I have used LazyCache for several projects (The Things Network V2 HTTP, The Things Industries V2 MQTT The Things Industries V3 and Swarm Space Azure IoT Connector etc.) to cache Azure IoT Hub DeviceClient and other object instances.
The note on the wiki page “For LazyCache v2+ users, you should consider switching away from LazyCache to IDistributedCache. More information at #59“ caught my attention.
I have written other posts about caching Dapper query results with the Dapper Extension Library which worked well but had some configuration limitations. I also have posts about off-loading read-only workloads with Azure Active geo-replication or SQL Data Sync for Azure, which worked well in some scenarios but had limitations (performance and operational costs).
The IDistributedCache has Memory, SQL Server and Redis implementations so I built an Azure AppService to explore the functionality in more detail. In another project I had been working with the Azure SignalR Service and the use of the MessagePack library(rather than serialised JSON) caught my attention so I have added basic support for that as well.
I explored the in-memory implementation (AddDistributedMemoryCache) on my development machine and found “tinkering” with the configuration options had little impact on the performance of my trivial sample application.
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
// Add services to the container.
builder.Services.AddApplicationInsightsTelemetry();
// Add services to the container.
builder.Services.AddSingleton<IDapperContext>(s => new DapperContext(builder.Configuration));
builder.Services.AddControllers();
#if SERIALISATION_MESSAGE_PACK
//MessagePackSerializer.DefaultOptions = MessagePack.Resolvers.ContractlessStandardResolver.Options;
//MessagePackSerializer.DefaultOptions = MessagePack.Resolvers.ContractlessStandardResolver.Options.WithCompression(MessagePackCompression.Lz4Block);
MessagePackSerializer.DefaultOptions = MessagePack.Resolvers.ContractlessStandardResolver.Options.WithCompression(MessagePackCompression.Lz4BlockArray);
#endif
#if DISTRIBUTED_CACHE_MEMORY
builder.Services.AddDistributedMemoryCache(options =>
{
options.SizeLimit = 1000 * 1024 * 1024; // 1000MB
});
builder.Services.AddDistributedMemoryCache();
#endif
#if DISTRIBUTED_CACHE_REDIS
var configurationOptions = new ConfigurationOptions
{
EndPoints = { builder.Configuration.GetSection("RedisConnection").GetValue<string>("EndPoints") },
AllowAdmin = true,
Password = builder.Configuration.GetSection("RedisConnection").GetValue<string>("Password"),
Ssl = true,
ConnectRetry = 5,
ConnectTimeout = 10000,
SslProtocols = System.Security.Authentication.SslProtocols.Tls12,
AbortOnConnectFail = false,
};
builder.Services.AddStackExchangeRedisCache(options =>
{
options.InstanceName = "Dapper WebAPI Instance";
options.ConfigurationOptions = configurationOptions;
});
#endif
#if DISTRIBUTED_CACHE_SQL_SERVER
builder.Services.AddDistributedSqlServerCache(options =>
{
options.ConnectionString = builder.Configuration.GetConnectionString("CacheDatabase");
options.SchemaName = "dbo";
options.TableName = "StockItemsCache";
});
#endif
var app = builder.Build();
// Configure the HTTP request pipeline.
app.UseHttpsRedirection();
app.MapControllers();
app.Run();
}
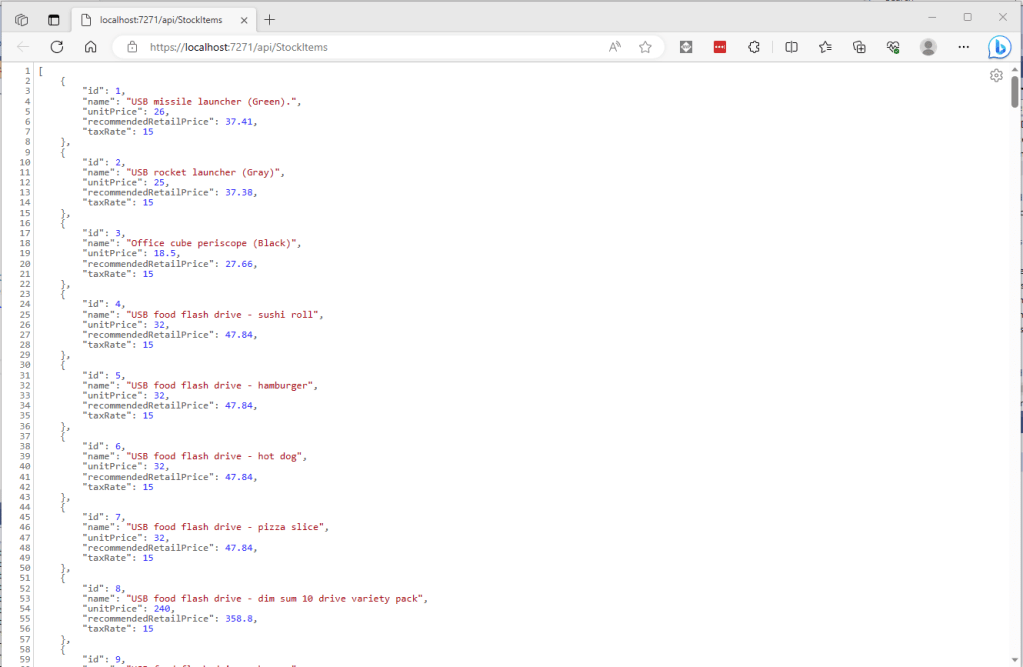
I tested the SQL Server implementation (AddDistributedSqlServerCached) using the SQL Server on my development machine, and Azure SQL as a backing store. I did consider using SQL Azure In-Memory OLTP but the performance improvement with my trivial example would most probably not worth the additional cost of the required SKU.
CREATE TABLE [dbo].[StockItemsCache](
[Id] [nvarchar](449) NOT NULL,
[Value] [varbinary](max) NOT NULL,
[ExpiresAtTime] [datetimeoffset](7) NOT NULL,
[SlidingExpirationInSeconds] [bigint] NULL,
[AbsoluteExpiration] [datetimeoffset](7) NULL,
PRIMARY KEY CLUSTERED
(
[Id] ASC
)WITH (PAD_INDEX = OFF, STATISTICS_NORECOMPUTE = OFF, IGNORE_DUP_KEY = OFF, ALLOW_ROW_LOCKS = ON, ALLOW_PAGE_LOCKS = ON, OPTIMIZE_FOR_SEQUENTIAL_KEY = OFF) ON [PRIMARY]
) ON [PRIMARY] TEXTIMAGE_ON [PRIMARY]
GO
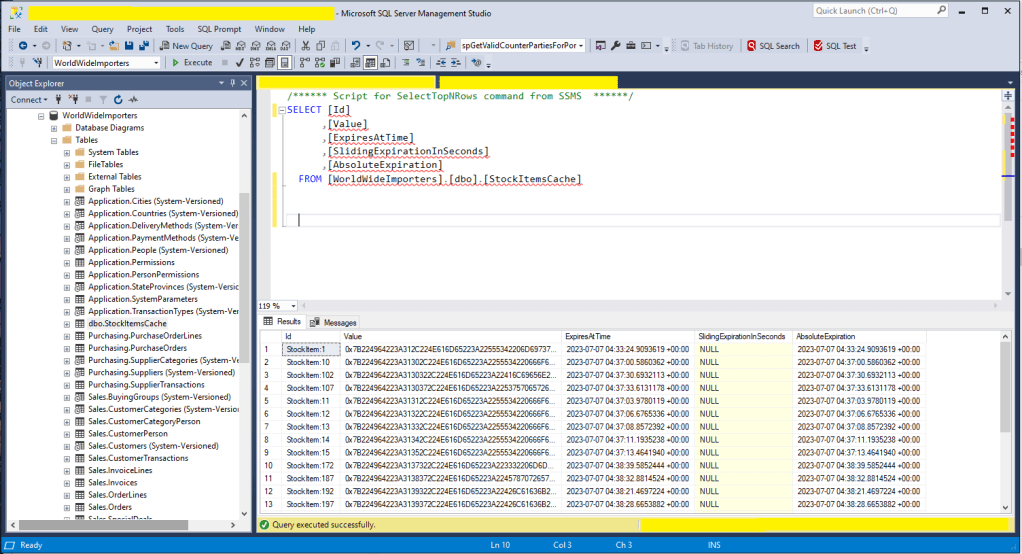
The table used to store the data wasn’t very complex and I could view the data associated with a cache key in SQL Server Mangement studio.
One of the applications I work on uses a complex SQL Server Stored procedure to load reference data (updated daily) and being able to purge the cache at the end of this process like this might be useful. For a geographically distributed application putting the Azure SQL instance “closer” to the application’s users might be worth considering.
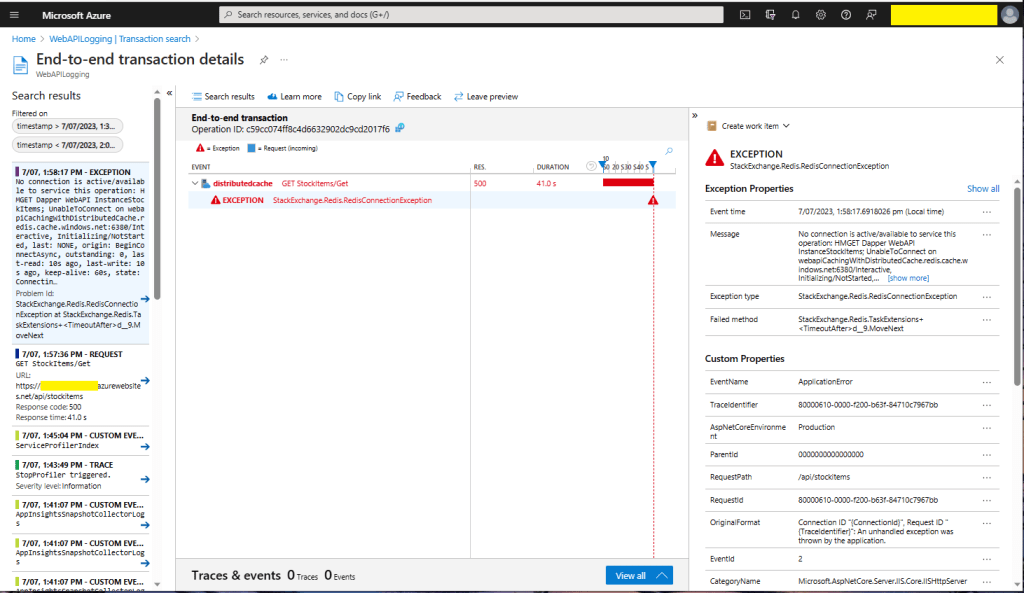
I trialed the Redis implementation with Memurai (on my development machine) and Azure Cache for Redis with multiple Azure AppService clients and there was a significant improvement in performance.
[HttpGet]
public async Task<ActionResult<IEnumerable<Model.StockItemListDtoV1>>> Get()
{
var utcNow = DateTime.UtcNow;
var cached = await distributedCache.GetAsync("StockItems");
if (cached != null)
{
#if SERIALISATION_JSON
return this.Ok(JsonSerializer.Deserialize<List<Model.StockItemListDtoV1>>(cached));
#endif
#if SERIALISATION_MESSAGE_PACK
return this.Ok(MessagePackSerializer.Deserialize<List<Model.StockItemListDtoV1>>(cached));
#endif
}
var stockItems = await dbConnection.QueryWithRetryAsync<Model.StockItemListDtoV1>(sql: sqlCommandText, commandType: CommandType.Text);
#if SERIALISATION_JSON
await distributedCache.SetAsync("StockItems", JsonSerializer.SerializeToUtf8Bytes(stockItems), new DistributedCacheEntryOptions()
#endif
#if SERIALISATION_MESSAGE_PACK
await distributedCache.SetAsync("StockItems", MessagePackSerializer.Serialize(stockItems), new DistributedCacheEntryOptions()
#endif
{
AbsoluteExpiration = new DateTime(utcNow.Year, utcNow.Month, DateTime.DaysInMonth(utcNow.Year, utcNow.Month), StockItemListAbsoluteExpiration.Hours, StockItemListAbsoluteExpiration.Minutes, StockItemListAbsoluteExpiration.Seconds)
});
return this.Ok(stockItems);
}
[HttpGet("NoLoad")]
public async Task<ActionResult<IEnumerable<Model.StockItemListDtoV1>>> GetNoLoad()
{
var cached = await distributedCache.GetAsync("StockItems");
if (cached == null)
{
return this.NoContent();
}
#if SERIALISATION_JSON
return this.Ok(JsonSerializer.Deserialize<List<Model.StockItemListDtoV1>>(cached));
#endif
#if SERIALISATION_MESSAGE_PACK
return this.Ok(MessagePackSerializer.Deserialize<List<Model.StockItemListDtoV1>>(cached));
#endif
}
In my test environment the JSON payload for a list of stock items was a bit “chunky” at 25K bytes, so I added compile time configurable support for the MessagePack library. This significantly reduced the size of the payload LZ4Block (5K bytes) and LZ4BlockArray (5K2 bytes) which should reduce network traffic.
Assuming the overheads of JSON vs. MessagePack serialisation are similar and the much smaller MessagePack library payload I would most probably use MessagePack and LZ4BlockArray (For improved compatibility with other implementations) compression.