A couple of recent contracts have been maintaining and “remediating” legacy codebases which have been in production for upto a decade. The applications are delivering business value (can’t stop working) and the customer’s budgets are limited (they can only afford incremental change). As a result of this we end up making tactical decisions to keep the application working and longer-term ones to improve the “ilities“(taking into account the customer’s priorities).
It is rare to have a “green fields” project, so my plan was to use the next couple of WebAPI + Dapper posts to illustrate the sort of challenges we have encountered.
Customer: “we want to put a nice webby frontend on our existing bespoke solution” (“putting lipstick on a pig”).
Customer: The user’s login details are stored in the database and we can’t change the login process as the help desk won’t cope.
The remediation of Authentication and Authorisation(A&A) functionality can be particularly painful and is often driven by compliance issues e.g. EU GDPR, The Privacy Act 202 etc.
The World Wide Importers database would be a representative example of databases we have worked with.
CREATE TABLE [Application].[People](
[PersonID] [int] NOT NULL,
[FullName] [nvarchar](50) NOT NULL,
[PreferredName] [nvarchar](50) NOT NULL,
[SearchName] AS (concat([PreferredName],N' ',[FullName])) PERSISTED NOT NULL,
[IsPermittedToLogon] [bit] NOT NULL,
[LogonName] [nvarchar](50) NULL,
[IsExternalLogonProvider] [bit] NOT NULL,
[HashedPassword] [varbinary](max) NULL,
[IsSystemUser] [bit] NOT NULL,
[IsEmployee] [bit] NOT NULL,
[IsSalesperson] [bit] NOT NULL,
[UserPreferences] [nvarchar](max) NULL,
[PhoneNumber] [nvarchar](20) NULL,
[FaxNumber] [nvarchar](20) NULL,
[EmailAddress] [nvarchar](256) NULL,
[Photo] [varbinary](max) NULL,
[CustomFields] [nvarchar](max) NULL,
[OtherLanguages] AS (json_query([CustomFields],N'$.OtherLanguages')),
[LastEditedBy] [int] NOT NULL,
[ValidFrom] [datetime2](7) GENERATED ALWAYS AS ROW START NOT NULL,
[ValidTo] [datetime2](7) GENERATED ALWAYS AS ROW END NOT NULL,
CONSTRAINT [PK_Application_People] PRIMARY KEY CLUSTERED
(
[PersonID] ASC
)WITH (PAD_INDEX = OFF, STATISTICS_NORECOMPUTE = OFF, IGNORE_DUP_KEY = OFF, ALLOW_ROW_LOCKS = ON, ALLOW_PAGE_LOCKS = ON, OPTIMIZE_FOR_SEQUENTIAL_KEY = OFF) ON [USERDATA],
PERIOD FOR SYSTEM_TIME ([ValidFrom], [ValidTo])
) ON [USERDATA] TEXTIMAGE_ON [USERDATA]
WITH
(
SYSTEM_VERSIONING = ON (HISTORY_TABLE = [Application].[People_Archive])
)
Initial observations
- The LogonName column doesn’t have an index and uniqueness is not enforced which is a bit odd.
- The table has SYSTEM_VERSIONING enabled so any structural changes are going to be hard work.
- There are a couple of computed columns, so we need to be careful with any changes.
- A password hash is a varbinary max column, so we need to figure out how this is generated and updated
- Surprising number of nullable columns
- The code associated with IsExternalLogonProvider needs to be investigated.
- Looks like the granularity of permissions i.e. IsSystemUser, IsEmployee, IsSalesperson is low.
- The database must be old there is a FaxNumber column.
- Looks like there are internal and external (maybe IsSystemUser, IsEmployee, IsSalesperson are all false) people.
- The PersonId is a Sequence rather than an Identity column which is unusual.
- IsPermittedToLogin indicates that login process might be a bit more complex than expected
- The terms Login and Logon appear to be used interchangeably.
- No lockout after several failed logon attempts, lockout until etc. functionality.
- No concurrency control (optimistic or pessimistic) for updates (with TimeStamp or Version column) so last update wins.
The next step would be to have a look at the contents of the People table with SQL Server Management Studio(SSMS)
Initial observations
- Looks like the system administrators are in the first couple of rows. (makes Indirect Object Reference Attack easier).
- Lots of NULL values which often makes application code more complex
- Duplicates in LoginName column e.g. “NO LOGON”
- Some “magic” values e.g. “NO LOGON”
- Why does the “Data Conversion Only” person have a photo?
- The IsExternalLogonProvider is always false.
- The UserPreferences, CustomFields and OtherLanguages columns contain Java Script Object Notation(JSON), need to see how these a generated, updated and used.
The application must have an existing external user provisioning process. It looks like a Person record is created by an Administrator then the User sets their password on first Logon. (not certain if there are any password complexity rules enforced)
An application I worked on didn’t have any enforcement of password complexity and minimum length in earlier versions. This caused issues when a number of their clients couldn’t logon to the new application because their existing password was too short. We updated the logon field rules and retained minimum complexity and length rules on change and reset password field validation. We then forced 5-10% of users per month (so the helpdesk wasn’t overwhelmed by support calls) to update their passwords.
ALTER PROCEDURE [Website].[ActivateWebsiteLogon]
@PersonID int,
@LogonName nvarchar(50),
@InitialPassword nvarchar(40)
WITH EXECUTE AS OWNER
AS
BEGIN
SET NOCOUNT ON;
SET XACT_ABORT ON;
UPDATE [Application].People
SET IsPermittedToLogon = 1,
LogonName = @LogonName,
HashedPassword = HASHBYTES(N'SHA2_256', @InitialPassword + FullName),
UserPreferences = (SELECT UserPreferences FROM [Application].People WHERE PersonID = 1) -- Person 1 has User Preferences template
WHERE PersonID = @PersonID
AND PersonID <> 1
AND IsPermittedToLogon = 0;
IF @@ROWCOUNT = 0
BEGIN
PRINT N'The PersonID must be valid, must not be person 1, and must not already be enabled';
THROW 51000, N'Invalid PersonID', 1;
RETURN -1;
END;
END;
Initial observations
- The password hashing uses SHA2_256 which is good
- The password hash is seeded with the persons FullName, this could be a problem if a user changes their name.
- The user selects their LoginName, this needs further investigate as duplicates could be an issue
- XACT_ABORT ON + THROW for validation and state management is odd, need to check how SqlExceptions are handled in application code.
- PersonID magic number handling adds complexity and needs further investigation.
- EXECUTE AS OWNER caught my attention, checked only one Database user for application.
- The LastEditBy isn’t set to the PersonID which seems a bit odd.
Based on the [Website].[ActivateWebsiteLogon] (couldn’t find Logon so reviewed ChangePassword) this is my first attempt at a stored procedure which validates a user’s LogonName and Password.
CREATE PROCEDURE [Application].[PersonAuthenticateLookupByLogonNameV1]
@LogonName nvarchar(50),
@Password nvarchar(40)
AS
BEGIN
SELECT PersonID, FullName, EmailAddress
FROM [Application].[People]
WHERE (( LogonName = @LogonName)
AND (IsPermittedToLogon = 1)
AND (HASHBYTES(N'SHA2_256', @Password + FullName) = HashedPassword))
END
GO
We use the ..VX approach to reduce issues when doing canary and rolling deployments. If the parameter list or return dataset of a stored procedure changes (even if we think it is backwards compatible) the version number is incremented so that different versions of the application can be run concurrently and backing out application updates is less fraught.
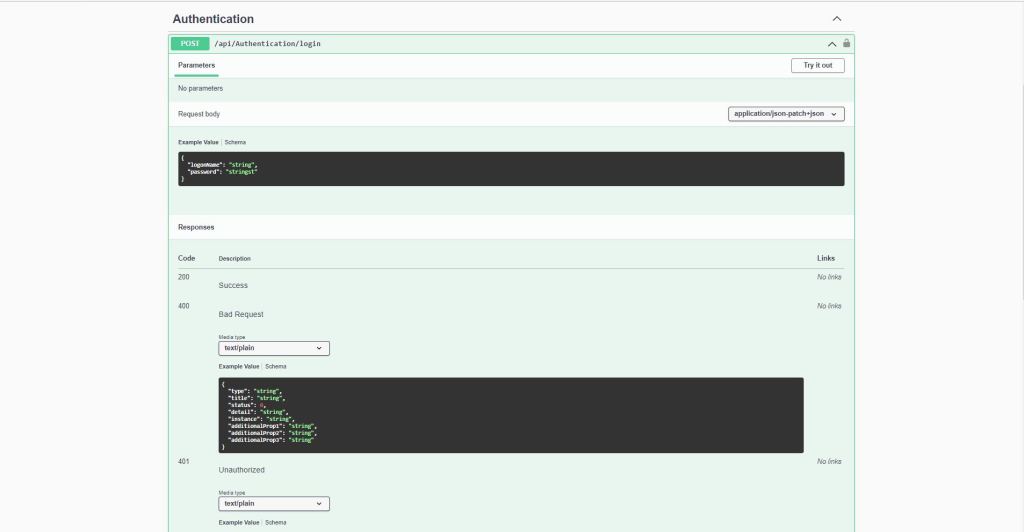
The next step was to create a Data Transfer Object(DTO) for the Logon request payload
public class LogonRequest
{
[JsonRequired]
[MinLength(Constants.LogonNameLengthMinimum)]
[MaxLength(Constants.LogonNameLengthMaximum)]
public string LogonName { get; set; }
[JsonRequired]
[MinLength(Constants.PasswordLengthMinimum)]
[MaxLength(Constants.PasswordLengthMaximum)]
public string Password { get; set; }
}
Then a Proof of Concept (PoC) AuthenticationController to process a login request.
The Logon method calls the PersonAuthenticateLookupByLogonNameV1 stored procedure to validate the LoginName and password. In this iteration the only claim added to the JSON Web Token(JWT) is the PersonId. We try and keep the JWTs small as possible as one customer’s application failed randomly because a couple of user’s JWTs were so large (lots of roles) that some versions of browsers choked.
public AuthenticationController(IConfiguration configuration, ILogger<AuthenticationController> logger, IOptions<Model.JwtIssuerOptions> jwtIssuerOptions)
{
this.configuration = configuration;
this.logger = logger;
this.jwtIssuerOptions = jwtIssuerOptions.Value;
}
[HttpPost("login")]
public async Task<ActionResult> Login([FromBody] Model.LoginRequest request )
{
var claims = new List<Claim>();
using (SqlConnection db = new SqlConnection(configuration.GetConnectionString("WorldWideImportersDatabase")))
{
UserLogonUserDetailsDto userLogonUserDetails = await db.QuerySingleOrDefaultWithRetryAsync<UserLogonUserDetailsDto>("[Application].[PersonAuthenticateLookupByLogonNameV1]", param: request, commandType: CommandType.StoredProcedure);
if (userLogonUserDetails == null)
{
logger.LogWarning("Login attempt by user {0} failed", request.LogonName);
return this.Unauthorized();
}
// Setup the primary SID + name info
claims.Add(new Claim(ClaimTypes.PrimarySid, userLogonUserDetails.PersonID.ToString()));
}
var authSigningKey = new SymmetricSecurityKey(Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(jwtIssuerOptions.SecretKey));
var token = new JwtSecurityToken(
issuer: jwtIssuerOptions.Issuer,
audience: jwtIssuerOptions.Audience,
expires: DateTime.UtcNow.Add(jwtIssuerOptions.TokenExpiresAfter),
claims: claims,
signingCredentials: new SigningCredentials(authSigningKey, SecurityAlgorithms.HmacSha256));
return this.Ok(new
{
token = new JwtSecurityTokenHandler().WriteToken(token),
expiration = token.ValidTo,
});
}
}
After a successful logon the Token has to be copied (I regularly miss the first or the last character) from the response payload to the Authorisation form.
I decorated the SystemController DeploymentVersion deployment with the [Authorize] attribute to force a check that the user is authenticated.
/// <summary>
/// WebAPI controller for handling System Dapper functionality.
/// </summary>
[Route("api/[controller]")]
[ApiController]
public class SystemController : ControllerBase
{
/// <summary>
/// Returns the Application version in [Major].[Minor].[Build].Revision] format.
/// </summary>
/// <response code="200">List of claims returned.</response>
/// <response code="401">Unauthorised, bearer token missing or expired.</response>
/// <returns>Returns the Application version in [Major].[Minor].[Build].Revision] format.</returns>
[HttpGet("DeploymentVersion"), Authorize]
public string DeploymentVersion()
{
return Assembly.GetExecutingAssembly().GetName().Version.ToString();
}
}
If the bearer token is missing, invalid (I accidentally didn’t copy either the first or last character) or expired the method call will fail with a 401 Unauthorized error.
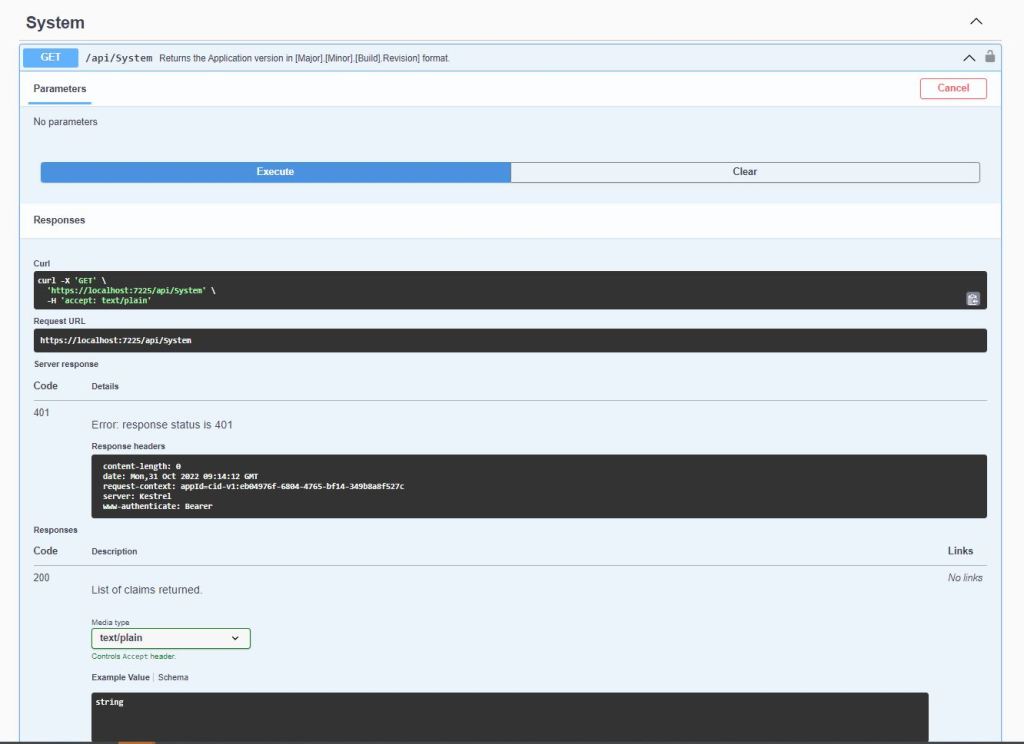
Controlling access to controllers and methods of controllers is probably not granular for most applications so adding “coarse” and “fine grained” authorisation to an existing application and the configuration of Swashbuckle and application request processing middleware to support JWTs will be covered in a couple of future posts.
For remediation projects we try to keep the code as simple as possible (but no simpler), by minimising the plumbing and only using advanced language features etc. where it adds value.
I’m leaning towards using Dependency Injection for configuration information, so the way connection strings and jwtIssuerOptions is going to be harmonised. In a future version of the application the jwtIssuerOptions will be migrated to an Azure Key Vault.


Pingback: .NET Core web API + Dapper – Authorisation Permissions | devMobile's blog