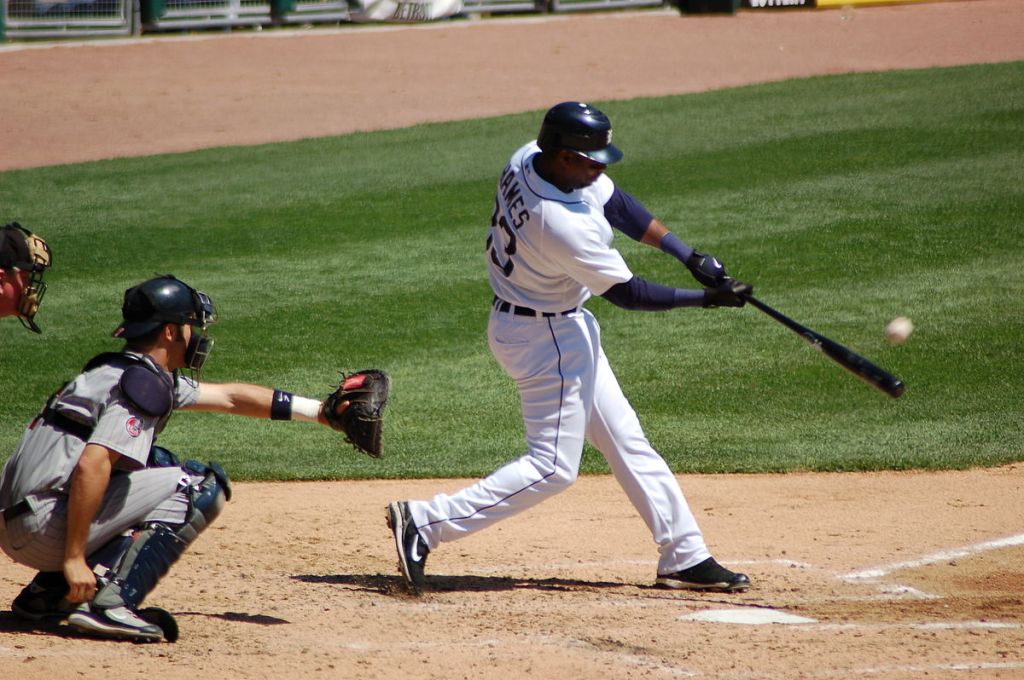
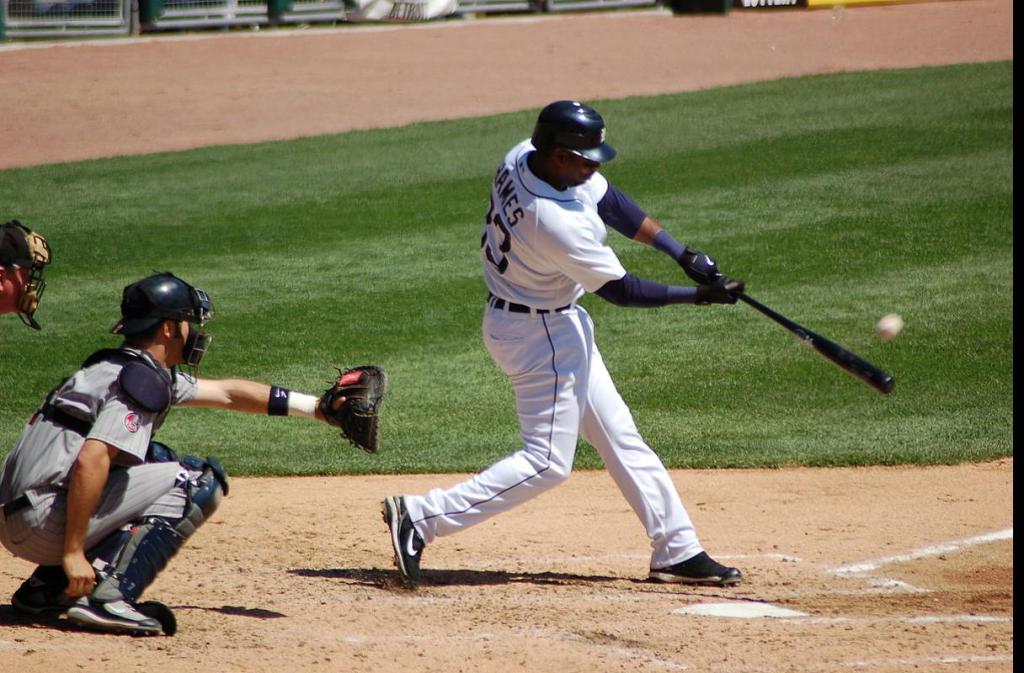
Introduction
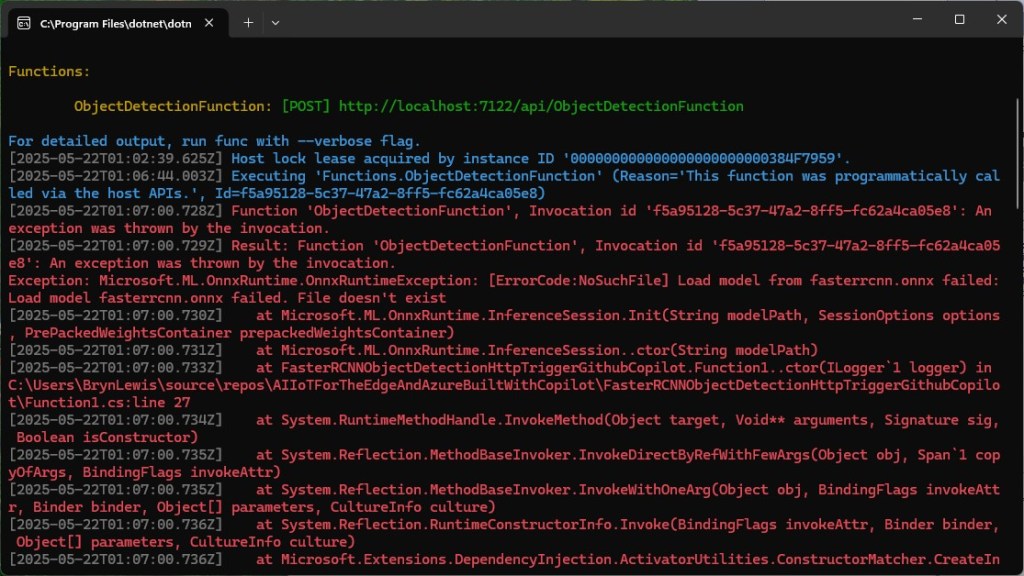
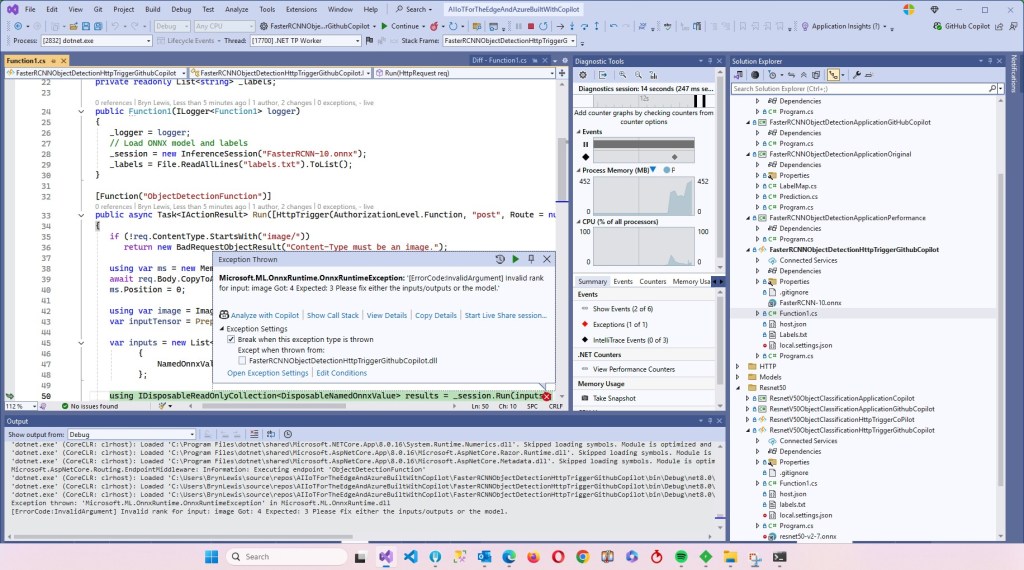
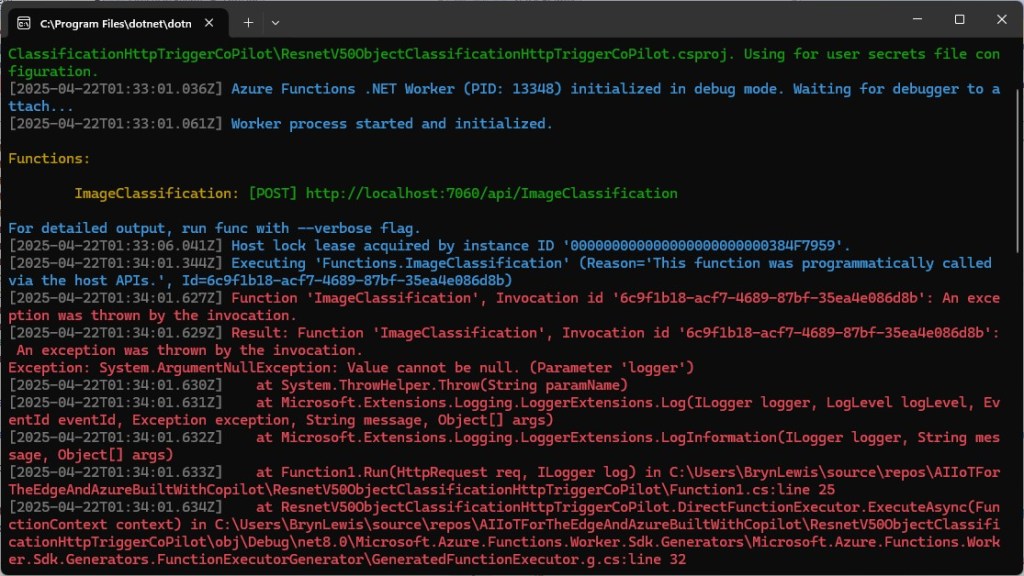
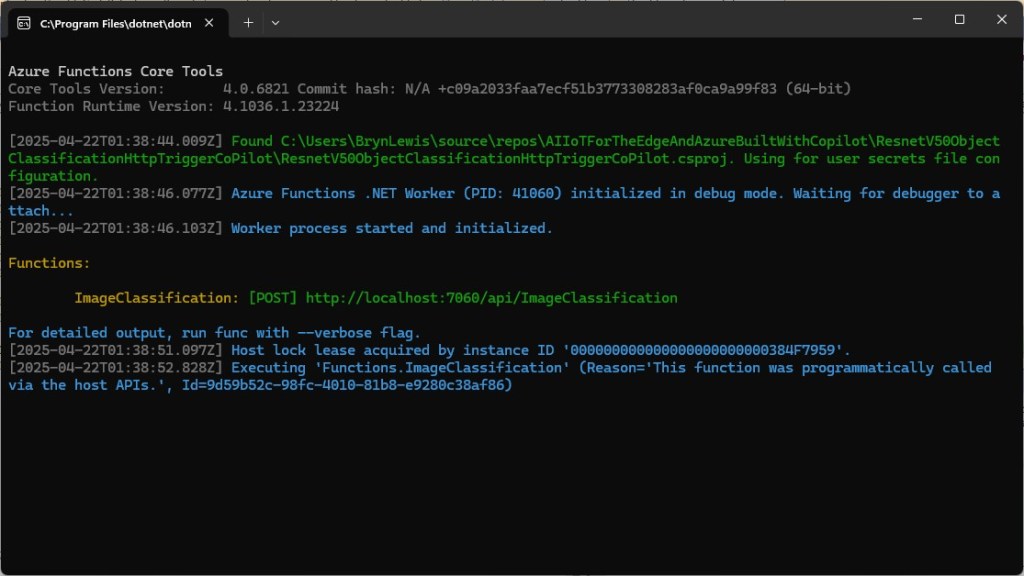
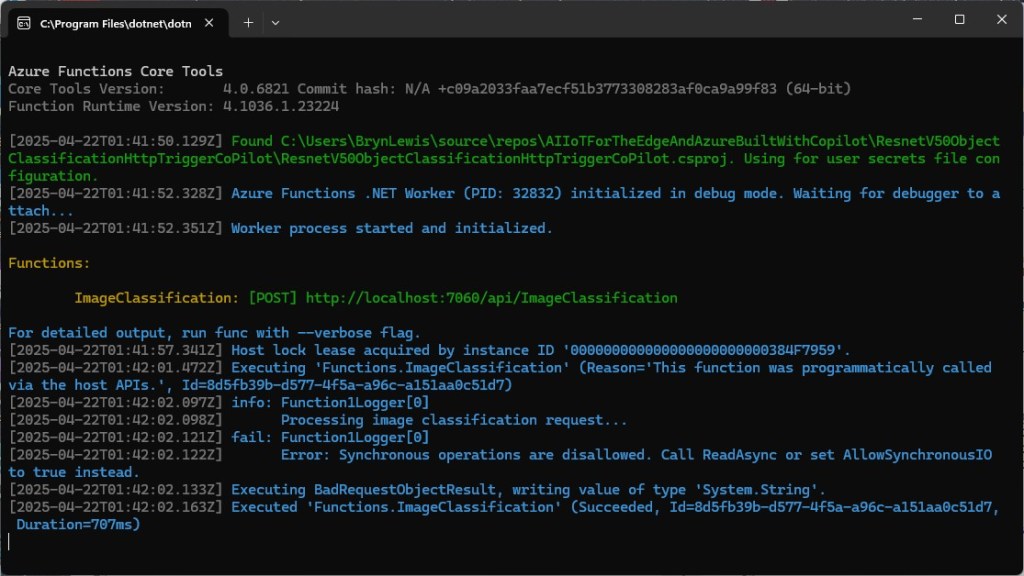
The Faster R-CNN Azure HTTP Trigger function performed (not unexpectedly) differently when invoked with Fiddler Classic in the Azure Functions emulator vs. when deployed in an Azure App Plan.
The code used is a “tidied” up version of the version of the code from the Building Cloud AI with Copilot – Faster R-CNN Azure HTTP Function “Dog Food” post
public class Function1
{
private readonly ILogger<Function1> _logger;
private readonly List<string> _labels;
private readonly InferenceSession _session;
public Function1(ILogger<Function1> logger)
{
_logger = logger;
_labels = File.ReadAllLines(Path.Combine(AppContext.BaseDirectory, "labels.txt")).ToList();
_session = new InferenceSession(Path.Combine(AppContext.BaseDirectory, "FasterRCNN-10.onnx"));
}
[Function("ObjectDetectionFunction")]
public async Task<IActionResult> Run([HttpTrigger(AuthorizationLevel.Function, "post", Route = null)] HttpRequest req, ExecutionContext context)
{
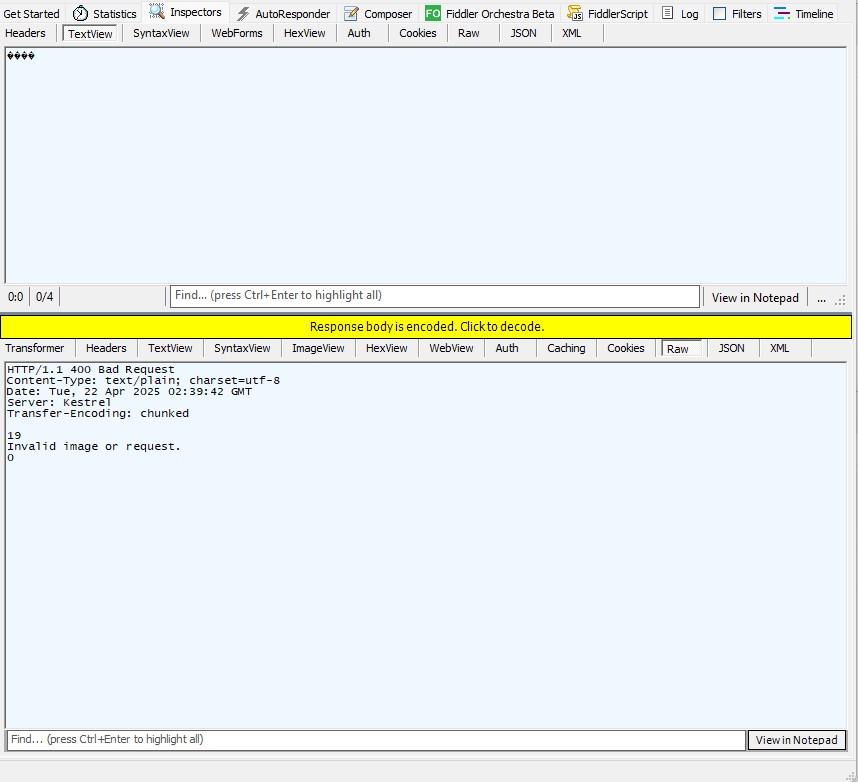
if (!req.ContentType.StartsWith("image/"))
return new BadRequestObjectResult("Content-Type must be an image.");
using var ms = new MemoryStream();
await req.Body.CopyToAsync(ms);
ms.Position = 0;
using var image = Image.Load<Rgb24>(ms);
var inputTensor = PreprocessImage(image);
var inputs = new List<NamedOnnxValue>
{
NamedOnnxValue.CreateFromTensor("image", inputTensor)
};
using IDisposableReadOnlyCollection<DisposableNamedOnnxValue> results = _session.Run(inputs);
var output = results.ToDictionary(x => x.Name, x => x.Value);
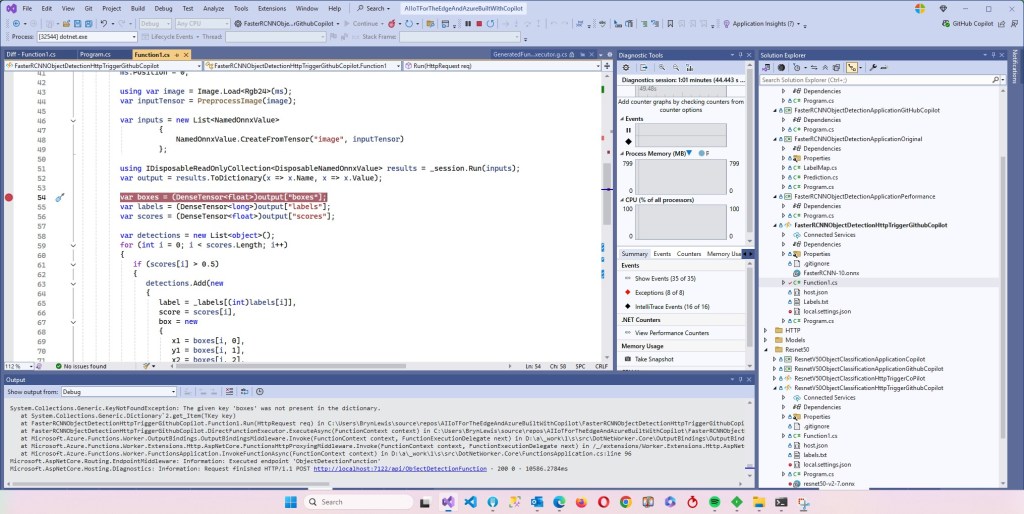
var boxes = (DenseTensor<float>)output["6379"];
var labels = (DenseTensor<long>)output["6381"];
var scores = (DenseTensor<float>)output["6383"];
var detections = new List<object>();
for (int i = 0; i < scores.Length; i++)
{
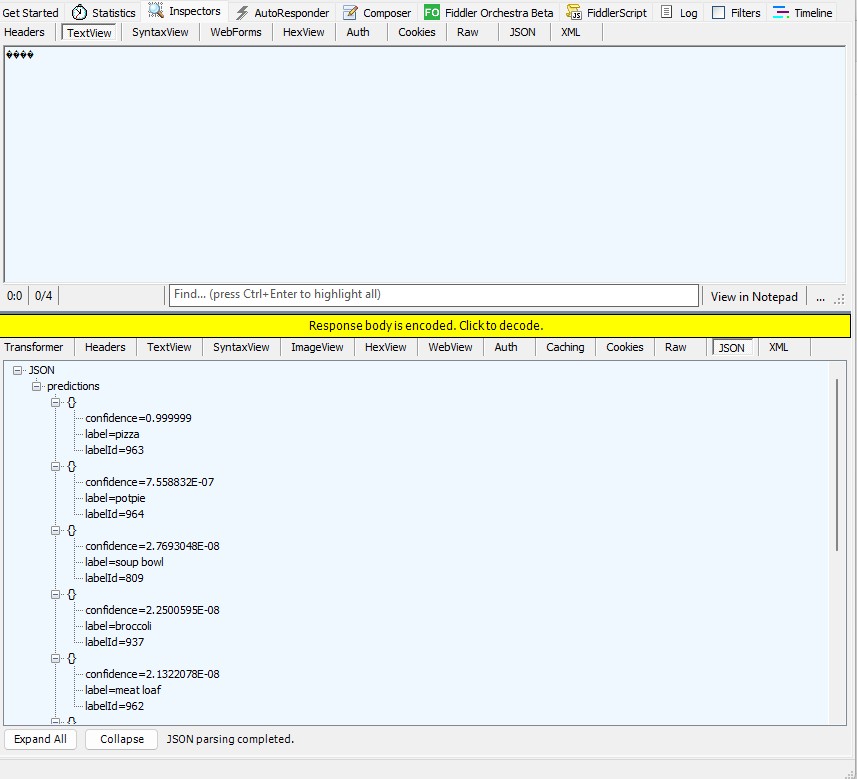
if (scores[i] > 0.5)
{
detections.Add(new
{
label = _labels[(int)labels[i]],
score = scores[i],
box = new
{
x1 = boxes[i, 0],
y1 = boxes[i, 1],
x2 = boxes[i, 2],
y2 = boxes[i, 3]
}
});
}
}
return new OkObjectResult(detections);
}
private static DenseTensor<float> PreprocessImage(Image<Rgb24> image)
{
// Step 1: Resize so that min(H, W) = 800, max(H, W) <= 1333, keeping aspect ratio
int origWidth = image.Width;
int origHeight = image.Height;
int minSize = 800;
int maxSize = 1333;
float scale = Math.Min((float)minSize / Math.Min(origWidth, origHeight),
(float)maxSize / Math.Max(origWidth, origHeight));
int resizedWidth = (int)Math.Round(origWidth * scale);
int resizedHeight = (int)Math.Round(origHeight * scale);
image.Mutate(x => x.Resize(resizedWidth, resizedHeight));
// Step 2: Pad so that both dimensions are divisible by 32
int padWidth = ((resizedWidth + 31) / 32) * 32;
int padHeight = ((resizedHeight + 31) / 32) * 32;
var paddedImage = new Image<Rgb24>(padWidth, padHeight);
paddedImage.Mutate(ctx => ctx.DrawImage(image, new Point(0, 0), 1f));
// Step 3: Convert to BGR and normalize
float[] mean = { 102.9801f, 115.9465f, 122.7717f };
var tensor = new DenseTensor<float>(new[] { 3, padHeight, padWidth });
for (int y = 0; y < padHeight; y++)
{
for (int x = 0; x < padWidth; x++)
{
Rgb24 pixel = default;
if (x < resizedWidth && y < resizedHeight)
pixel = paddedImage[x, y];
tensor[0, y, x] = pixel.B - mean[0];
tensor[1, y, x] = pixel.G - mean[1];
tensor[2, y, x] = pixel.R - mean[2];
}
}
paddedImage.Dispose();
return tensor;
}
}
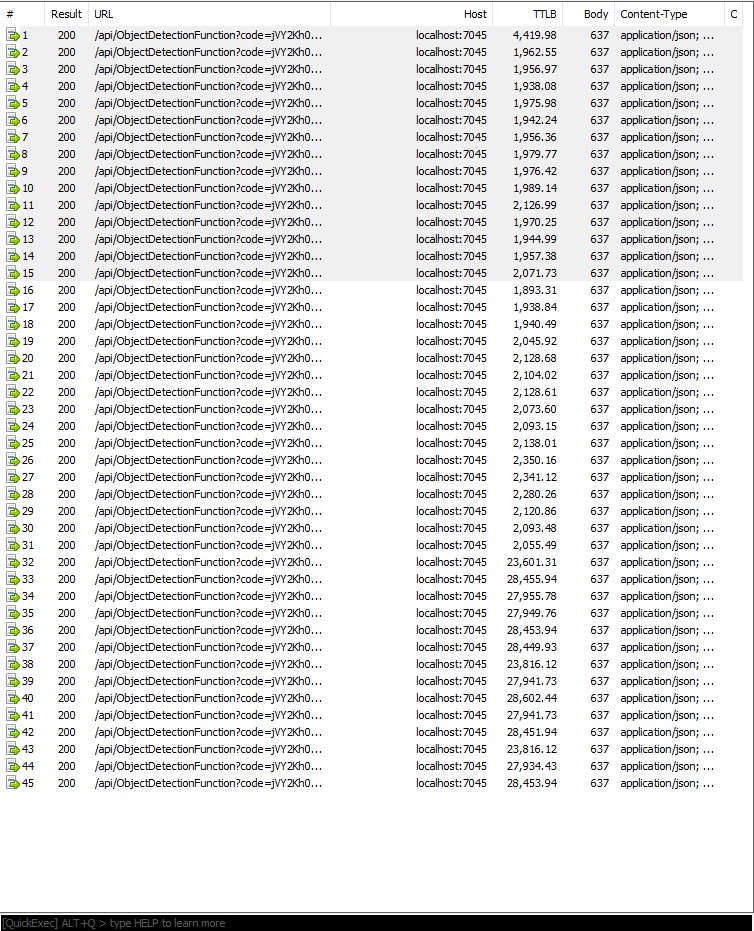
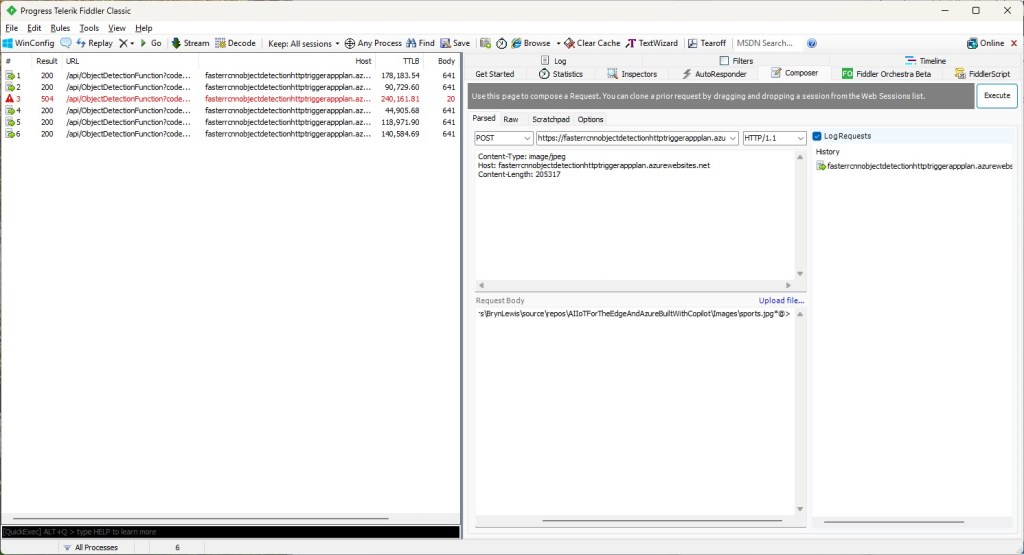
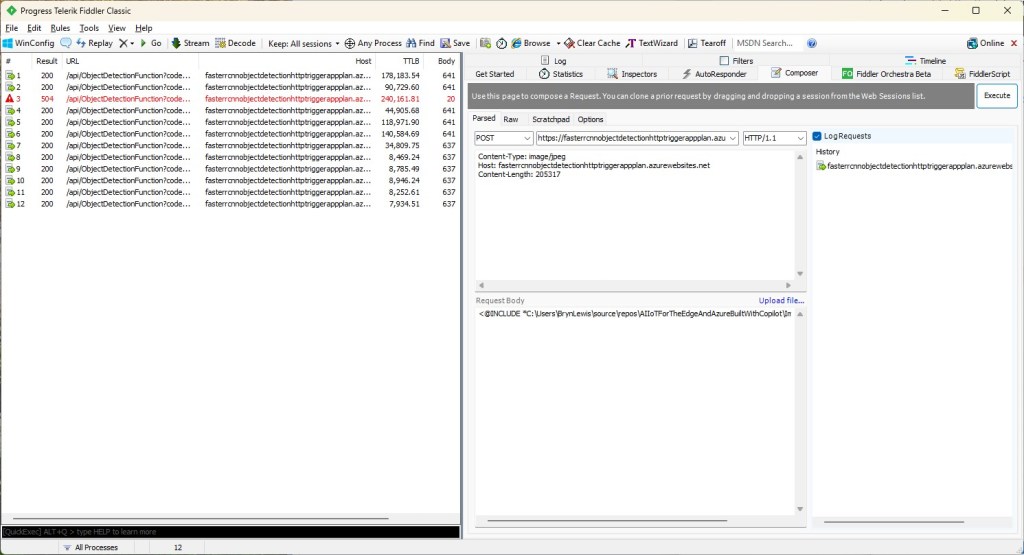
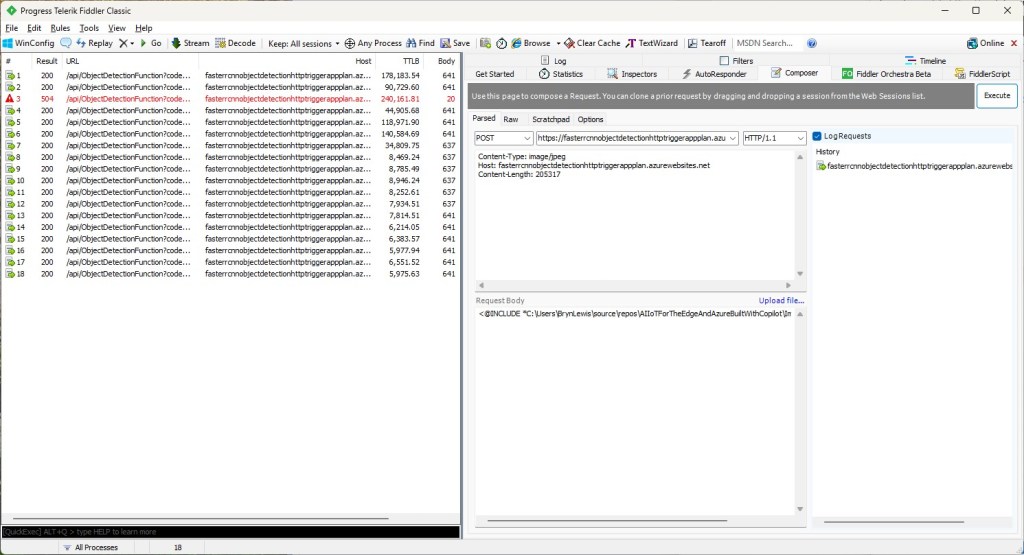
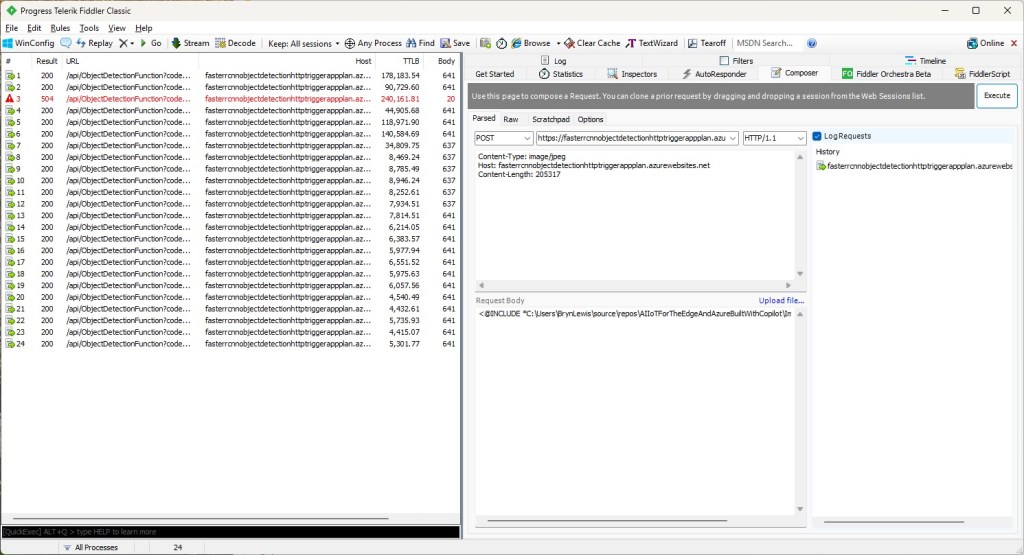
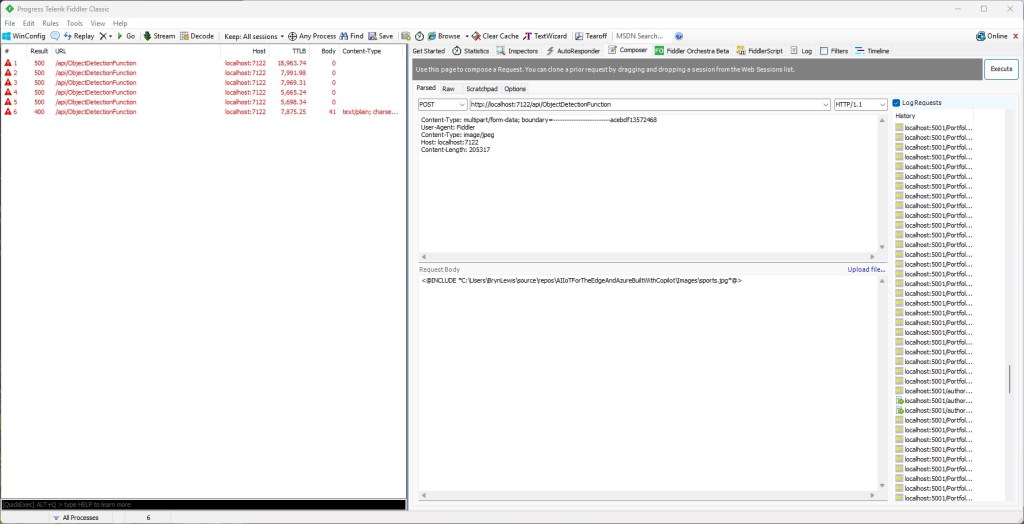
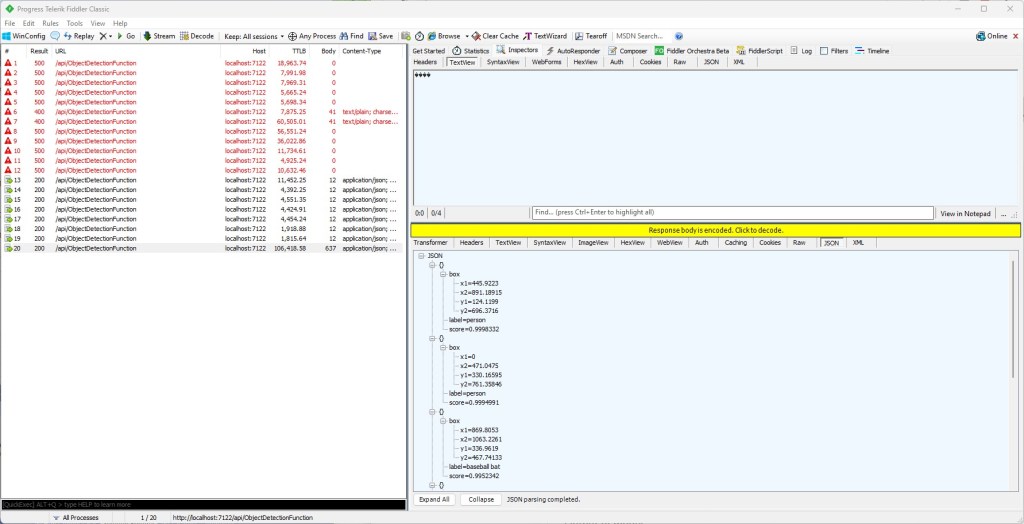
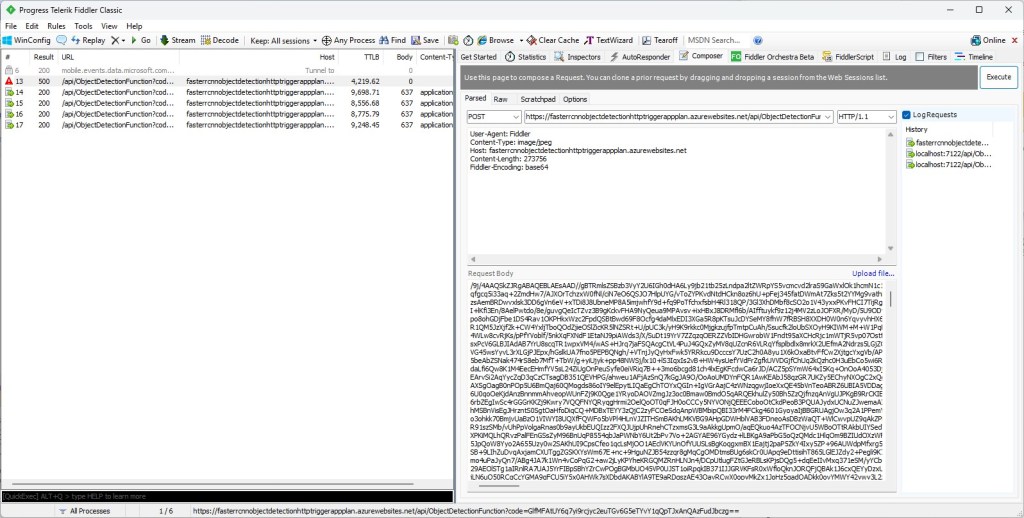
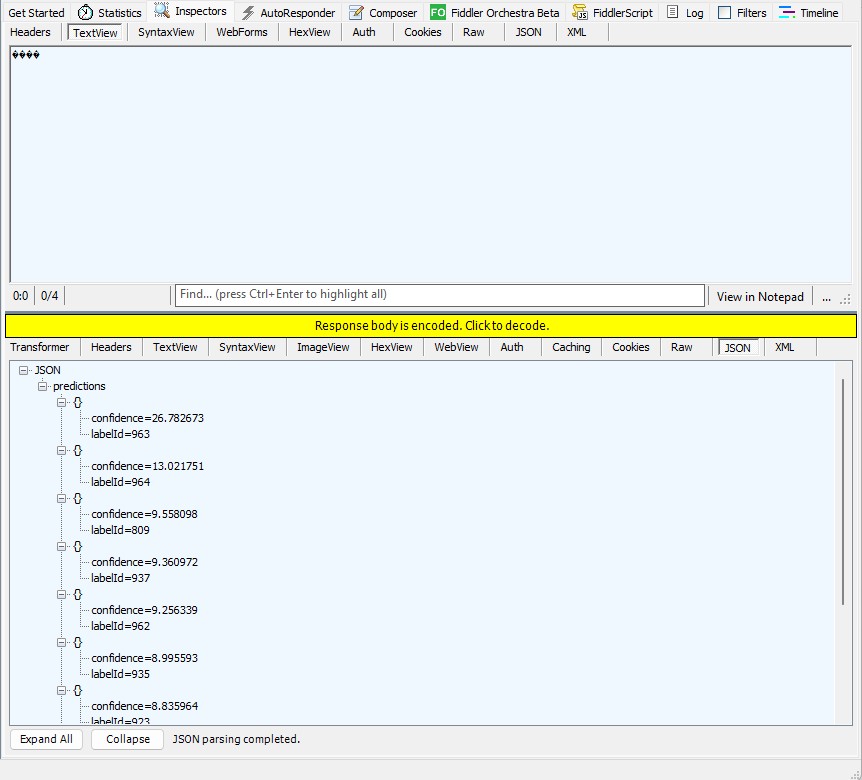
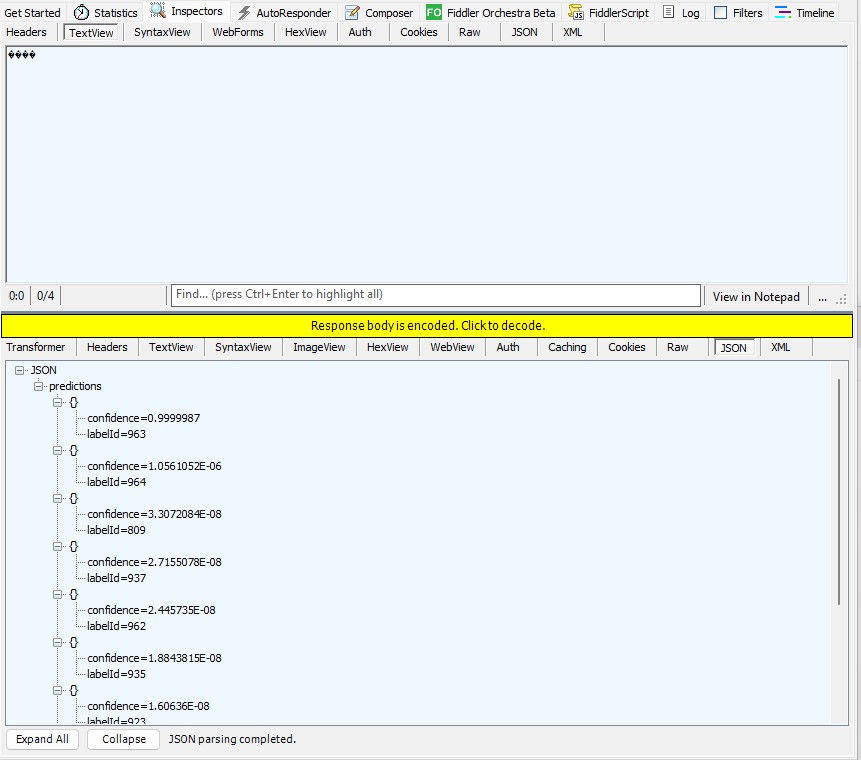
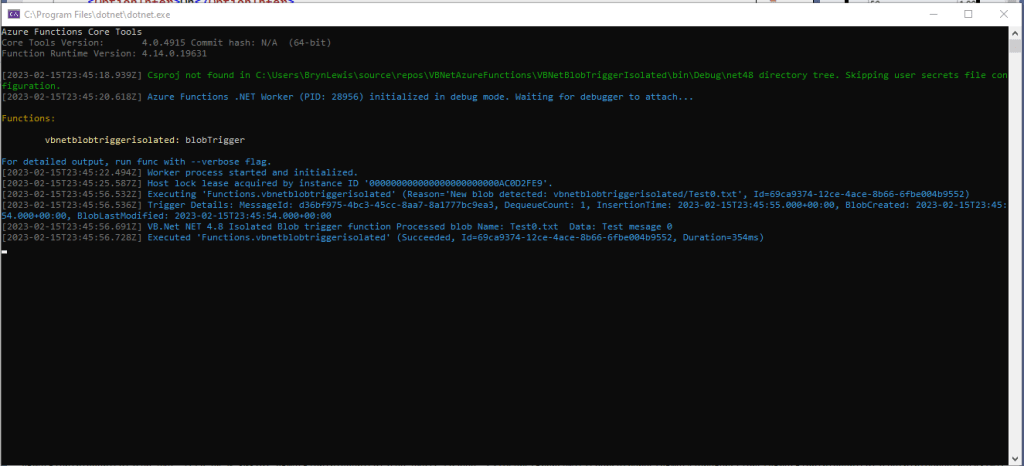
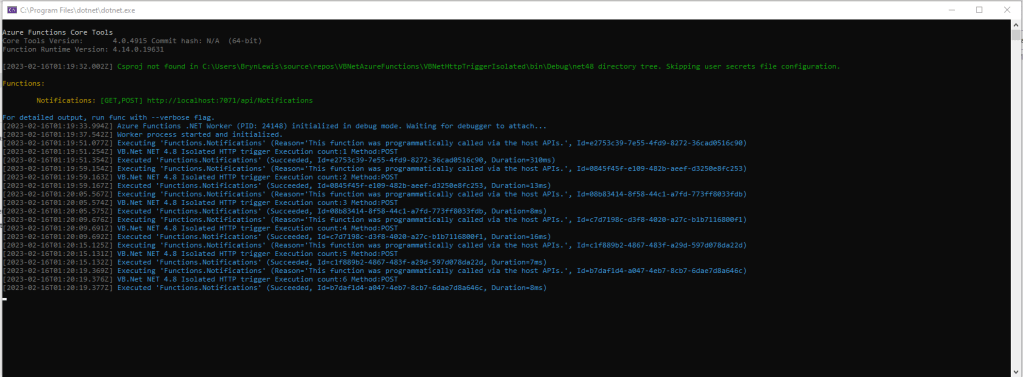
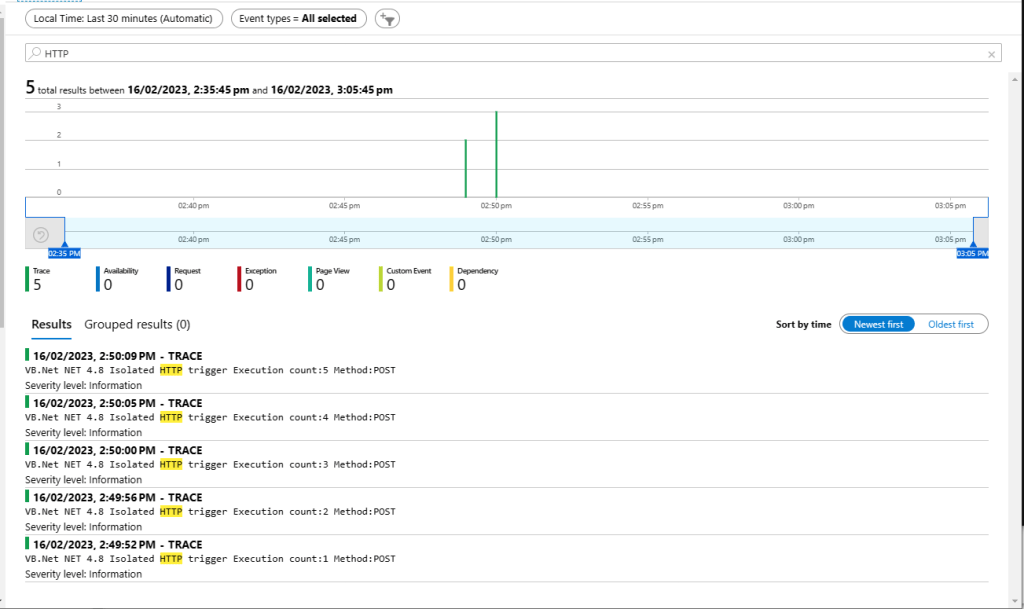
For my initial testing in the Azure Functions emulator using Fiddler Classic I manually generated 10 requests, then replayed them sequentially, and then finally concurrently.
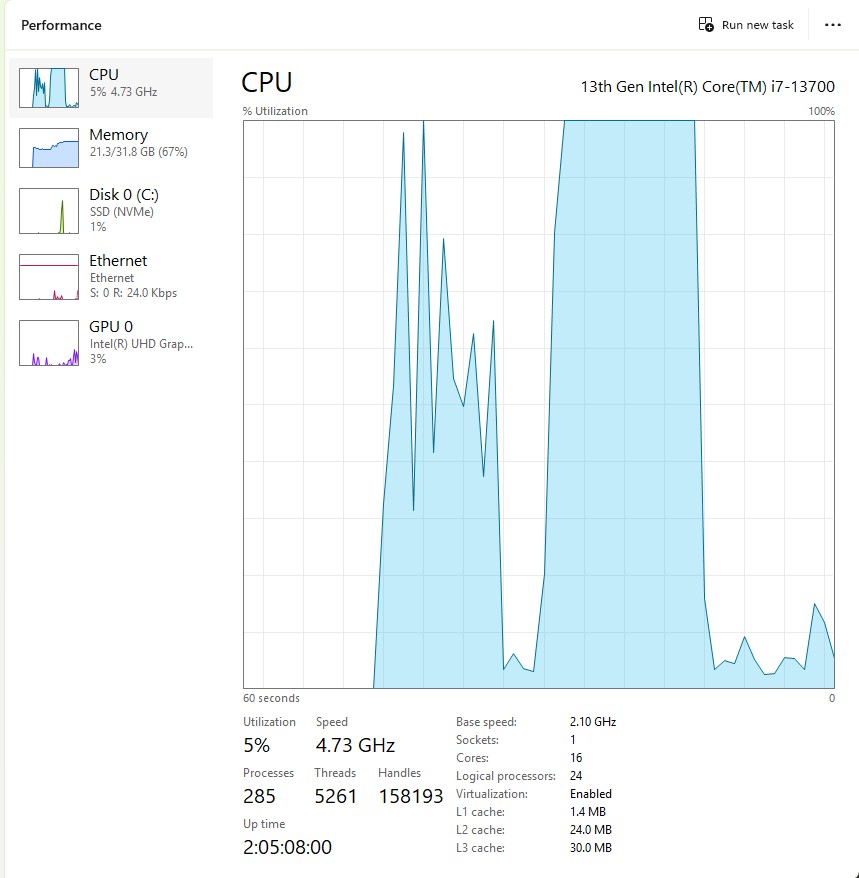
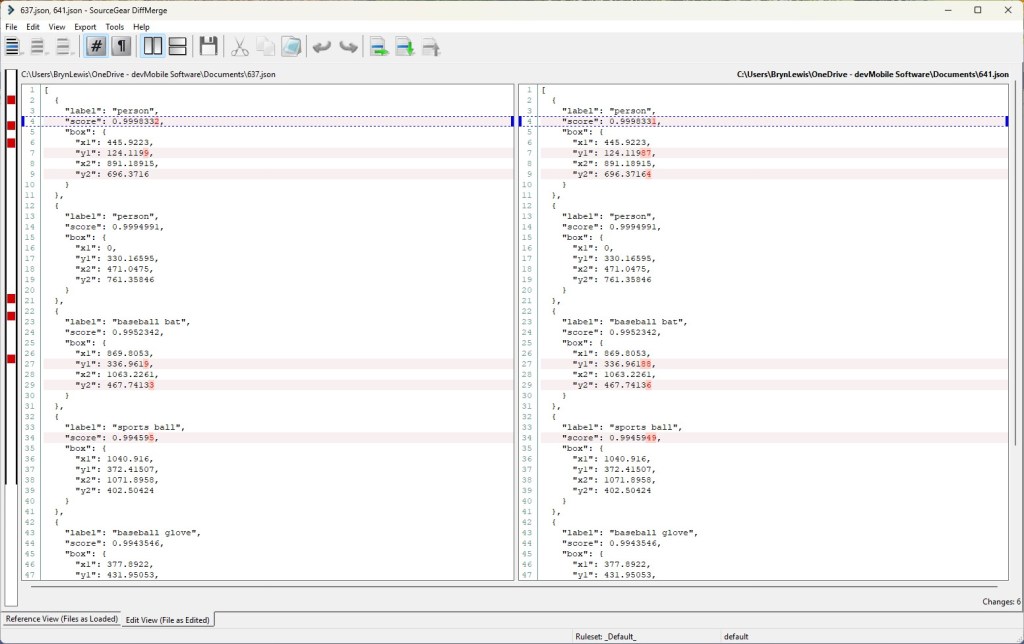
The results for the manual, then sequential results were fairly consistent but the 10 concurrent requests each to took more than 10x longer. In addition, the CPU was at 100% usage while the concurrently executed functions were running.
Cloud Deployment
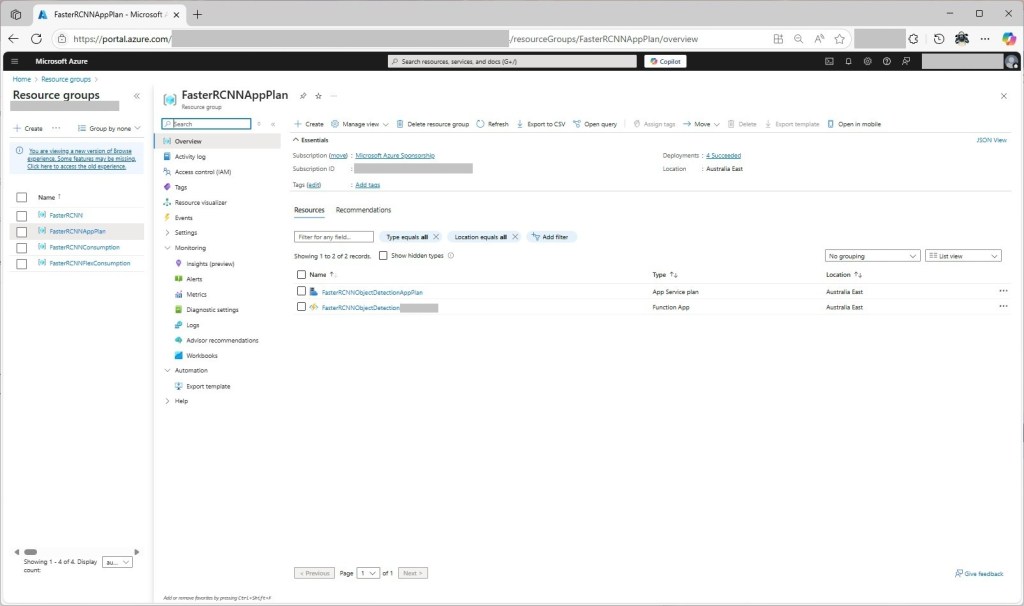
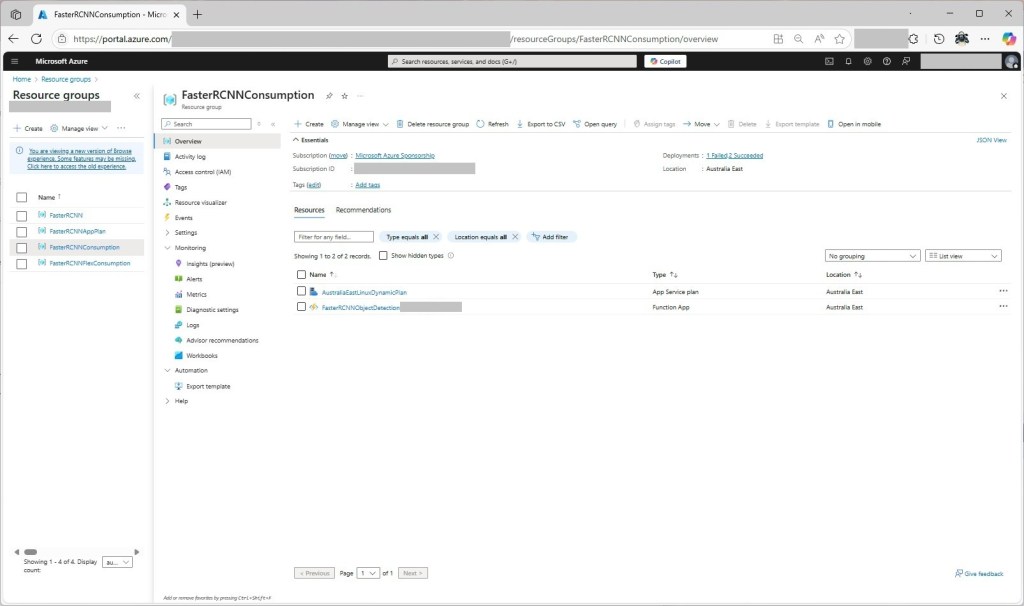
To see how the Faster R-CNN Azure HTTP Trigger function performed I created four resource groups.
The first contained resources used by the three different deployment models being tested
The second resource group was for testing a Dedicated hosting plan deployment.
The third resource group was for testing an Azure Functions Consumption plan hosting.
The fourth resource group was for testing Azure Functions Flex Consumption plan hosting.
Summary
The next couple of posts will compare and look at options for improving the “performance” (scalability, execution duration, latency, jitter, billing etc.) of the Github Copilot generated code.