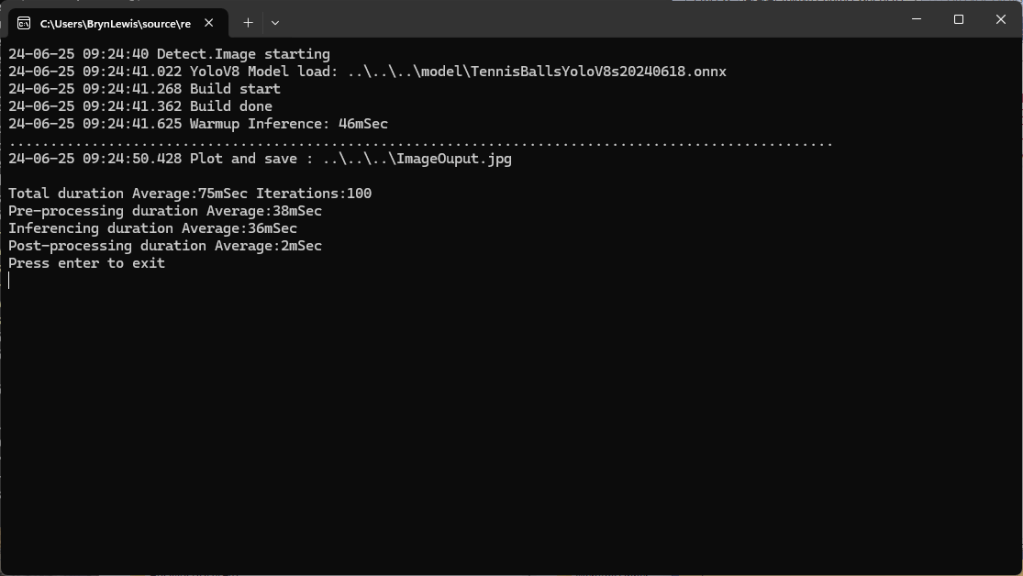
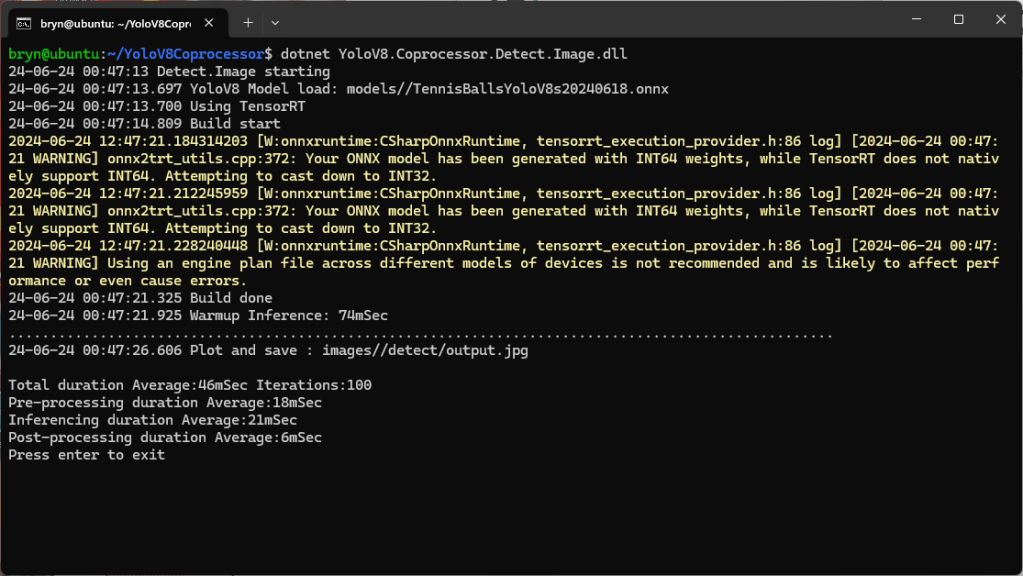
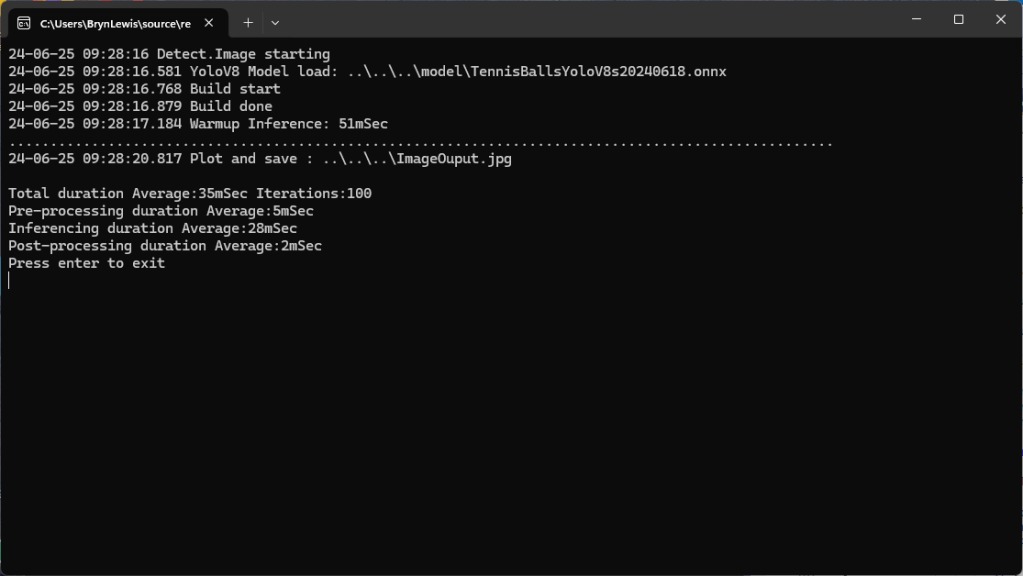
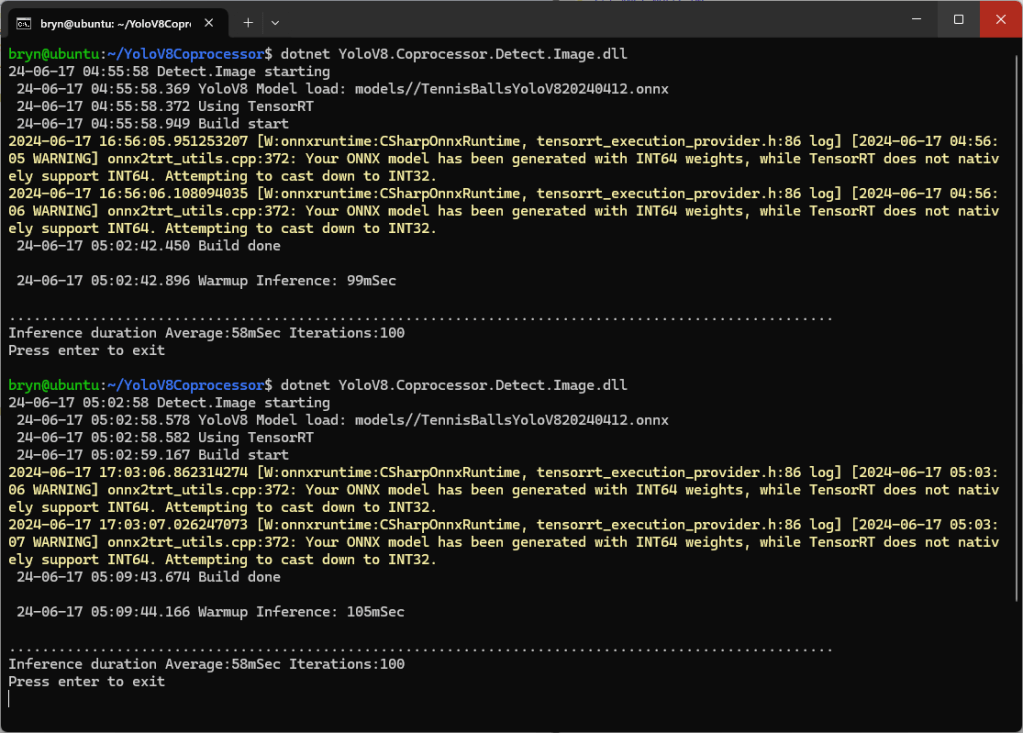
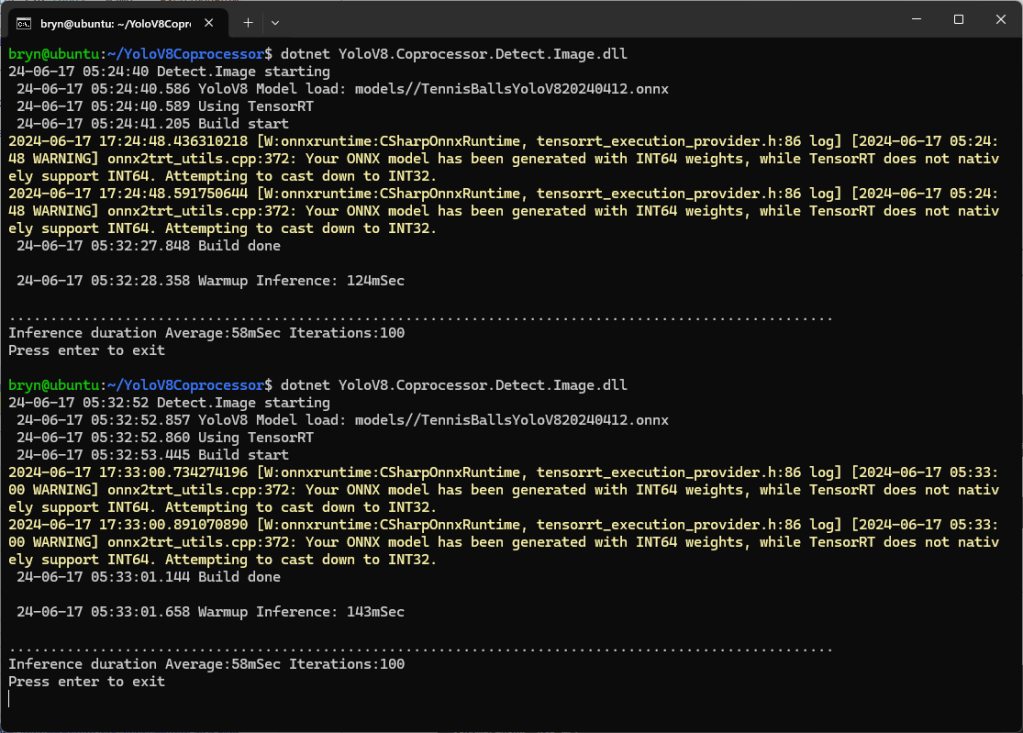
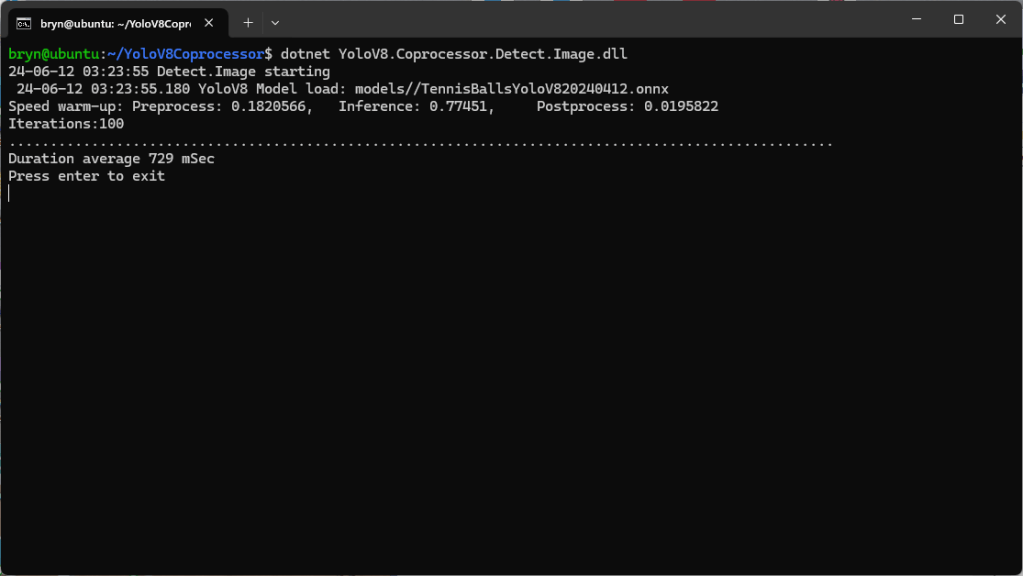
When running the YoloV8 Coprocessor demonstration on the Nividia Jetson Orin inferencing looked a bit odd, the dotted line wasn’t moving as fast as expected. To investigate this further I split the inferencing duration into pre-processing, inferencing and post-processing times. Inferencing and post-processing were “quick”, but pre-processing was taking longer than expected.
When I ran the demonstration Ultralytics YoloV8 object detection console application on my development desktop (13th Gen Intel(R) Core(TM) i7-13700 2.10 GHz with 32.0 GB) the pre-processing was much faster.
The much shorter pre-processing and longer inferencing durations were not a surprise as my development desktop does not have a Graphics Processing Unit(GPU)
The test image taken with my mobile was 3606×2715 pixels which was representative of the security cameras images to be processed by the solution.

On my development box running the application with Redgate ANTS Performance Profiler highlighted that the Computnet YoloV8 code converting the image to a DenseTensor could be an issue.
public static void ProcessToTensor(Image<Rgb24> image, Size modelSize, bool originalAspectRatio, DenseTensor<float> target, int batch)
{
var options = new ResizeOptions()
{
Size = modelSize,
Mode = originalAspectRatio ? ResizeMode.Max : ResizeMode.Stretch,
};
var xPadding = (modelSize.Width - image.Width) / 2;
var yPadding = (modelSize.Height - image.Height) / 2;
var width = image.Width;
var height = image.Height;
// Pre-calculate strides for performance
var strideBatchR = target.Strides[0] * batch + target.Strides[1] * 0;
var strideBatchG = target.Strides[0] * batch + target.Strides[1] * 1;
var strideBatchB = target.Strides[0] * batch + target.Strides[1] * 2;
var strideY = target.Strides[2];
var strideX = target.Strides[3];
// Get a span of the whole tensor for fast access
var tensorSpan = target.Buffer;
// Try get continuous memory block of the entire image data
if (image.DangerousTryGetSinglePixelMemory(out var memory))
{
Parallel.For(0, width * height, index =>
{
int x = index % width;
int y = index / width;
int tensorIndex = strideBatchR + strideY * (y + yPadding) + strideX * (x + xPadding);
var pixel = memory.Span[index];
WritePixel(tensorSpan.Span, tensorIndex, pixel, strideBatchR, strideBatchG, strideBatchB);
});
}
else
{
Parallel.For(0, height, y =>
{
var rowSpan = image.DangerousGetPixelRowMemory(y).Span;
int tensorYIndex = strideBatchR + strideY * (y + yPadding);
for (int x = 0; x < width; x++)
{
int tensorIndex = tensorYIndex + strideX * (x + xPadding);
var pixel = rowSpan[x];
WritePixel(tensorSpan.Span, tensorIndex, pixel, strideBatchR, strideBatchG, strideBatchB);
}
});
}
}
private static void WritePixel(Span<float> tensorSpan, int tensorIndex, Rgb24 pixel, int strideBatchR, int strideBatchG, int strideBatchB)
{
tensorSpan[tensorIndex] = pixel.R / 255f;
tensorSpan[tensorIndex + strideBatchG - strideBatchR] = pixel.G / 255f;
tensorSpan[tensorIndex + strideBatchB - strideBatchR] = pixel.B / 255f;
}
For a 3606×2715 image the WritePixel method would be called tens of millions of times so its implementation and the overall approach used for ProcessToTensor has a significant impact on performance.
Resizing the images had a significant impact on performance on the development box and Nividia Jetson Orin. This will need some investigation to see how much reducing the resizing the images impacts on the performance and accuracy of the model.
The ProcessToTensor method has already had some performance optimisations which improved performance by roughly 20%. There have been discussions about optimising similar code e.g. Efficient Bitmap to OnnxRuntime Tensor in C#, and Efficient RGB Image to Tensor in dotnet which look applicable and these will be evaluated.