“Lets start at the very beginning, A very good place to start”
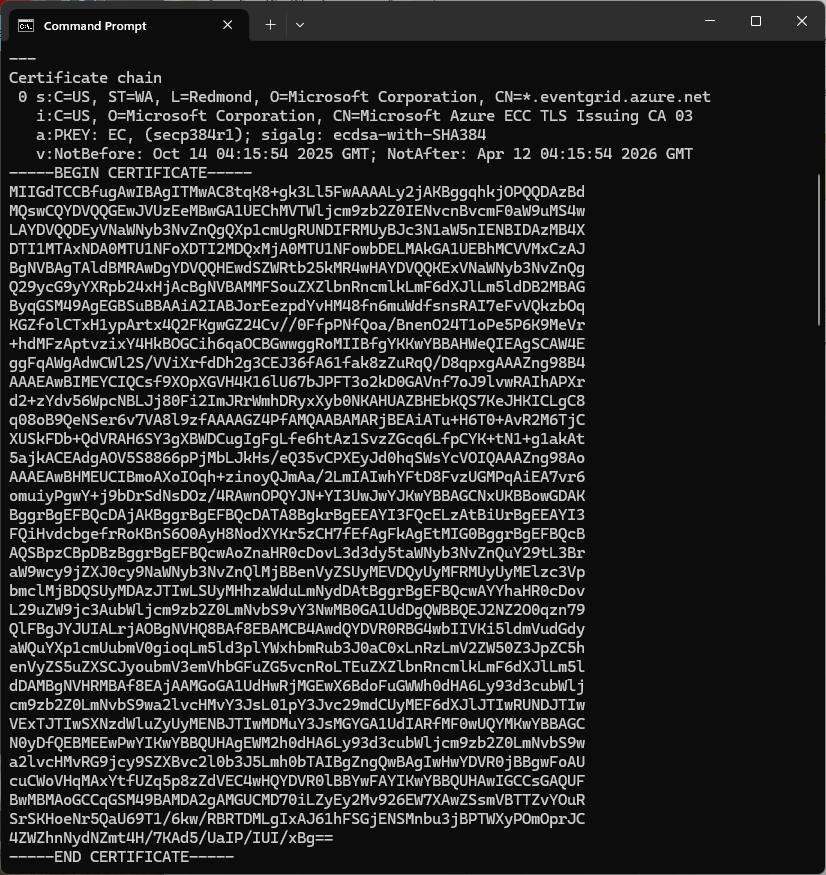
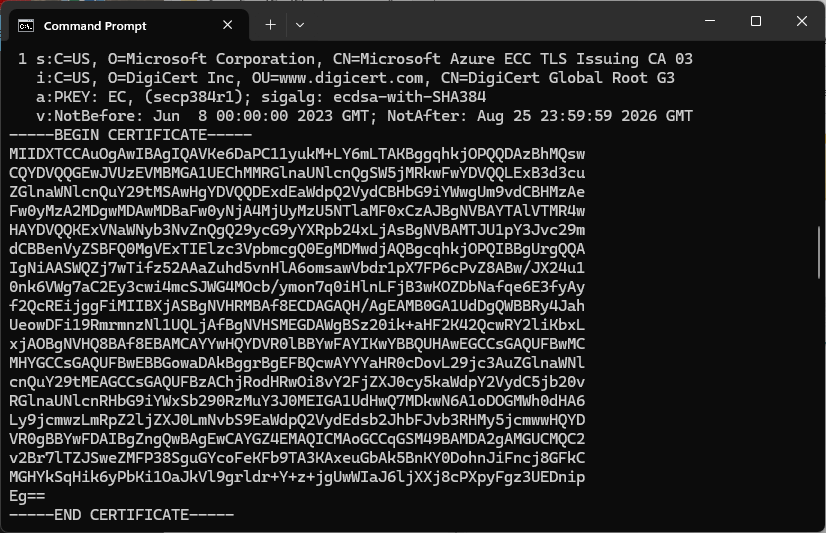
The Azure Event Grid MQTT Broker server X509 certificate chain can be copy ‘n’ paste from the output of the openssl command
openssl s_client -connect YourNamespace.newzealandnorth-1.ts.eventgrid.azure.net:8883 -showcerts
A self-signed X509 root certificate which can sign intermediate X509 certificates and key file can be generated with a single openssl command.
openssl req -x509 -newkey rsa:4096 -keyout rootCA.key -out rootCA.crt -days 3650 -nodes -subj "/CN=devMobile /O=devMobile.co.nz /C=NZ" -addext "basicConstraints=critical,CA:TRUE" -addext "keyUsage=critical,keyCertSign"
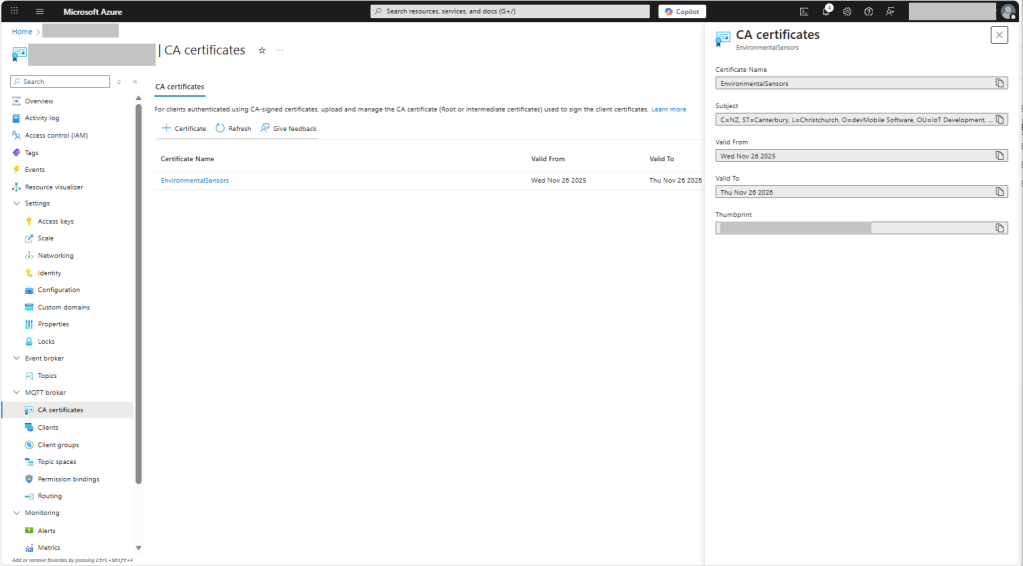
For a non-trivial system there should be a number of intermediate certificates. I have tried creating intermediate certificates for a device type, geography, application, customer and combinations of these. The first couple of times got it wrong so start with a field trial so that it isn’t so painful to go back and fix. (beware the sunk cost fallacy)
openssl genrsa -out intermediate.key 4096
openssl req -new -key intermediate.key -out intermediate.csr -subj "/CN=intermediate /O=devMobile.co.nz /C=NZ"
I found creating an intermediate certificate that could sign device certificates required a conf file for the basicConstraints and keyUsage configuration.
[ v3_intermediate_ca ]
basicConstraints = critical, CA:TRUE, pathlen:0
keyUsage = critical, keyCertSign
- critical-The extension must be understood and processed by any application validating the certificate. If the application does not understand it, the certificate must be rejected.
- CA:TRUE-This certificate is allowed to act as a Certificate Authority (CA), meaning it can sign other certificates.
- pathlen:0-This CA can only issue end-entity (leaf) certificates and cannot issue further intermediate CA certificates.
- keyCertSig- The certificate can be used to sign other certificates (i.e., it’s a CA certificate).
openssl x509 -req -in intermediate.csr -CA rootCA.crt -CAkey rootCA.key -CAcreateserial -out intermediate.crt -days 1825 -extfile intermediate_ext.cnf -extensions v3_intermediate_ca
Creating a device certificate is similar to the process for the intermediate certificate but doesn’t need to be able to sign certificates.
openssl genrsa -out EdgeBox100A.key 4096
openssl req -new -key EdgeBox100A.key -out EdgeBox100A.csr -subj "/CN=EdgeBox100A"
openssl x509 -req -in EdgeBox100A.csr -CA intermediate.crt -CAkey intermediate.key -CAcreateserial -out EdgeBox100A.crt -days 365
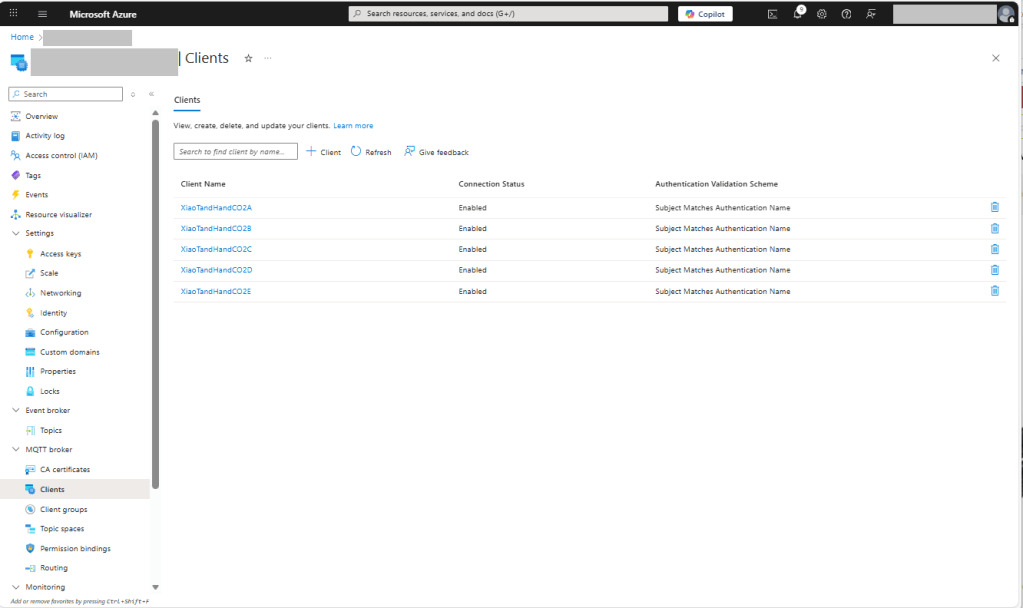
For production systems putting some thought into the Common name(CN), Organizational unit name(OU), Organization name(O), locality name(L), state or province name(S) and Country name(C)
// Minimalist ESP32 + Event Grid MQTT (mTLS) with PubSubClient
// Copyright (c) November 2025, devMobile Software
#include <PubSubClient.h>
#include <WiFi.h>
#include <WiFiClientSecure.h>
#include "constants.h"
#include "secrets.h"
// --- Wi-Fi ---
//const char* WIFI_SSID = "";
//const char* WIFI_PASSWORD = "";
// --- Event Grid MQTT ---
//const char* MQTT_SERVER = "";
const uint16_t MQTT_PORT = 8883;
//const char* MQTT_CLIENTID = "";
//const char* MQTT_USERNAME = "";
//const char* MQTT_PASSWORD = "";
//const char* MQTT_TOPIC_PUBLISH = "devices/";
//const char* MQTT_TOPIC_SUBSCRIBE = "devices/";
/*
// The certificate that is used to authenticate the MQTT Broker
const char CA_ROOT_PEM[] PROGMEM = R"PEM(
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
Thumbprint: 56D955C849887874AA1767810366D90ADF6C8536
CN: CN=Microsoft Azure ECC TLS Issuing CA 03
-----END CERTIFICATE-----
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
Thumbprint: 7E04DE896A3E666D00E687D33FFAD93BE83D349E
CN: CN=DigiCert Global Root G3
-----END CERTIFICATE-----
)PEM";
The certificate that is used to authenticate the device
static const char CLIENT_CERT_PEM[] PROGMEM = R"PEM(
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
CN=Self signed device certificate
-----END CERTIFICATE-----
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
CN=Self signed Intermediate certificate
-----END CERTIFICATE-----
)PEM";
The PEM encoded private key of device
static const char CLIENT_KEY_PEM[] PROGMEM = R"PEM(
-----BEGIN PRIVATE KEY-----
-----END PRIVATE KEY-----
)PEM";
*/
WiFiClientSecure secureClient;
PubSubClient mqttClient(secureClient);
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
delay(5000);
Serial.println();
// Connect to WiFi
Serial.println("WiFi connecting");
WiFi.begin(WIFI_SSID, WIFI_PASSWORD);
Serial.print("*");
while (WiFi.status() != WL_CONNECTED) {
delay(500);
Serial.print("*");
}
Serial.println("\nWiFi connected");
// Sync time for TLS
Serial.println("\nTime synchronising");
configTime(0, 0, "pool.ntp.org", "time.nist.gov");
Serial.print("*");
while (time(nullptr) < 100000) {
delay(500);
Serial.print("*");
}
Serial.println("\nTime synchronised");
Serial.println("\nValidating ServerFQDN-Certificate combination");
secureClient.setCACert(CA_ROOT_PEM);
Serial.println("TCP connecting");
if (secureClient.connect(MQTT_SERVER, MQTT_PORT)) {
Serial.println("\nTCP connected");
} else {
Serial.println("\nTCP connection failed");
return;
}
secureClient.setCertificate(CLIENT_CERT_A_PEM);
secureClient.setPrivateKey(CLIENT_KEY_A_PEM);
mqttClient.setServer(MQTT_SERVER, MQTT_PORT);
Serial.println("\nMQTT connecting");
Serial.print("*");
while (!mqttClient.connect(MQTT_CLIENTID, MQTT_USERNAME, MQTT_PASSWORD)) {
Serial.println(mqttClient.state());
delay(5000);
Serial.print("*");
}
Serial.println("\nMQTT connected");
}
static uint32_t sequenceNumber = 0;
void loop() {
mqttClient.loop();
Serial.print("'.");
delay(10000);
}
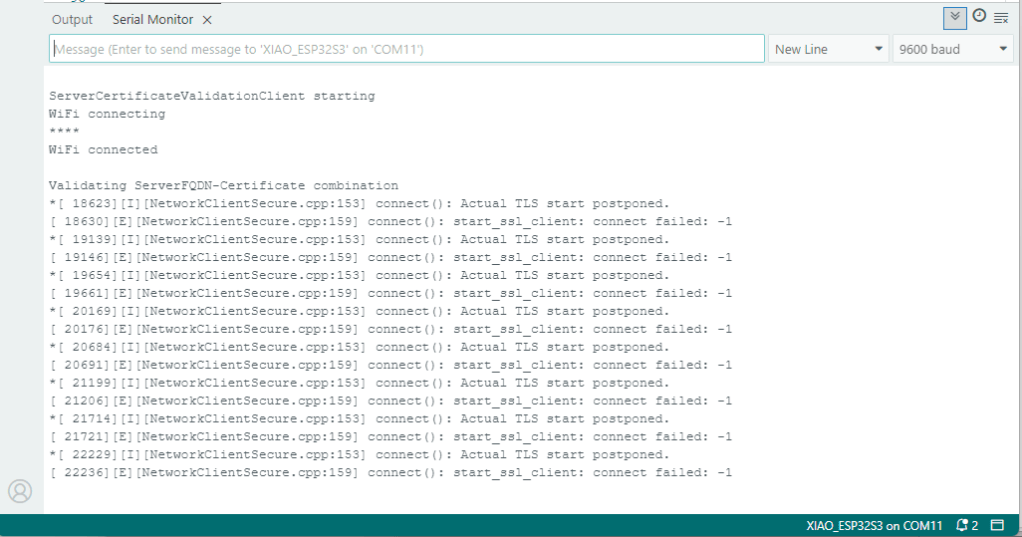
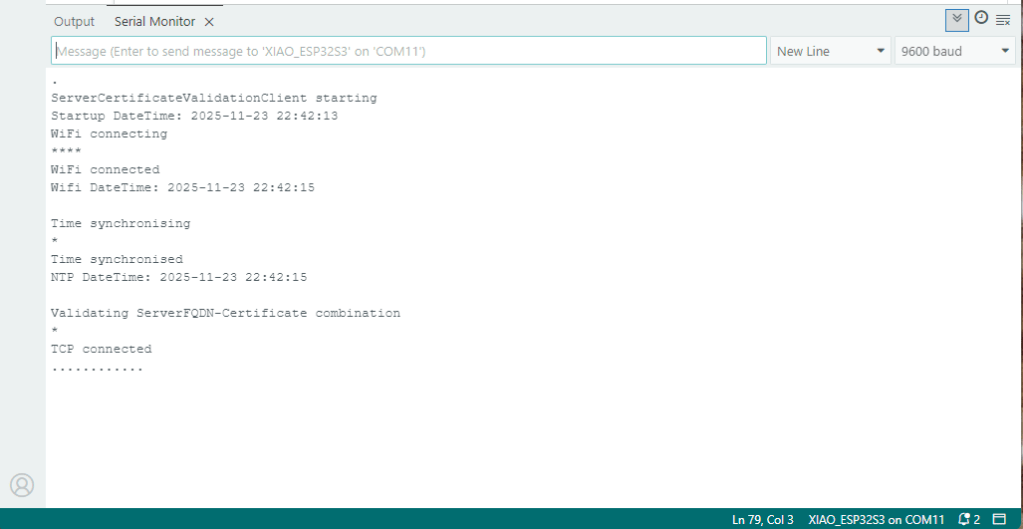
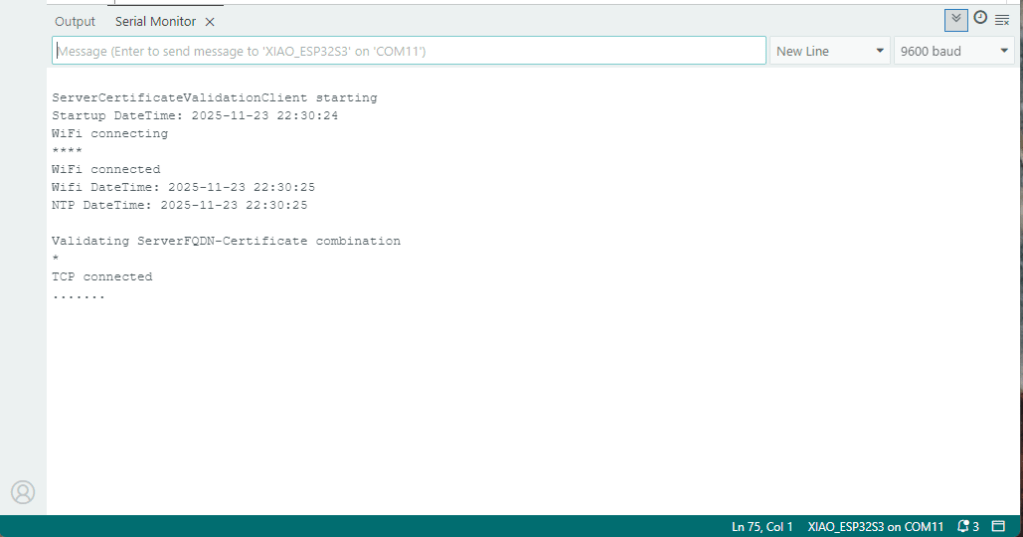
My Arduino Xiao ESP32S3 and EdgeBox-ESP-100-Industrial Edge Controller devices could connect to the local Wi-Fi, get the time and date using the network time protocol(NTP), and validate the Azure Event Grid MQTT broker certificate. Then connect to the Azure Event Grid MQTT broker with the client name specified in the subject name of its X509 certificate.
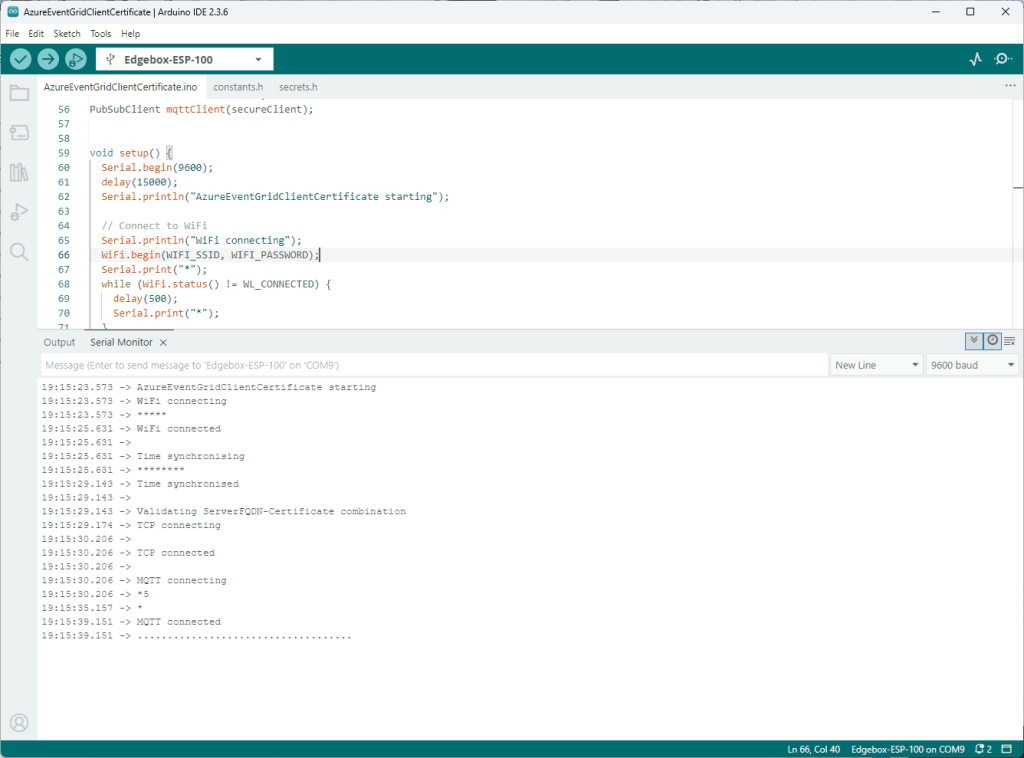
Establishing a connection to the Azure Event Grid MQTT broker often failed which surprised me. Initially I didn’t have any retry logic which meant I wasted quite a bit of time trying to debug failed connections