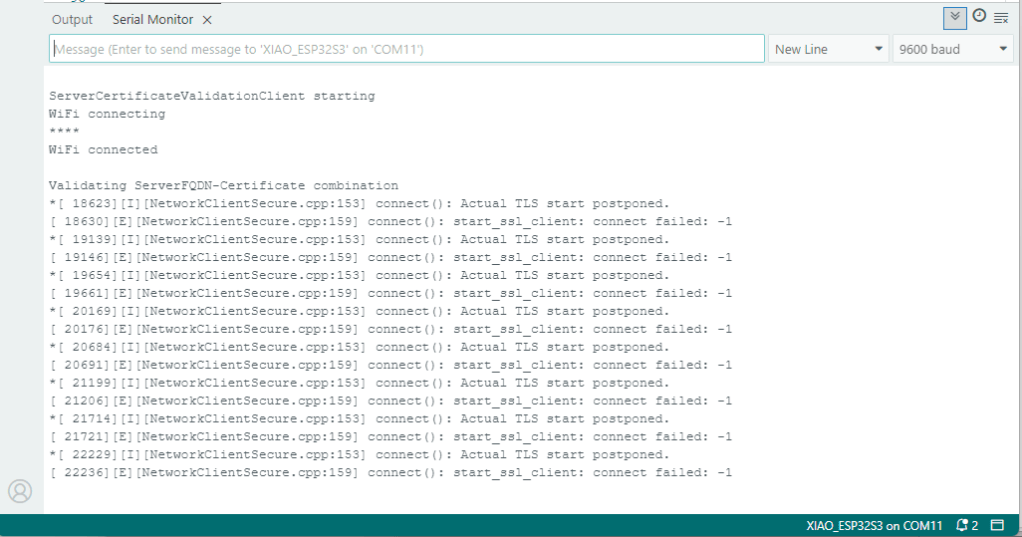
After a hard reset the WiFiClientSecure connect failed because the device time had not been initialised so the device/server time offset was too large (see rfc9325)
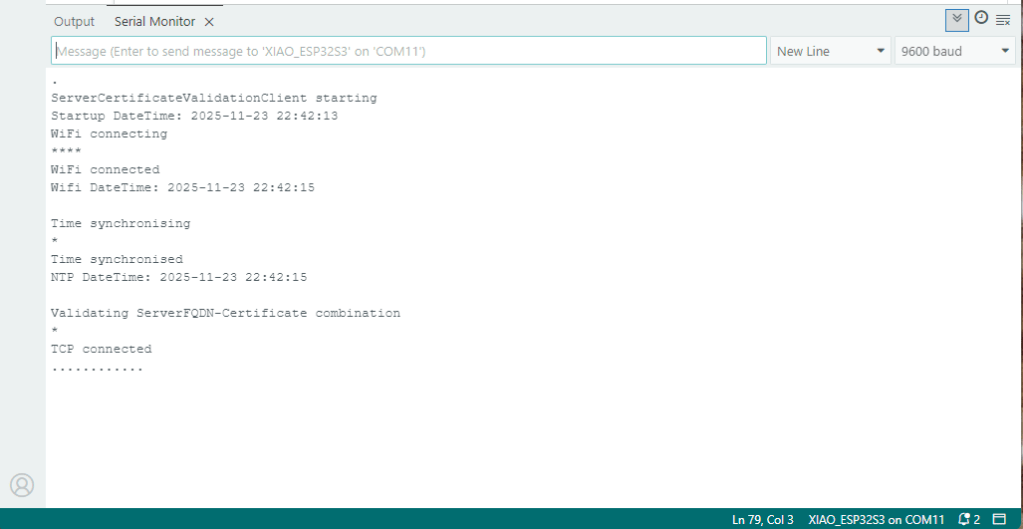
After a “hard” reset the Network Time Protocol(NTP) client was used to set the device time.
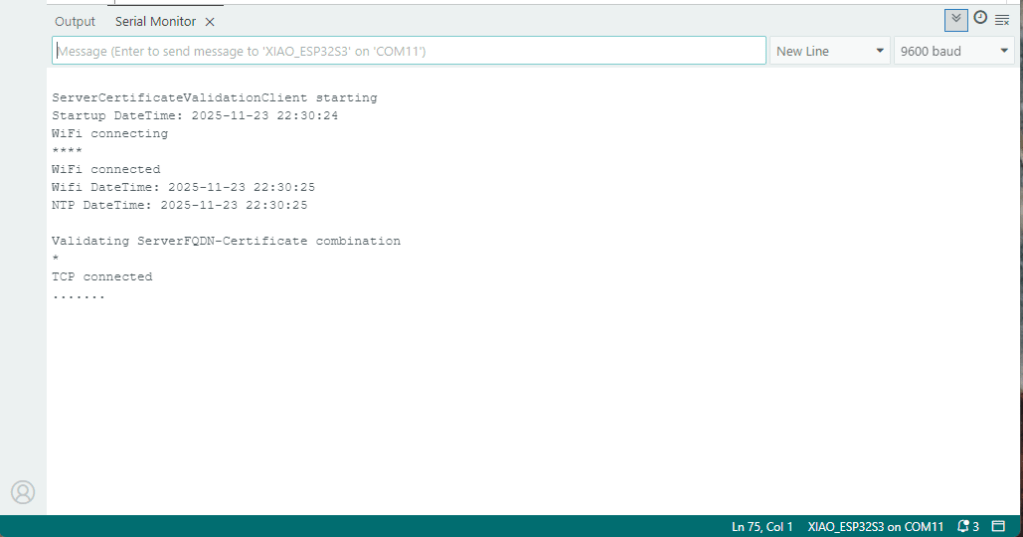
After a “soft” reset the Network Time Protocol(NTP) client did not have to be called.