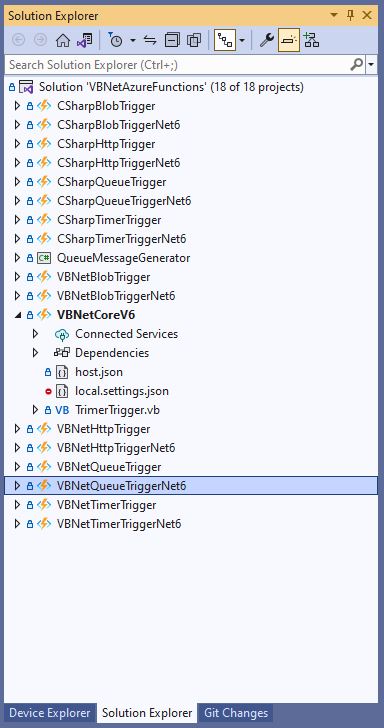
A year and a half ago I wrote a post about how to build Azure functions with VB.Net and the .NET Framework 4.X. The Microsoft VB team posted about Visual Basic Support for .NET 5.0 in March 2020 then went quiet, so my customer put the project on hold. Since then, a lot has changed .NET Core 3.1 LTS ends December 12, 2022, and .NET Core 5.0 support (no LTS) ended May 10, 2022 so I have ported the samples to .NET Core V6.
The process is similar (but different) to the original approach
First step is to create a Visual Basic .NET Core V6 console application
The specify a name for the new project.
Then select the version of .NET Core used
Then rename program.cs to a name which highlights that it is a trigger
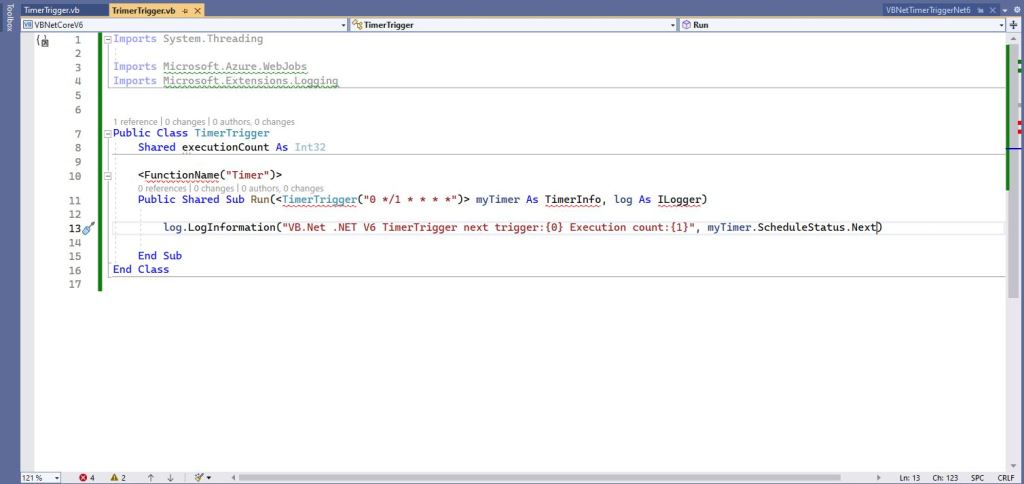
The initial version of the TimerTrigger code was “inspired” by the VB.Net 4.8 version.
'---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
' Copyright (c) November 2022, devMobile Software
'
' Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
' you may Not use this file except in compliance with the License.
' You may obtain a copy of the License at
'
' http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
'
' Unless required by applicable law Or agreed to in writing, software
' distributed under the License Is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
' WITHOUT WARRANTIES Or CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express Or implied.
' See the License for the specific language governing permissions And
' limitations under the License.
'
'---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Imports System.Threading
Imports Microsoft.Azure.WebJobs
Imports Microsoft.Extensions.Logging
Public Class TimerTrigger
Shared executionCount As Int32
<FunctionName("Timer")>
Public Shared Sub Run(<TimerTrigger("0 */1 * * * *")> myTimer As TimerInfo, log As ILogger)
Interlocked.Increment(executionCount)
log.LogInformation("VB.Net .NET V6 TimerTrigger next trigger:{0} Execution count:{1}", myTimer.ScheduleStatus.Next, executionCount)
End Sub
End Class
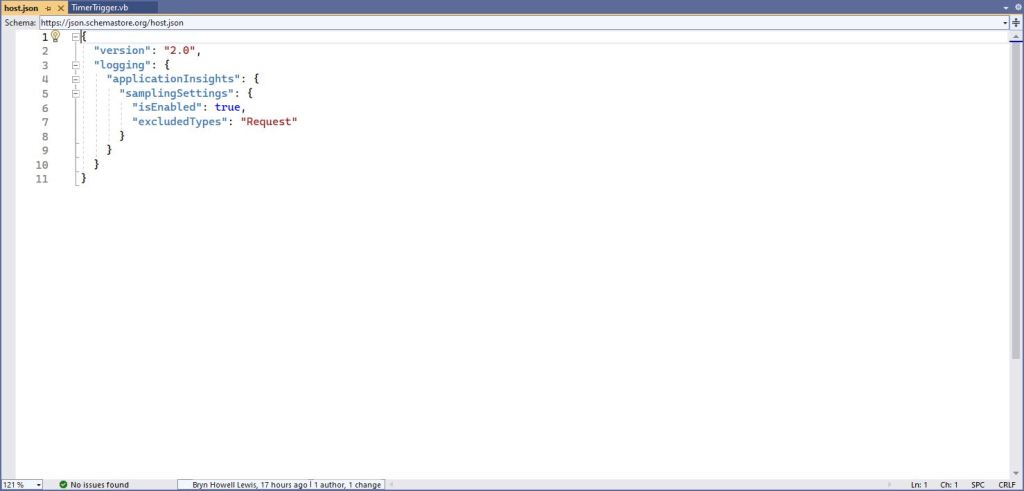
The next step is to add the hosts.json(empty for timer tigger) and localsettings.json to configure the function
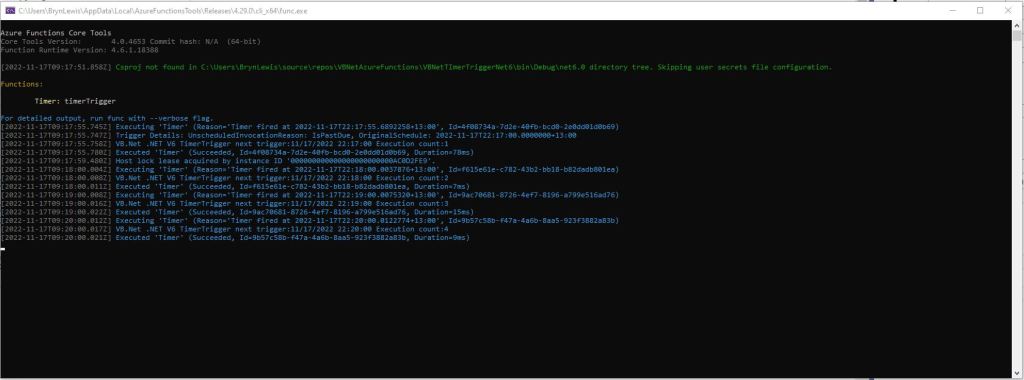
Then I could run the function in the Azure Functions runtime emulator and “single step” in the Visual Studio 2022 Debugger.
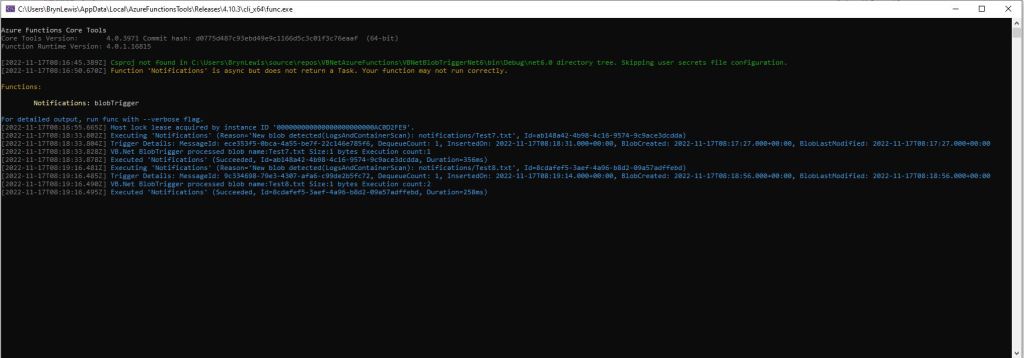
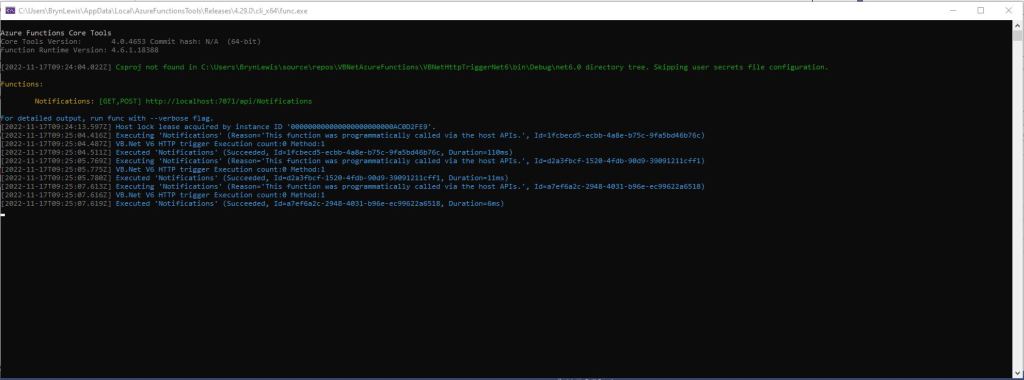
For completeness I also built sample BlobTrigger, HttpTrigger and QueueTrigger versions
I also deployed the Azure Storage QueueTrigger to Microsoft Azure, configured it, and then stress tested it with multiple instances of my QueueMessageGenerator.
What if it goes wrong…
“Can’t determine project language from files. Please add one of [–csharp, –javascript, –typescript, –java, –powershell, –customer]

Check “FUNCTIONS_WORKER_RUNTIME” in the local.settings.json file.

The baked in error logging doesn’t handle broken message formats very well. Look at the call stack or single step through the application to find the message format that is broken

WARNING
I assume this is not a supported approach so use
“at your own risk”