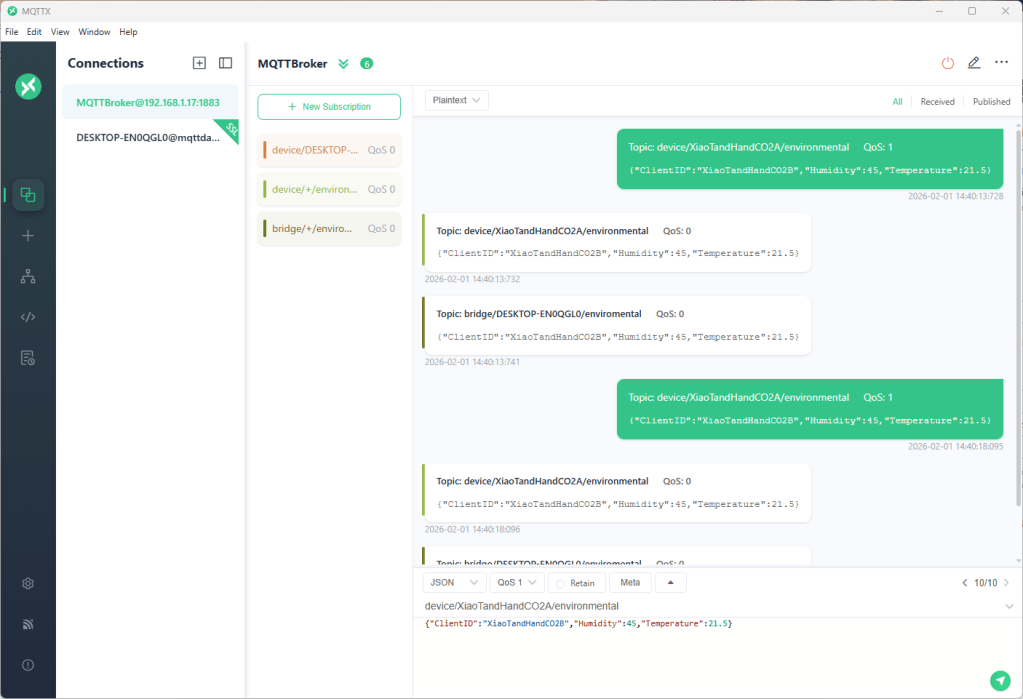
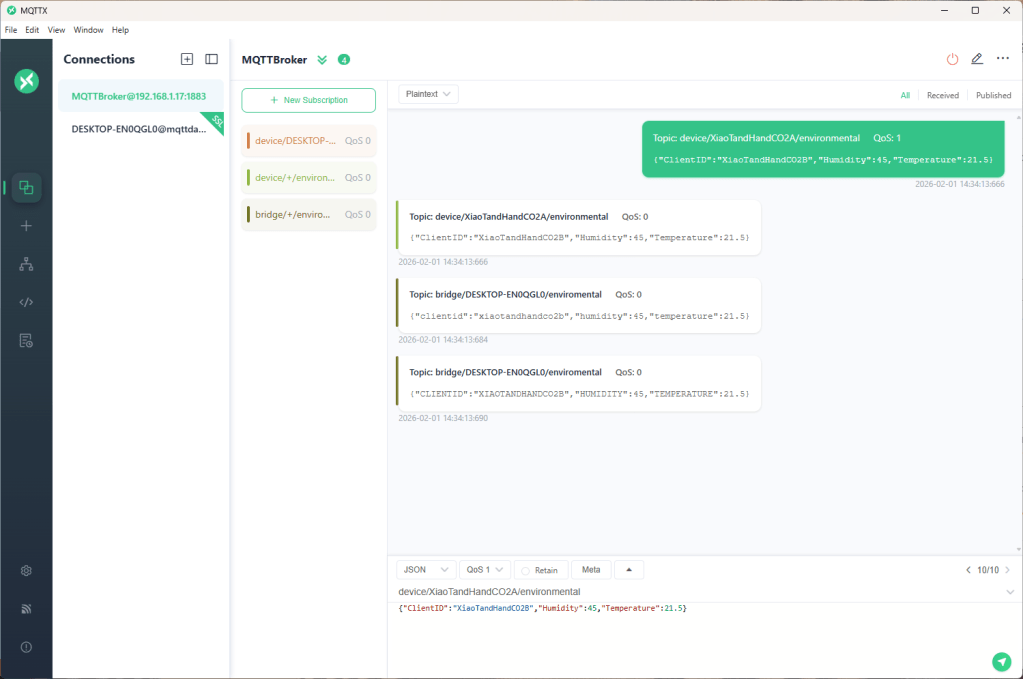
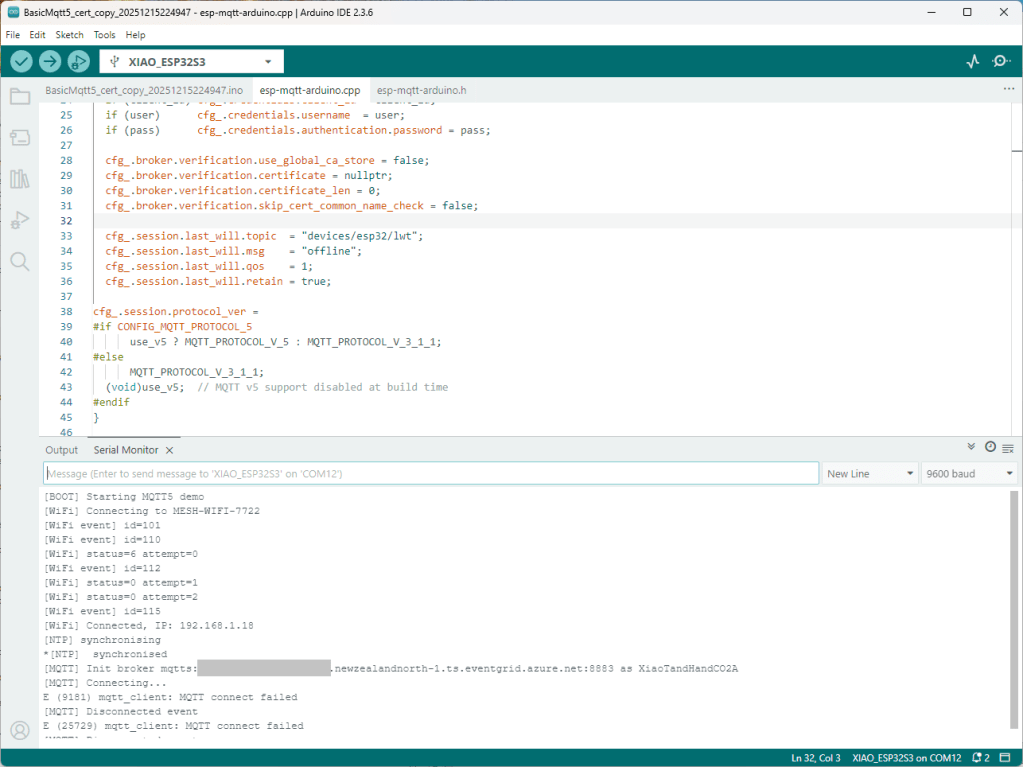
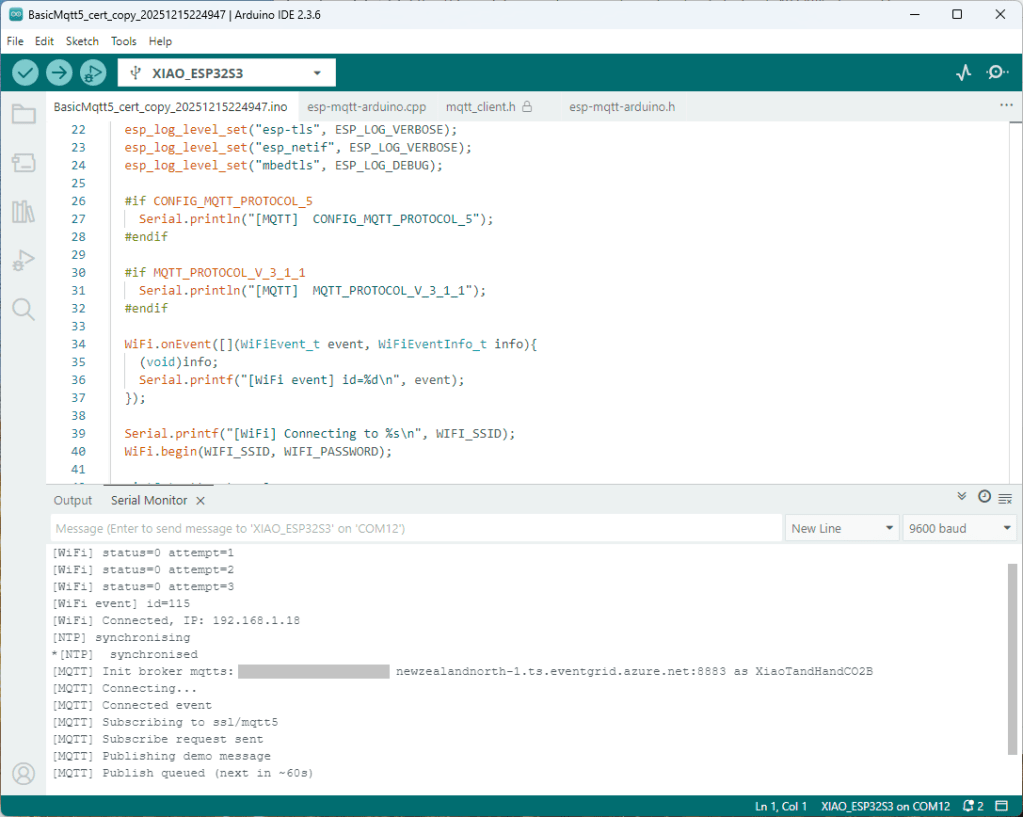
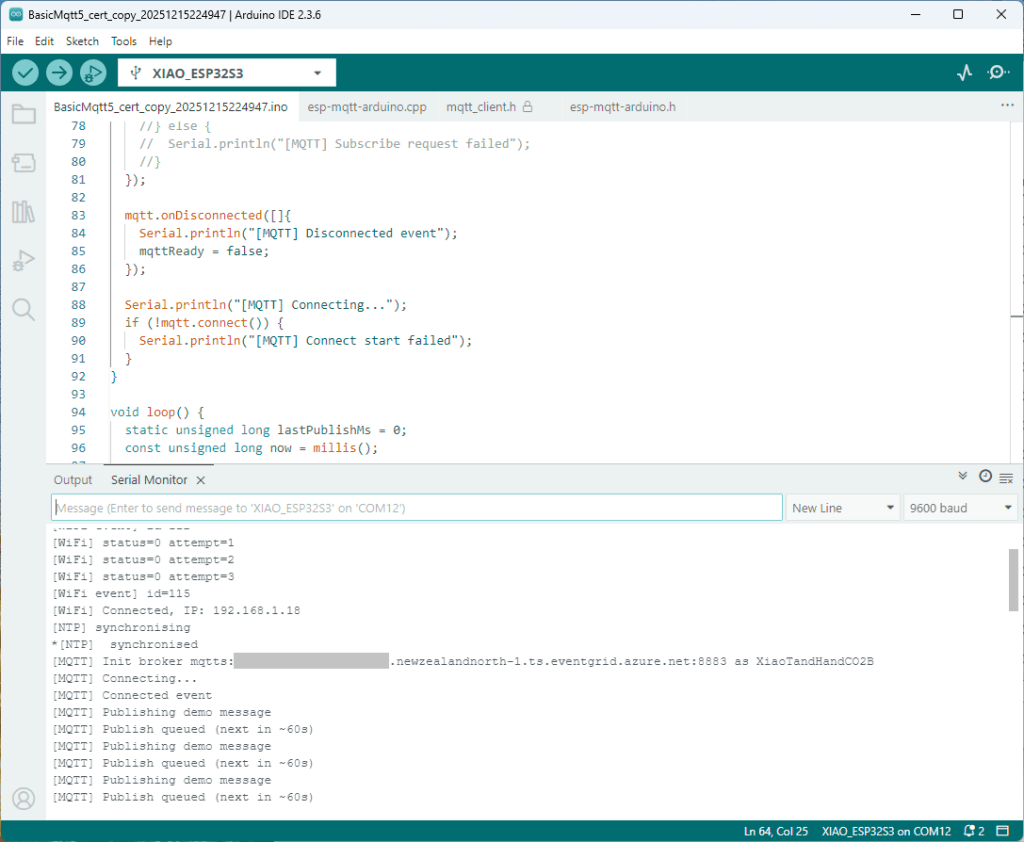
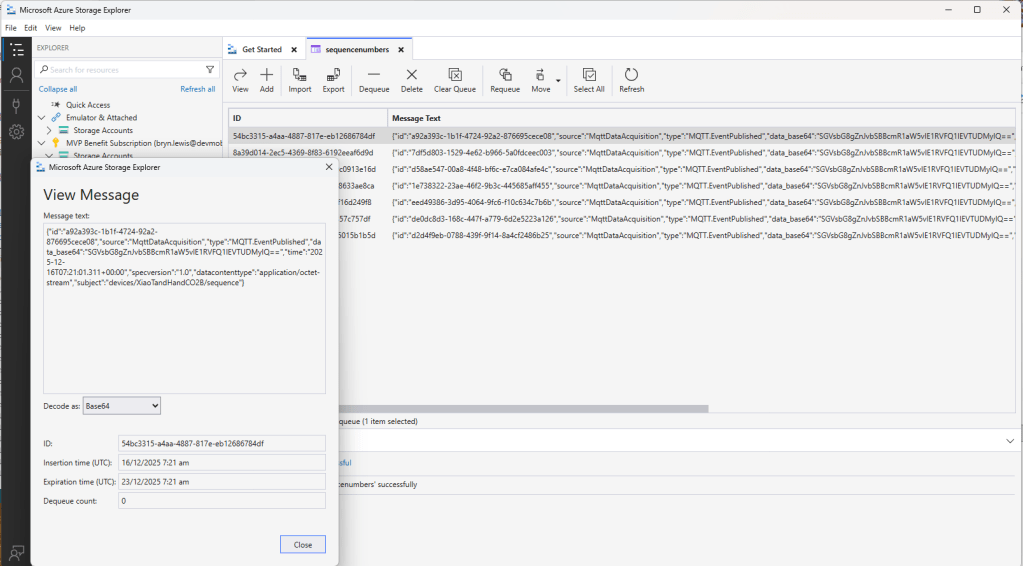
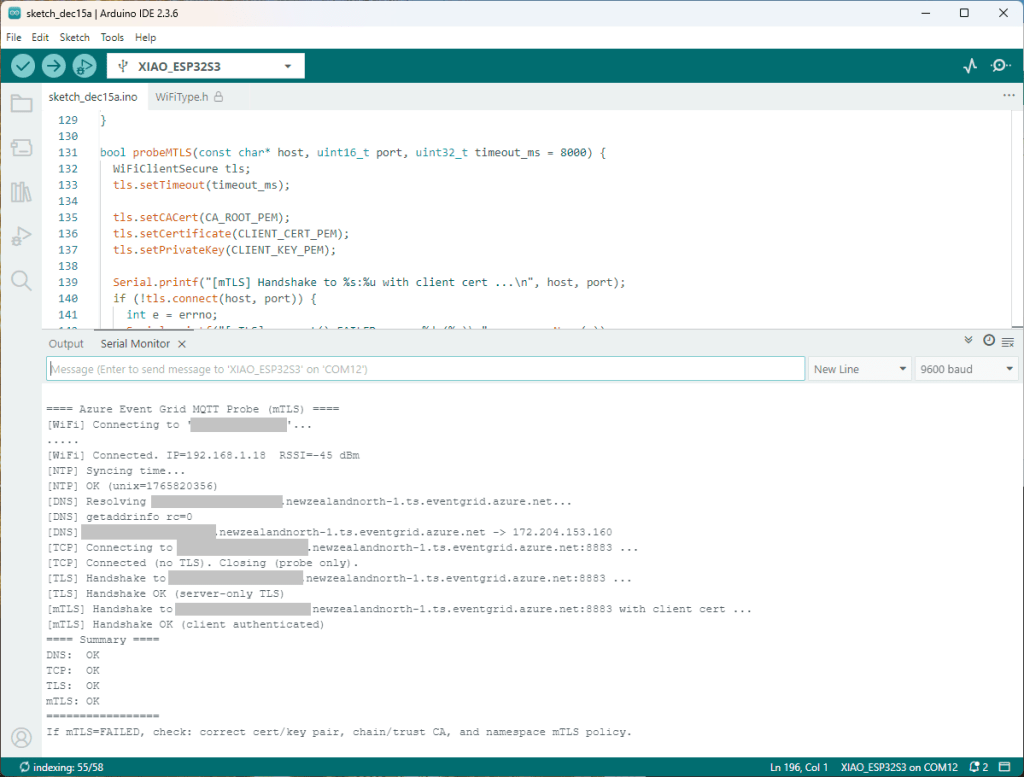
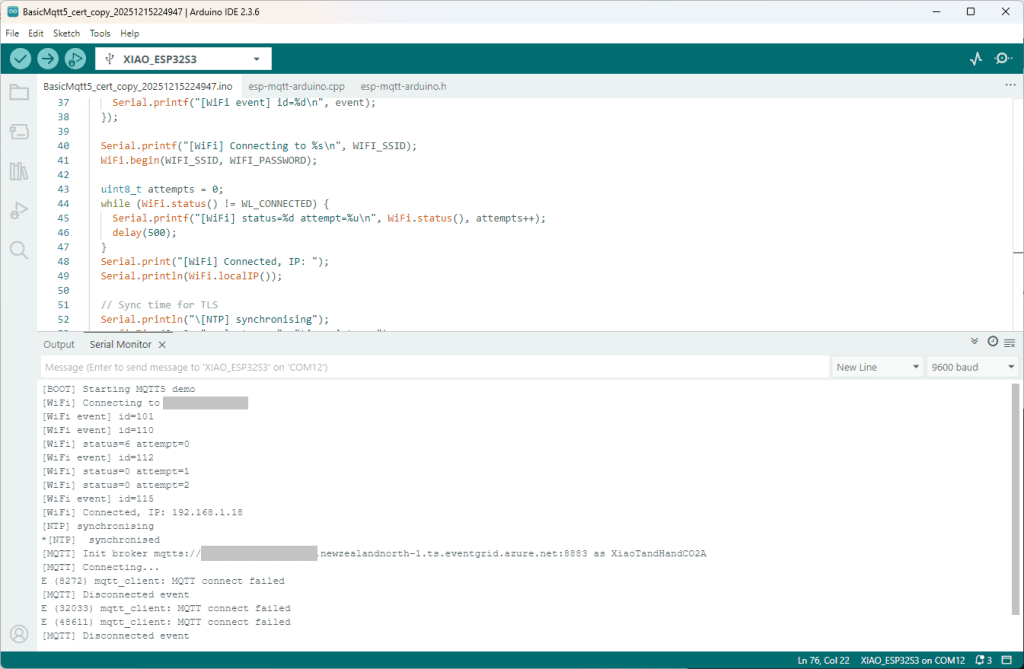
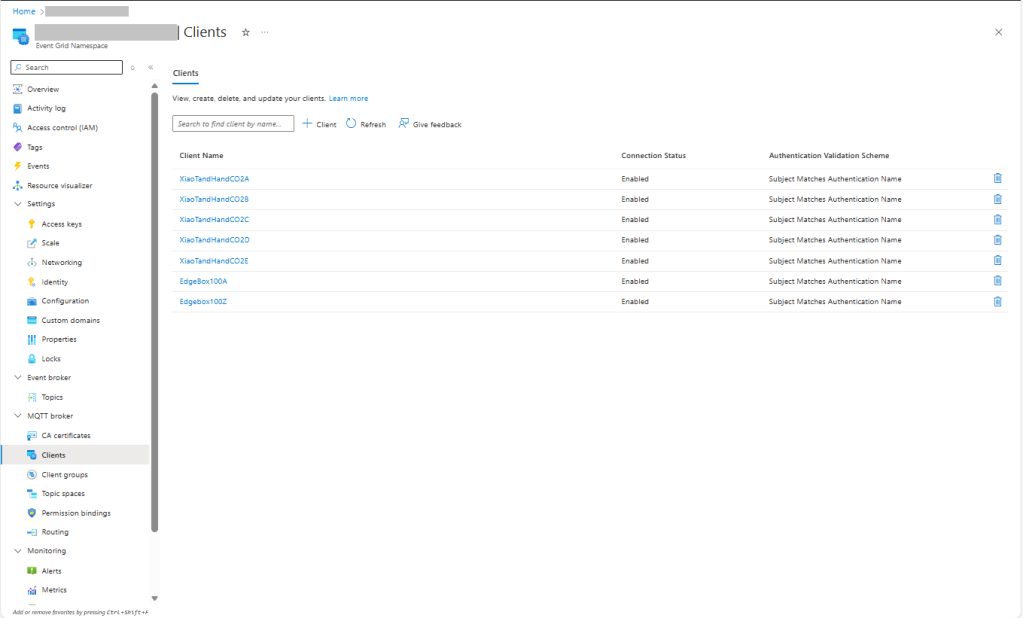
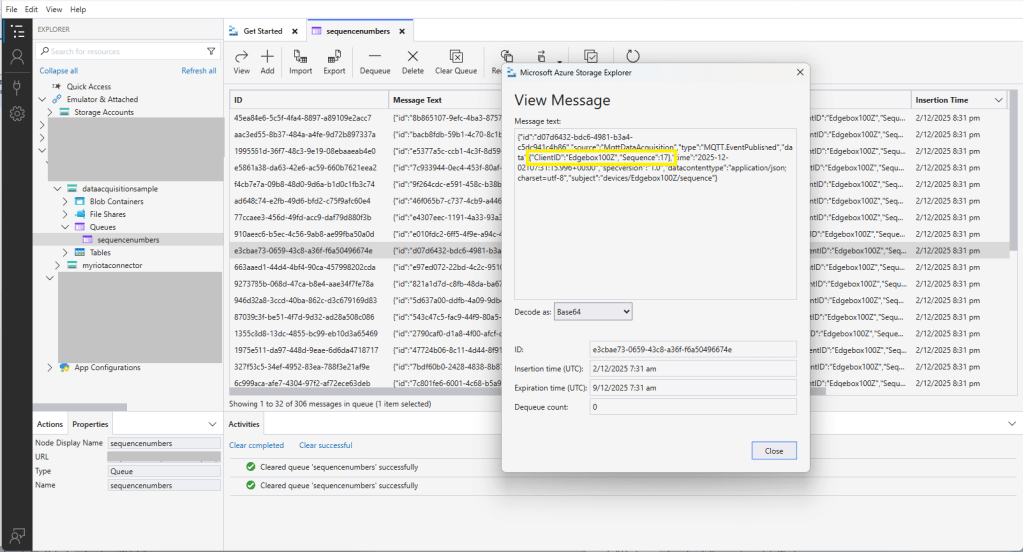
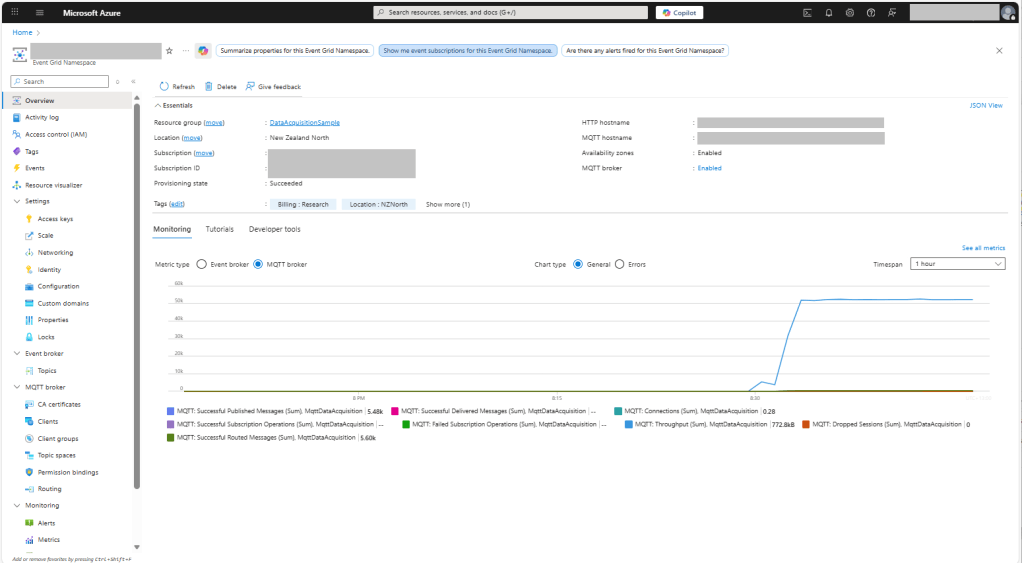
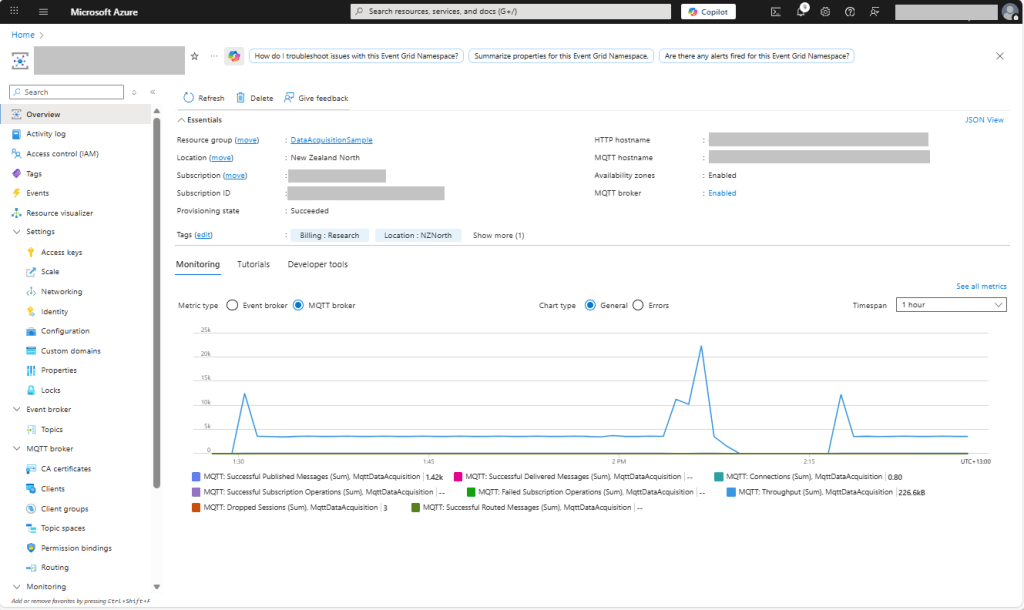
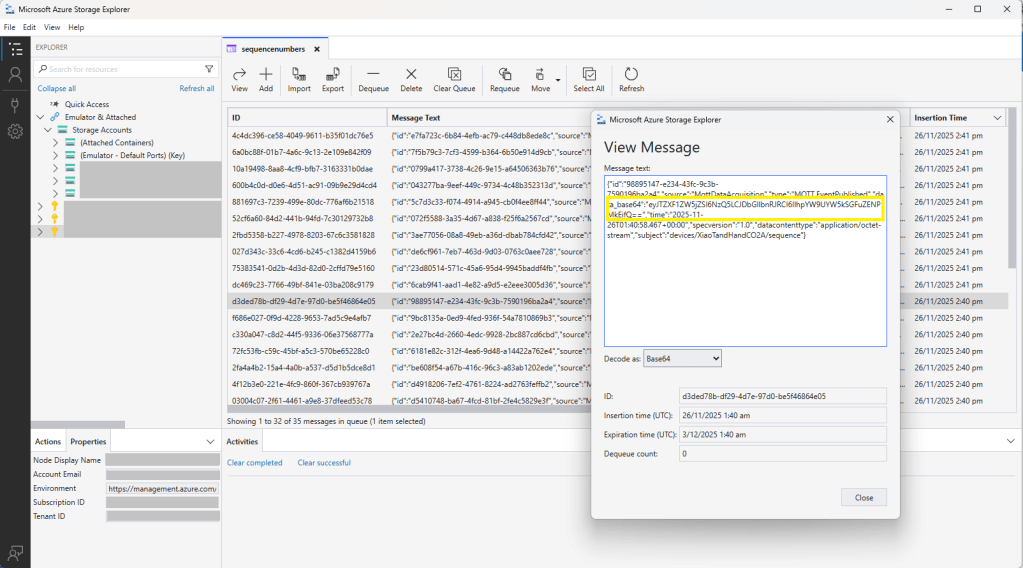
The first prototype of “transforming” telemetry data used C# code complied with the application. The HiveMQClient based application subscribes to topics (devices publishing environmental measurements) and then republishes them to multiple topics.
private static void OnMessageReceived(object? sender, HiveMQtt.Client.Events.OnMessageReceivedEventArgs e)
{
HiveMQClient client = (HiveMQClient)sender!;
Console.WriteLine($"{DateTime.UtcNow:yy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss:fff} HiveMQ.receive start");
Console.WriteLine($" Topic:{e.PublishMessage.Topic} QoS:{e.PublishMessage.QoS} Payload:{e.PublishMessage.PayloadAsString}");
Console.WriteLine($"{DateTime.UtcNow:yy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss:fff} HiveMQ.Publish start");
foreach (string topic in _applicationSettings.PublishTopics.Split(',', StringSplitOptions.RemoveEmptyEntries | StringSplitOptions.TrimEntries))
{
e.PublishMessage.Topic = string.Format(topic, _applicationSettings.ClientId);
Console.WriteLine($"{DateTime.UtcNow:yy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss:fff} Topic:{e.PublishMessage.Topic} HiveMQ Publish start ");
var resultPublish = client.PublishAsync(e.PublishMessage).GetAwaiter().GetResult();
Console.WriteLine($"{DateTime.UtcNow:yy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss:fff} Published:{resultPublish.QoS1ReasonCode} {resultPublish.QoS2ReasonCode}");
}
Console.WriteLine($"{DateTime.UtcNow:yy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss:fff} HiveMQ.Receive finish");
}
The MQTTX application subscribed to topics that devices (XiaoTandHandCO2A, XiaoTandHandCO2B etc.) and the simulated bridge (DESKTOP-EN0QGL0) published.
The second prototype “transforms” the telemetry message payloads with C# code that is compiled (with CSScript) as the application starts. The application subscribes to the topics which devices publish (environmental measurements), transforms the payloads, and then republishes the transformed messages to “bridge” topics
private static void OnMessageReceived(object? sender, HiveMQtt.Client.Events.OnMessageReceivedEventArgs e)
{
HiveMQClient client = (HiveMQClient)sender!;
Console.WriteLine($"{DateTime.UtcNow:yy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss:fff} HiveMQ.receive start");
Console.WriteLine($" Topic:{e.PublishMessage.Topic} QoS:{e.PublishMessage.QoS} Payload:{e.PublishMessage.PayloadAsString}");
Console.WriteLine($"{DateTime.UtcNow:yy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss:fff} HiveMQ.Publish start");
foreach (string topic in _applicationSettings.PublishTopics.Split(',', StringSplitOptions.RemoveEmptyEntries | StringSplitOptions.TrimEntries))
{
e.PublishMessage.Topic = string.Format(topic, _applicationSettings.ClientId);
foreach (MQTT5PublishMessage message in _evaluator.Transform(e.PublishMessage))
{
Console.WriteLine($"{DateTime.UtcNow:yy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss:fff} Topic:{e.PublishMessage.Topic} HiveMQ Publish start ");
var resultPublish = client.PublishAsync(message).GetAwaiter().GetResult();
Console.WriteLine($"{DateTime.UtcNow:yy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss:fff} Published:{resultPublish.QoS1ReasonCode} {resultPublish.QoS2ReasonCode}");
}
}
Console.WriteLine($"{DateTime.UtcNow:yy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss:fff} HiveMQ.Receive finish");
}
// This code is compiled as the application starts up, it implements the IMessageTransformer interface
const string sampleTransformCode = @"
using System.Text;
using HiveMQtt.MQTT5.Types;
public class messageTransformer : devMobile.IoT.MqttTransformer.CSScriptLoopback.IMessageTransformer
{
public MQTT5PublishMessage[] Transform(MQTT5PublishMessage message)
{
// Example: echo the payload to a new topic
var payload = Encoding.UTF8.GetString(message.Payload);
// Simple transformations: convert to uppercase or lowercase
var toLower = new MQTT5PublishMessage
{
Topic = message.Topic,
Payload = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(payload.ToLower()),
QoS = QualityOfService.AtLeastOnceDelivery
};
var toUpper = new MQTT5PublishMessage
{
Topic = message.Topic,
Payload = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(payload.ToUpper()),
QoS = QualityOfService.AtLeastOnceDelivery
};
return new[] { toLower, toUpper };
}
}";
The sample C# code implements the IMessageTransformer interface and republishes lower and upper case versions of the message.
public interface IMessageTransformer
{
public MQTT5PublishMessage[] Transform(MQTT5PublishMessage mqttPublishMessage);
}
...
_evaluator = CSScript.Evaluator.LoadCode<IMessageTransformer>(sampleTransformCode);
The SwarmSpace, and Myriota gateways both use an interface based approach to process uplink and downlink messages. Future versions will include support for isolating processing so that a rogue script can’t crash the application or reference unapproved assemblies