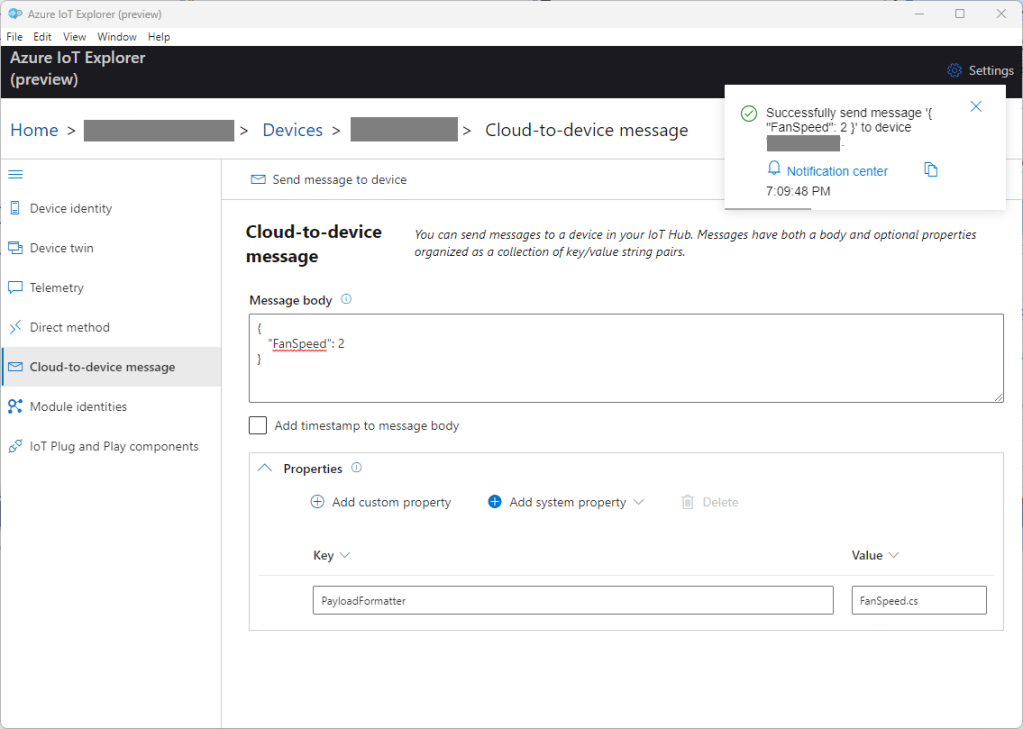
After several refactorings the code stabilised and the Azure IoT Hub downlink message handler (configured with SetMethodDefaultHandlerAsync ) was ready for testing. I used Azure IoT Explorer to send some “hand-crafted” JavaScript Object Notation(JSON) Cloud to Device(C2D) messages.
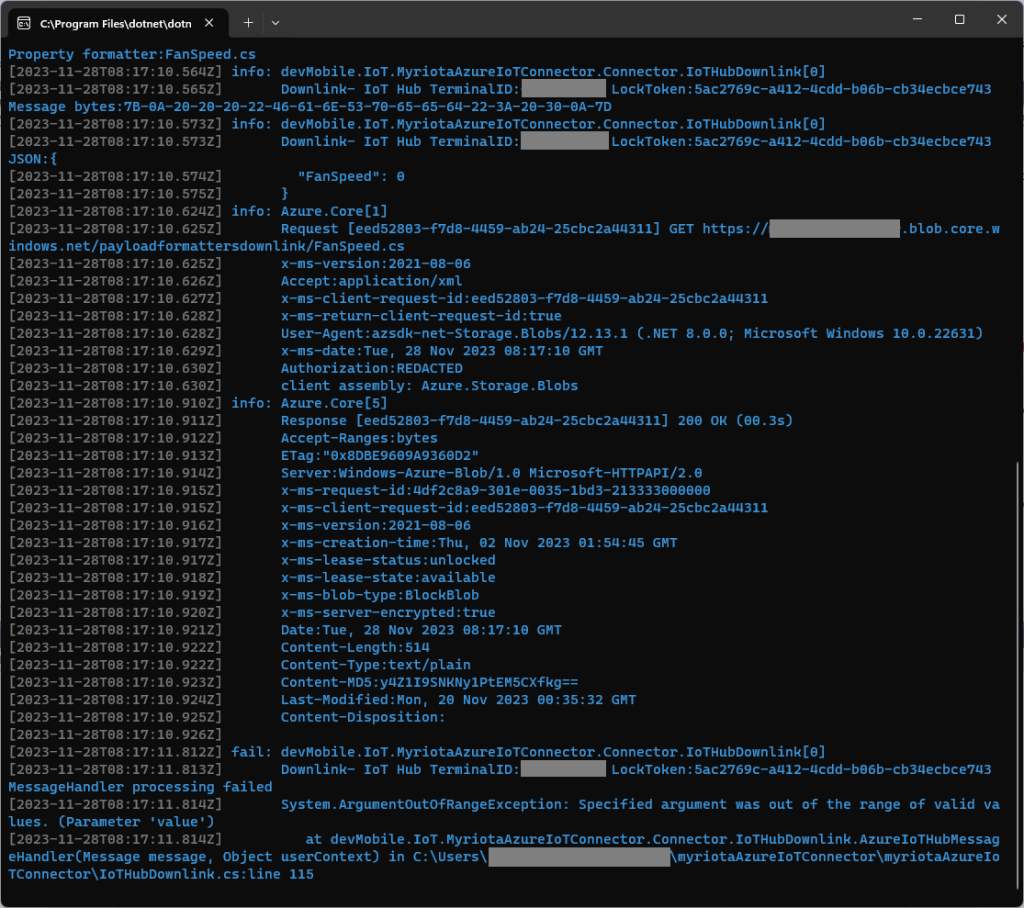
Each logging message starts with the TerminalID (to simplify searching for all the messages sent to a device) and the message LockToken (to simplify searching for all the “steps” associated with sending a message) with the rest of the logging message containing “step” specific diagnostic information.
If there is no PayloadFormatter attribute the default in the PayloadFormatters section of the function configuration is used.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using Newtonsoft.Json;
using Newtonsoft.Json.Linq;
public class FormatterDownlink : PayloadFormatter.IFormatterDownlink
{
public byte[] Evaluate(IDictionary<string, string> properties, string terminalId, JObject payloadJson, byte[] payloadBytes)
{
byte? status = payloadJson.Value<byte?>("FanSpeed");
if (!status.HasValue)
{
return new byte[] { };
}
return new byte[] { 1, status.Value };
}
}
The FanSpeed.cs payload formatter extracts the FanSpeed value from the JSON payload and returns a two byte array containing the message type and speed of the fan.
After re-reading the SetMethodHandlerAync documentation I refactored the code (back to the approach used a couple of branches ago) with the “using” wrapping the try/catch.
public async Task AzureIoTHubMessageHandler(Message message, object userContext)
{
Models.DeviceConnectionContext context = (Models.DeviceConnectionContext)userContext;
_logger.LogInformation("Downlink- IoT Hub TerminalId:{TermimalId} LockToken:{LockToken}", context.TerminalId, message.LockToken);
using (message) // https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/dotnet/api/microsoft.azure.devices.client.deviceclient.setreceivemessagehandlerasync?view=azure-dotnet
{
try
{
// Replace default formatter with message specific formatter if configured.
if (!message.Properties.TryGetValue(Constants.IoTHubDownlinkPayloadFormatterProperty, out string? payloadFormatterName) || string.IsNullOrEmpty(payloadFormatterName))
{
_logger.LogInformation("Downlink- IoT Hub TerminalID:{TermimalId} LockToken:{LockToken} Context formatter:{payloadFormatterName} ", context.TerminalId, message.LockToken, payloadFormatterName);
payloadFormatterName = context.PayloadFormatterDownlink;
}
else
{
_logger.LogInformation("Downlink- IoT Hub TerminalID:{TermimalId} LockToken:{LockToken} Property formatter:{payloadFormatterName} ", context.TerminalId, message.LockToken, payloadFormatterName);
}
// If GetBytes fails payload really badly broken
byte[] messageBytes = message.GetBytes();
_logger.LogInformation("Downlink- IoT Hub TerminalID:{TerminalId} LockToken:{LockToken} Message bytes:{messageBytes}", context.TerminalId, message.LockToken, BitConverter.ToString(messageBytes));
// Try converting the bytes to text then to JSON
JObject? messageJson = null;
try
{
// These will fail for some messages, payload formatter gets bytes only
string messageText = Encoding.UTF8.GetString(messageBytes);
try
{
messageJson = JObject.Parse(messageText);
_logger.LogInformation("Downlink- IoT Hub TerminalID:{TerminalId} LockToken:{LockToken} JSON:{messageJson}", context.TerminalId, message.LockToken, JsonConvert.SerializeObject(messageJson, Formatting.Indented));
}
catch (JsonReaderException jex)
{
_logger.LogInformation(jex, "Downlink- IoT Hub TerminalID:{TerminalId} LockToken:{LockToken} not valid JSON", context.TerminalId, message.LockToken);
}
}
catch (ArgumentException aex)
{
_logger.LogInformation(aex, "Downlink- IoT Hub TerminalID:{TerminalId} LockToken:{LockToken} message bytes not valid text", context.TerminalId, message.LockToken);
}
// This shouldn't fail, but it could for invalid path to blob, timeout retrieving blob, payload formatter syntax error etc.
IFormatterDownlink payloadFormatter = await _payloadFormatterCache.DownlinkGetAsync(payloadFormatterName);
// This will fail if payload formatter throws runtime exceptions like null reference, divide by zero, index out of range etc.
byte[] payloadBytes = payloadFormatter.Evaluate(message.Properties, context.TerminalId, messageJson, messageBytes);
// Validate payload before calling Myriota control message send API method
if (payloadBytes is null)
{
_logger.LogWarning("Downlink- IoT Hub TerminalID:{TerminalId} LockToken:{LockToken} payload formatter:{payloadFormatter} Evaluate returned null", context.TerminalId, message.LockToken, payloadFormatterName);
await context.DeviceClient.RejectAsync(message);
return;
}
if ((payloadBytes.Length < Constants.DownlinkPayloadMinimumLength) || (payloadBytes.Length > Constants.DownlinkPayloadMaximumLength))
{
_logger.LogWarning("Downlink- IoT Hub TerminalID:{TerminalId} LockToken:{LockToken} PayloadBytes:{payloadBytes} length:{Length} invalid must be {DownlinkPayloadMinimumLength} to {DownlinkPayloadMaximumLength} bytes", context.TerminalId, message.LockToken, Convert.ToHexString(payloadBytes), payloadBytes.Length, Constants.DownlinkPayloadMinimumLength, Constants.DownlinkPayloadMaximumLength);
await context.DeviceClient.RejectAsync(message);
return;
}
// Finally send Control Message to device using the Myriota API
_logger.LogInformation("Downlink- IoT Hub TerminalID:{TerminalId} LockToken:{LockToken} PayloadBytes:{payloadBytes} Length:{Length} sending", context.TerminalId, message.LockToken, BitConverter.ToString(payloadBytes), payloadBytes.Length);
string messageId = await _myriotaModuleAPI.SendAsync(context.TerminalId, payloadBytes);
_logger.LogInformation("Downlink- IoT Hub TerminalID:{TerminalId} LockToken:{LockToken} MessageID:{messageId} sent", context.TerminalId, message.LockToken, messageId);
await context.DeviceClient.CompleteAsync(message);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
_logger.LogError(ex, "Downlink- IoT Hub TerminalID:{TerminalId} LockToken:{LockToken} MessageHandler processing failed", context.TerminalId, message.LockToken);
await context.DeviceClient.RejectAsync(message);
}
}
}
The first time I ran the myriotaAzureIoTConnector Azure function in the Core Tools debugging environment there were no errors and the Microsoft.Azure.Devices.Client.DeviceClient connection cache loaded in the background.
The first time I sent a downlink message the handler failed spectacularly with a SystemArgumentOutOfRangeException
After adding some breakpoints, restarting the application, then single stepping through the code I found that I had accidentally used BitConverter.ToSingle(payloadBytes) instead of BitConverter.ToString(payloadBytes) to get the Hexadecimal representation of the payload bytes.
...
// Finally send Control Message to device using the Myriota API
_logger.LogInformation("Downlink- IoT Hub TerminalID:{TerminalId} LockToken:{LockToken} PayloadBytes:{payloadBytes} Length:{Length} sending", context.TerminalId, message.LockToken, BitConverter.ToString(payloadBytes), payloadBytes.Length);
string messageId = await _myriotaModuleAPI.SendAsync(context.TerminalId, payloadBytes);
...
The Encoding.UTF8.GetString and JObject.Parse are processed in a single Try with a specialised catch for when the payload cannot be converted to text. If the payload cannot be converted to JSON only the payloadBytes parameter of payload formatter is populated.